从国产SLG手游来说A星寻路算法
Posted 愿你走出半生
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了从国产SLG手游来说A星寻路算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 前文
先说SLG是什么,SLG=Simulation Game,策略类游戏。现特指回合制策略游戏以及即时SLG。有别于SIM(Simulation)类“生活“模拟游戏,SLG虽然也是缩写的simulation(模拟但与经营类意思不同),却是“战争策略“模拟游戏的总称。
而本文要说的是SLG游戏中的一种分类,国产手游中比较具有代表性的有:率土之滨、三国志战略版、宏图之下,由于我们是要介绍A*算法相关内容,所以我们贴几张关于战场的图,以方便我们有一个理解。
以下三个游戏由发行时间先后顺序展示:
-
率土之滨
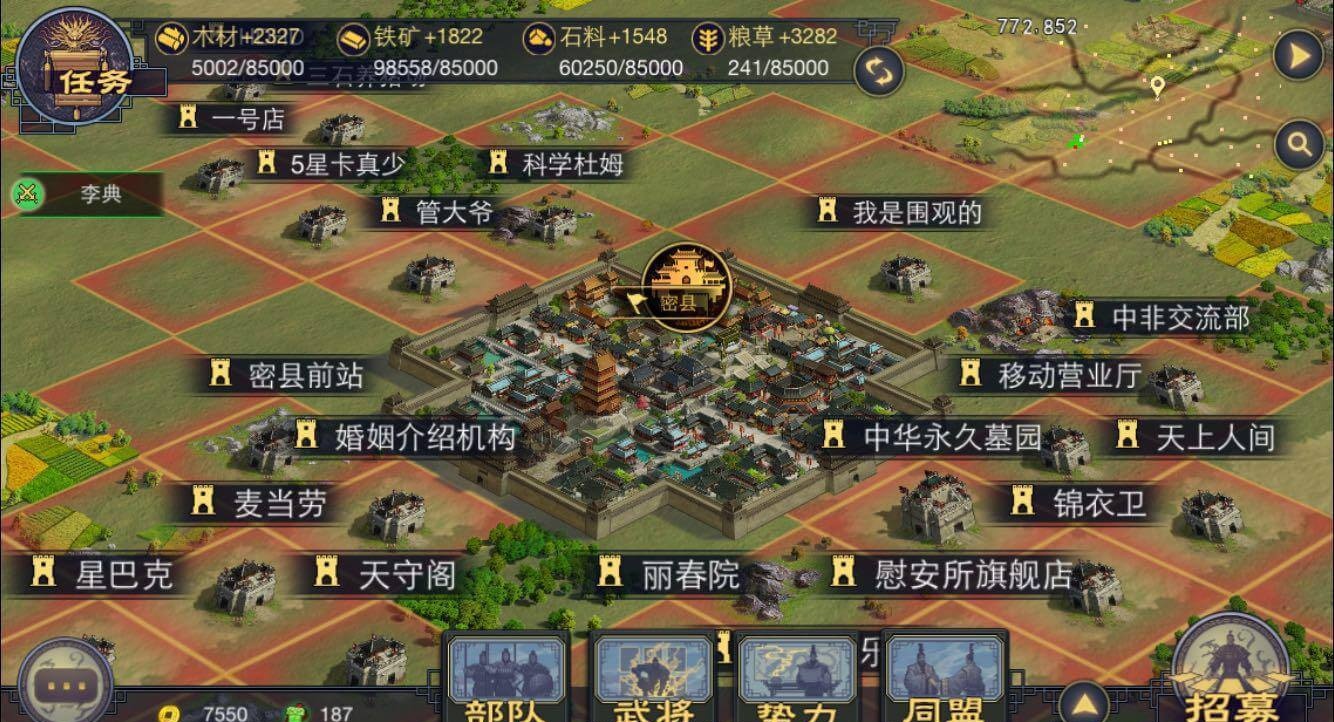
-
三国志战略版
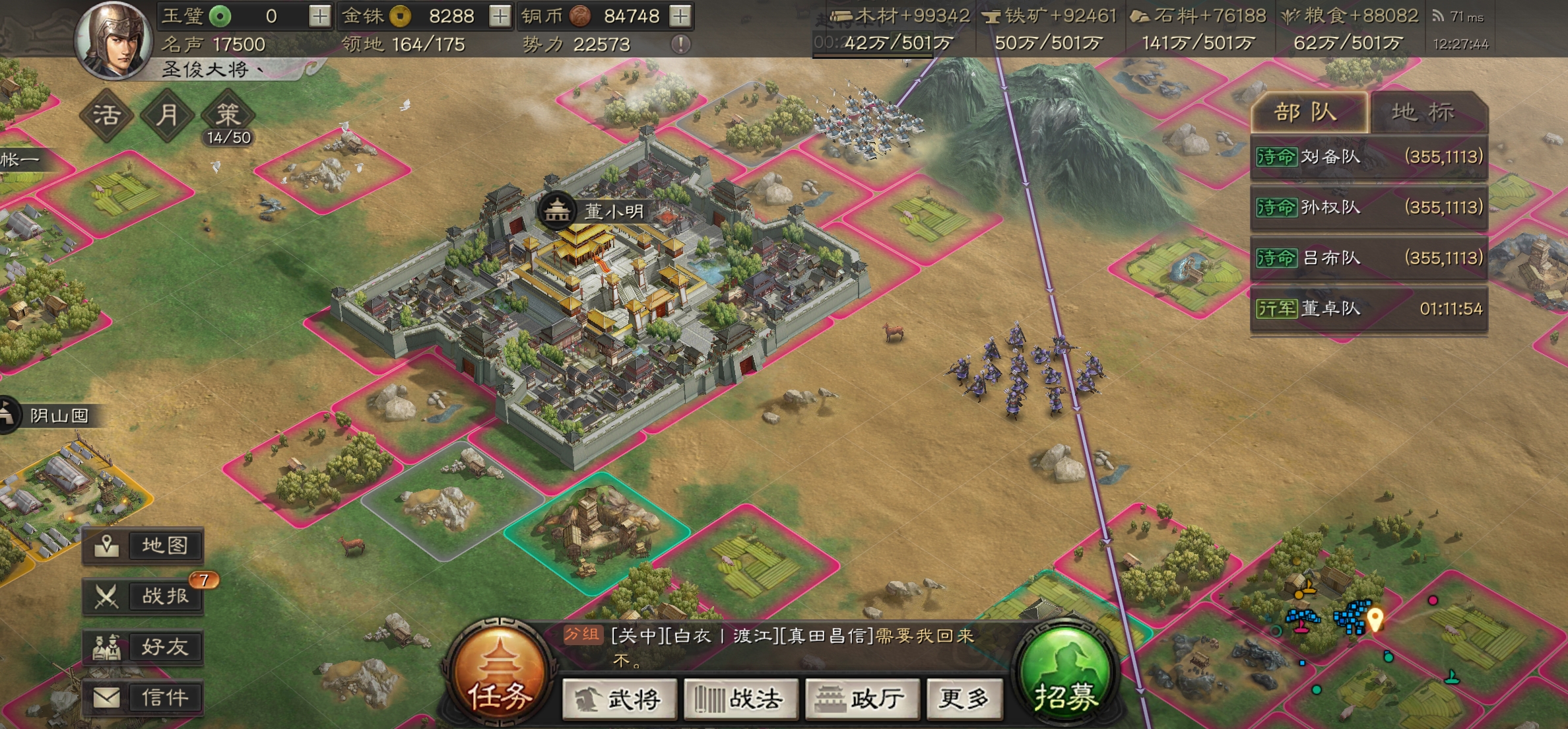
- 鸿图之下
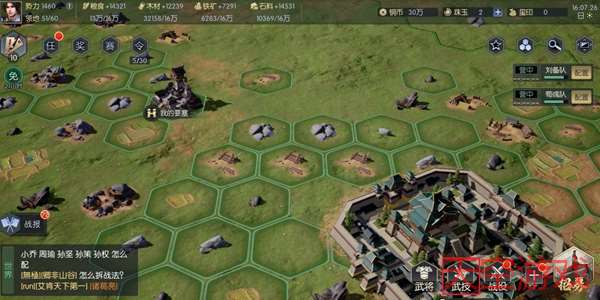
那么有上述三个游戏,其沙盘布局如下:
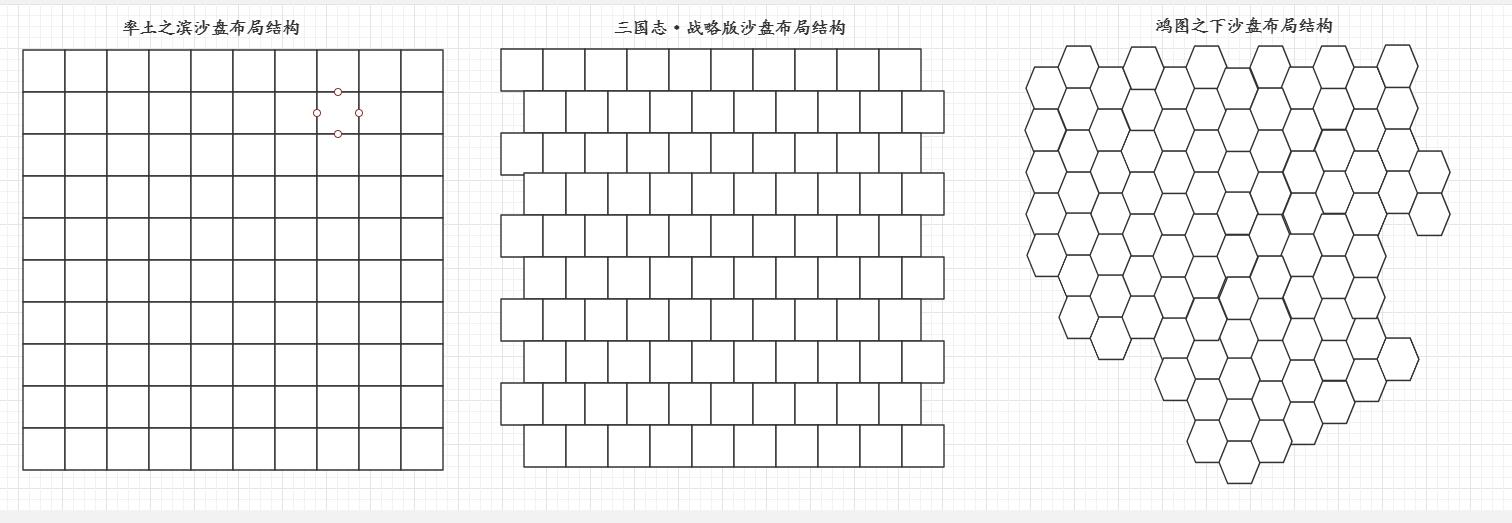
传统的A*算法就是用率土之滨的数据结构,而随着沙盘游戏的不断发展地图的嵌入方式发生了变化,三国志战略版错开了50%,鸿图之下则采用正六边形的方式展示。
2. 演示代码准备
以下使用C#+WPF,VS2019进行的代码演示。
3. 深度优先和广度优先
深度优先遍历(Depth First Search, 简称 DFS) 与广度优先遍历(Breath First Search)是图论中两种非常重要的算法,生产上广泛用于拓扑排序,寻路(走迷宫),搜索引擎,爬虫等,也频繁出现在 leetcode,高频面试题中。
3.1 深度优先
/// <summary>
/// 深度优先
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnDFS_Click(object sender,RoutedEventArgs e)
{
dicCache = new Dictionary<string, bool>();
Tuple<int, int> pStartIndex = pStartShapeSquare.Tag as Tuple<int, int>;
DFS_WayFinding(pStartIndex.Item1, pStartIndex.Item2);
}
private bool DFS_WayFinding(int index1, int index2)
{
if (index1 < 0 || index1 >= CrosswiseNodeCount)
{
return false;
}
if (index2 < 0 || index2 >= LengthwaysNodeCount)
{
return false;
}
string strTag = $"{index1},{index2}";
if (dicCache.ContainsKey(strTag))
{
return false;
}
else
{
dicCache.Add(strTag,true);
}
ShapeSquare shapeSquare = PlotShapeSquare[index1, index2];
if (shapeSquare is ShapeSquare_BlockingPoint)
{
return false;
}
else if (shapeSquare == pEndShapeSquare)
{
return true;
}
shapeSquare.Fill = Brushes.BurlyWood;
Thread.Sleep(10);
System.Windows.Forms.Application.DoEvents();
if (DFS_WayFinding(index1 - 1, index2))
{
return true;
}
else if (DFS_WayFinding(index1, index2 - 1))
{
return true;
}
else if (DFS_WayFinding(index1 + 1, index2))
{
return true;
}
else if (DFS_WayFinding(index1, index2 + 1))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
3.2 广度优先
private void btnBFS_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
dicCache = new Dictionary<string, bool>();
Tuple<int, int> pStartIndex = pStartShapeSquare.Tag as Tuple<int, int>;
BFS_WayFinding(pStartIndex);
}
/// <summary>
/// 广度优先
/// </summary>
/// <param name=""></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool BFS_WayFinding(Tuple<int, int> pIndex)
{
Queue<Tuple<int, int>> BFSQueue = new Queue<Tuple<int, int>>();
BFSQueue.Enqueue(pIndex);
string strTag = $"{pIndex.Item1},{pIndex.Item2}";
dicCache.Add(strTag, true);
while (BFSQueue.Count!=0)
{
Tuple<int, int> pShapeSquareIndex= BFSQueue.Dequeue();
ShapeSquare shapeSquare = PlotShapeSquare[pShapeSquareIndex.Item1, pShapeSquareIndex.Item2];
if (shapeSquare == pEndShapeSquare)
{
return true;
}
shapeSquare.Fill = Brushes.BurlyWood;
Thread.Sleep(10);
System.Windows.Forms.Application.DoEvents();
if (IsRange(pShapeSquareIndex.Item1-1, pShapeSquareIndex.Item2))
{
BFSQueue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int, int>(pShapeSquareIndex.Item1 - 1, pShapeSquareIndex.Item2));
}
if (IsRange(pShapeSquareIndex.Item1 , pShapeSquareIndex.Item2 - 1))
{
BFSQueue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int, int>(pShapeSquareIndex.Item1, pShapeSquareIndex.Item2 - 1));
}
if (IsRange(pShapeSquareIndex.Item1 + 1, pShapeSquareIndex.Item2))
{
BFSQueue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int, int>(pShapeSquareIndex.Item1 + 1, pShapeSquareIndex.Item2));
}
if (IsRange(pShapeSquareIndex.Item1 , pShapeSquareIndex.Item2 + 1))
{
BFSQueue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int, int>(pShapeSquareIndex.Item1, pShapeSquareIndex.Item2 + 1));
}
}
return false;
}
private bool IsRange(int index1, int index2)
{
if (index1 < 0 || index1 >= CrosswiseNodeCount)
{
return false;
}
if (index2 < 0 || index2 >= LengthwaysNodeCount)
{
return false;
}
ShapeSquare shapeSquare = PlotShapeSquare[index1, index2];
if (shapeSquare is ShapeSquare_BlockingPoint)
{
return false;
}
string strTag = $"{index1},{index2}";
if (dicCache.ContainsKey(strTag))
{
return false;
}
else
{
dicCache.Add(strTag, true);
}
return true;
}
3.3 特点
如果深搜是一个人,那么他的性格一定倔得像头牛!他从一点出发去旅游,只朝着一个方向走,除非路断了,他绝不改变方向!除非四个方向全都不通或遇到终点,他绝不后退一步!因此,他的姐姐广搜总是嘲笑他,说他是个一根筋、不撞南墙不回头的家伙。
深搜很讨厌他姐姐的嘲笑,但又不想跟自己的亲姐姐闹矛盾,于是他决定给姐姐讲述自己旅途中的经历,来改善姐姐对他的看法。他成功了,而且只讲了一次。从那以后他姐姐不仅再没有嘲笑过他,而且连看他的眼神都充满了赞赏。他以为是自己路上的各种英勇征服了姐姐,但他不知道,其实另有原因……
深搜是这样跟姐姐讲的:关于旅行呢,我并不把目的地的风光放在第一位,而是更注重于沿路的风景,所以我不会去追求最短路,而是把所有能通向终点的路都走一遍。可是我并不知道往哪走能到达目的地,于是我只能每到一个地方,就向当地的人请教各个方向的道路情况。为了避免重复向别人问同一个方向,我就给自己规定:先问北,如果有路,那就往北走,到达下一个地方的时候就在执行此规定,如果往北不通,我就再问西,其次是南、东,要是这四个方向都不通或者抵达了终点,那我回到上一个地方,继续探索其他没去过的方向。我还要求自己要记住那些帮过他的人,但是那些给我帮倒忙的、让我白费力气的人,要忘记他们。有了这些规定之后,我就可以大胆的往前走了,既不用担心到不了不目的地,也不用担心重复走以前的路。
如果广搜是一个人,那么她一定很贪心,而且喜新厌旧!她从一点出发去旅游,先把与起点相邻的地方全部游览一遍,然后再把与她刚游览过的景点相邻的景点全都游览一边……一直这样,直至所有的景点都游览一遍。
3.4 讲解与备忘
上文中深度优先我们使用的是递归的方式而广度优先使用的是队列。而在网络上标准写法是深度优先采用的栈,广度优先采用的队列,两者采用两个数据结构的不同特点,保证遍历节点的优先性。比如栈的特点是后进先出,从而保证其每一次遍历到的子节点都先遍历。而队列的特点是先进先出,从而保证每一次遍历的子节点都在后面排队,而队列前方的先遍历,从而保证同级子节点的遍历的优先性。
4. A星算法
书接上文,我们降到了深度优先和广度优先,上述两个算法都是穷举式算法。而(A-Star)算法是一种静态路网中求解最短路径最有效的直接搜索方法,也是许多其他问题的常用启发式算法。A*算法作为Dijkstra算法(后续再用篇幅来阐述Dijkstra算法)的扩展,因其高效性而被广泛应用于寻路及图的遍历。
名词解释:
- 直接搜索算法:直接在实际地图上进行搜索,不经过任何预处理;
- 启发式算法:通过启发函数引导算法的搜索方向;
- 静态图搜索算法:被搜索的图的权值不随时间变化(后被证明同样可以适用于动态图的搜索)。
公式表示为: f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
其中,
- f(n) 是从初始状态经由状态n到目标状态的代价估计,
- g(n) 是在状态空间中从初始状态到状态n的实际代价,
- h(n) 是从状态n到目标状态的最佳路径的估计代价(欧几里(斜边的长度)/曼哈顿距离(x的距离+y的距离差))。
少逼逼,我们来分析算法。
结合上文,我们说过深度优先和广度优先都是穷举算法而A星算法是属于启发式算法,那么是通过什么做到启发的呢!
鉴于视频比博客更加有代入感以及过程性,推荐大家看: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV147411u7r5?from=search&seid=14263924862056244840
4.1 基本原理
A星寻路算法的基本原理就是不停的找自己周围的点,选出一个新的点作为起点再次循环
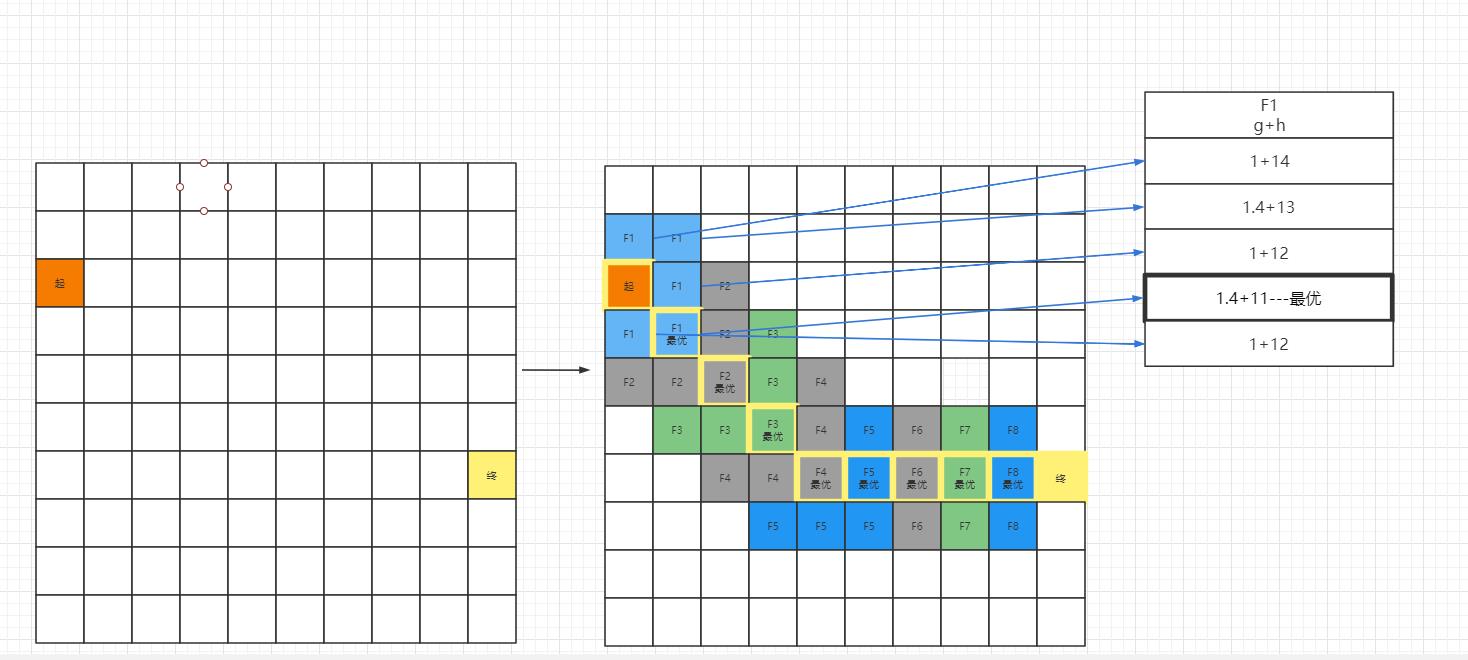
4.2 A星算法的详细原理
-
寻路消耗公式:
f(寻路消耗)=g(离起点的距离)+h(离终点的距离)
g(离起点的距离):代表离起点的距离:
g ( n ) = ( x 1 − x 2 ) 2 + ( y 1 − y 2 ) 2 g(n)=\\sqrt{(x1-x2)^2+(y1-y2)^2} g(n)=(x1−x2)2+(y1−y2)2
h(曼哈顿距离):图上数格子
h ( n ) = ∣ x 1 − x 2 ∣ + ∣ y 1 − y 2 ∣ h(n)=|x1-x2|+|y1-y2| h(n)=∣x1−x2∣+∣y1−y2∣

-
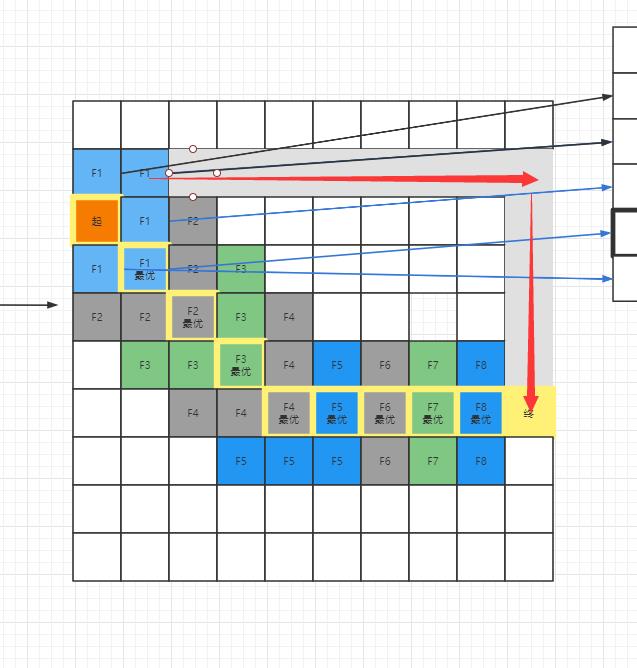
开启列表:
当前起点我们需要寻找的列表
-
关闭列表:
已经寻找完毕的列表
-
格子对象的父对象:
每一次寻找的格子节点的父对象,如
F1的父对象为起点,F2的父对象为F1,以此类推。最后基于
关闭列表中的集合,通过格子的父对象从节点开始逆推我们可以找到一条路径。
4.3 节选代码
using GraphBaseFramewark;
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Media;
namespace GraphAStarAlgorithm
{
/// <summary>
/// A星寻路算法
/// </summary>
class AStarAlgorithm
{
ShapeSquare[,] PlotShapeSquare = null;
int CrosswiseNodeCount = 0;
int LengthwaysNodeCount = 0;
public AStarAlgorithm(ShapeSquare[,] plotShapeSquare, int crosswiseNodeCount,int lengthwaysNodeCount)
{
PlotShapeSquare = plotShapeSquare;
CrosswiseNodeCount = crosswiseNodeCount;
LengthwaysNodeCount = lengthwaysNodeCount;
}
/// <summary>
/// 关闭列表
/// </summary>
Dictionary<ShapeSquare, ShapeSquare> dicClose = new Dictionary<ShapeSquare, ShapeSquare>();
/// <summary>
/// 算法运行
/// </summary>
/// <param name="pStartShapeSquare"></param>
/// <param name="pEndShapeSquare"></param>
public void AlgorithmRun(ShapeSquare pStartShapeSquare, ShapeSquare pEndShapeSquare)
{
Tuple<int, int> pStartIndex = pStartShapeSquare.Tag as Tuple<int, int>;
dicClose.Add(pStartShapeSquare, null);
FindWayInfo(pStartIndex, pStartShapeSquare, pEndShapeSquare);
ShapeSquare pWayShapeSquare = pEndShapeSquare;
while (pWayShapeSquare!= pStartShapeSquare)
{
pWayShapeSquare.Fill = Brushes.YellowGreen;
Thread.Sleep(10);
System.Windows.Forms.Application.DoEvents();
pWayShapeSquare = dicClose[pWayShapeSquare];
}
}
private bool FindWayInfo(Tuple<int, int> pStartIndex, ShapeSquare pStartShapeSquare, ShapeSquare pEndShapeSquare)
{
ConcurrentDictionary<ShapeSquare, double> dicOpen = new ConcurrentDictionary<ShapeSquare, double>();
IsRange(pStartIndex.Item1-1, pStartIndex.Item2-1,1.4, pStartShapeSquare, dicOpen);
IsRange(pStartIndex.Item1-1, pStartIndex.Item2,1, pStartShapeSquare, dicOpen);
IsRange(pStartIndex.Item1-1, pStartIndex.Item2+1,1.4, pStartShapeSquare, dicOpen);
IsRange(pStartIndex.Item1, pStartIndex.Item2+1,1, pStartShapeSquare, dicOpen);
IsRange(pStartIndex.Item1+1, pStartIndex.Item2+1,1.4, pStartShapeSquare, dicOpen);
IsRange(pStartIndex.Item1+1, pStartIndex.Item2,1, pStartShapeSquare, dicOpen);
IsRange(pStartIndex.Item1+1, pStartIndex.Item2-1,1.4, pStartShapeSquare, dicOpen);
IsRange(pStartIndex.Item1, pStartIndex.Item2-1,1, pStartShapeSquare, dicOpen);
Tuple<int, int> pEndIndex = pEndShapeSquare.Tag as Tuple<int, int>;
foreach (var item in dicOpen.Keys)
{
Tuple<int, int> pItemIndex = item.Tag as Tuple<int, int>;
dicOpen[item] += Math.Abs((pEndIndex.Item1 - pItemIndex.Item1)) + Math.Abs((pEndIndex.Item2 - pItemIndex.Item2));
if (item == pEndShapeSquare)
{
return true;
}
}
List<KeyValuePair<ShapeSquare, double>> listSortOpen =dicOpen.OrderBy(a => a.Value).ToList();
foreach (var item in listSortOpen)
{
Tuple<int, int> pIndex = item.Key.Tag as Tuple<int, int>;
if (FindWayInfo(pIndex, item.Key, pEndShapeSquare))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private bool IsRange(int index1, int index2,double dStartLength,ShapeSquare pStartShapeSquare, ConcurrentDictionary<ShapeSquare,double> dicOpen)
{
if (index1 < 0 || index1 >= CrosswiseNodeCount)
{
return false;
}
if (index2 < 0 || index2 >= LengthwaysNodeCount)
{
return false;
}
ShapeSquare shapeSquare = PlotShapeSquare[index1, index2];
if (shapeSquare is ShapeSquare_BlockingPoint)
{
return false;
}
if (dicClose.ContainsKey(shapeSquare))
{
return false;
}
else
{
dicClose.Add(shapeSquare, pStartShapeSquare);
dicOpen.TryAdd(shapeSquare, dStartLength);
shapeSquare.Fill = Brushes.BurlyWood;
Thread.Sleep(10);
System.Windows.Forms.Application.DoEvents();
}
return true;
}
}
}

5 结语
由于这个算法是一个启发式算法,所以需要处理一些特殊情况,如周围点的f(n)相同时,顺序问题等等。
这个时候我们再回过头来看看国产SLG游戏中,三款游戏由时间顺序的发展,地图的变化,在算法上它在解决什么问题呢?
以上是关于从国产SLG手游来说A星寻路算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章