SpringMvc入门
Posted 大忽悠爱忽悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringMvc入门相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
SpringMvc入门
- 概述
- SpringMVC思想是一个前段控制器能拦截所有请求,并智能派发
- 这个前段控制器是一个servlet,应该在web.xml中配置这个servlet来拦截所有请求
- 快速入门
- 运行流程分析
- @RequestMapping分析
- 如果不在web.xml中指定配置文件位置的解决办法
- url-pattern的配置
- 使用@RequestMapping映射请求
- REST风格的URL地址约束
- Rest风格增删改查搭建
- 获取请求参数
概述

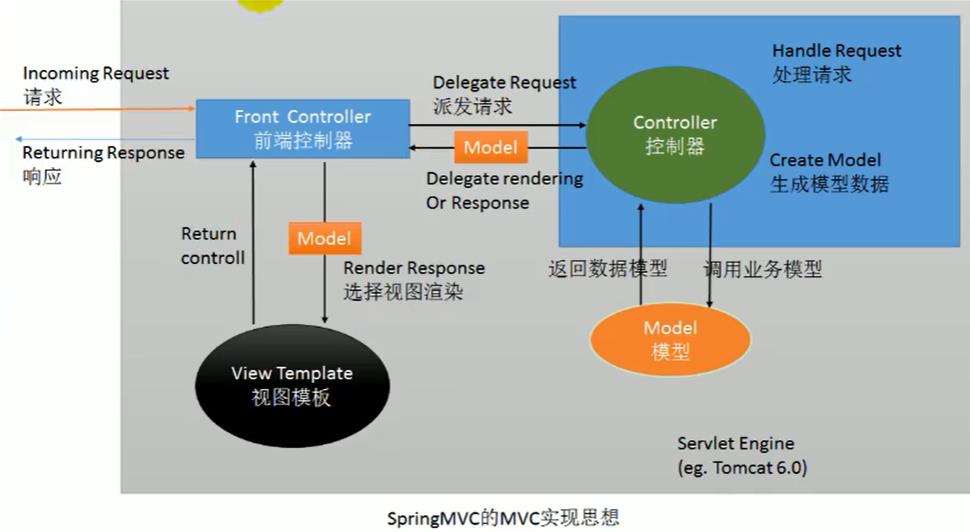
Spring的mvc实现思想
POJO
简单的Java对象(Plain Ordinary Java Objects)实际就是普通JavaBeans
SpringMVC思想是一个前段控制器能拦截所有请求,并智能派发
这个前段控制器是一个servlet,应该在web.xml中配置这个servlet来拦截所有请求
快速入门

1.导入相关坐标
SpringMvc是SpringWeb模块,所有模块的运行都是依赖于核心模块(IOC模块)
核心模块相关坐标
spring坐标:
<!--导入spring的坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
SpringWeb模块相关坐标
spring-web坐标:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.2.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
spring-webmvc坐标:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.15.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
aop模块相关坐标
<!--导入aspectj的坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.4</version>
</dependency>
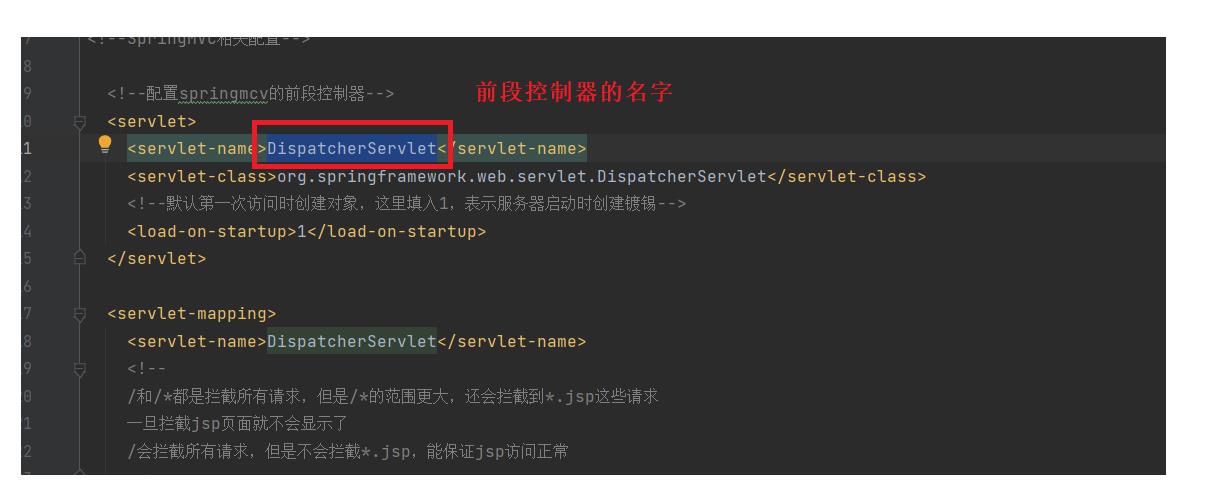
2.配置springmvc的前段控制器—web.xml
<!--SpringMVC相关配置-->
<!--配置springmcv的前段控制器-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!--SpringMvc.xml是前段控制器需要使用-->
<!--sevlet的初始化参数-->
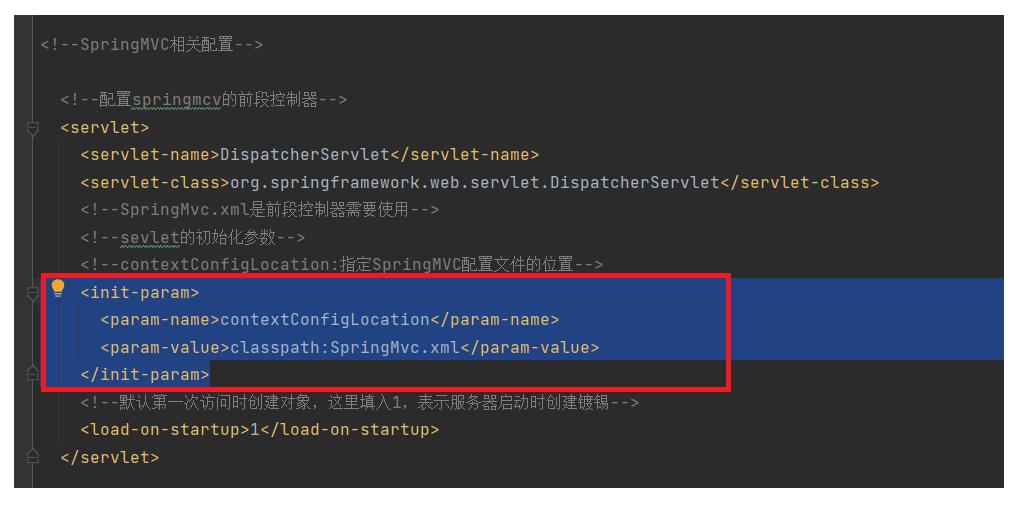
<!--contextConfigLocation:指定SpringMVC配置文件的位置-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:SpringMVC.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--默认第一次访问时创建对象,这里填入1,表示服务器启动时创建镀锡-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<!--
/和/*都是拦截所有请求,但是/*的范围更大,还会拦截到*.jsp这些请求
一旦拦截jsp页面就不会显示了
/会拦截所有请求,但是不会拦截*.jsp,能保证jsp访问正常
-->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
3.配置SpringMvc.xml----组件扫描(注解配置)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--context的组件扫描,需要引入context命名空间-->
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.SpringMvc"/>
</beans>
5.在web.xml中配置监听器,通过监听器的初始化方法,来加载applicationContext.xml配置文件
<!--全局初始化参数-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--配置监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
7.userController类
/*
* 1.告诉SpringMvc这是一个处理器,可以处理请求
* @Controller:标识哪个组件是控制器,能够区分其他组件,这个注解不能乱加
* */
@Controller
public class userController {
/*
* /代表从当前项目开始
* 处理当前项目下的hello请求
* 请求映射
* */
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
return "Success.jsp";
}
}
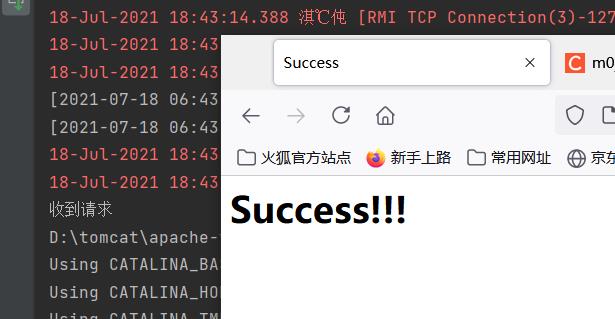
8.success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Success</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Success!!!</h1>
</body>
</html>
9.index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>小朋友</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>小朋友</h1>
<br>
<a href="hello">点击跳转页面</a>
</body>
</html>
10.配置视图解析器,帮助我们拼接页面地址
springmvc.xml:
<!--视图解析器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/"/><!--前缀-->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/><!--后缀-->
</bean>
/*
* 1.告诉SpringMvc这是一个处理器,可以处理请求
* @Controller:标识哪个组件是控制器
* */
@Controller
public class userController {
/*
* /代表从当前项目开始
* 处理当前项目下的hello请求
* 请求映射
* */
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
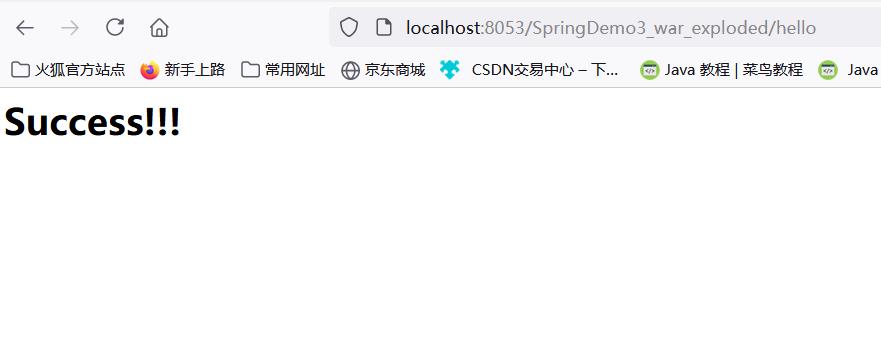
地址栏没变,说明这是一次转发操作
运行流程分析
1.客户端点击链接发送http://localhost:8080/springmvc/hello 请求
2.来到tomcat服务器
3.springmvc的前段控制器收到所有请求
4.查看请求地址和@RequestMapping标注的哪一个匹配,来找到到底使用哪个类的哪个方法来处理
5.前段控制器找到了目标处理器和目标方法,直接利用反射执行目标方法
6.方法执行完成以后,会有一个返回值,springmvc认为这个返回值就是要去的页面地址
7.拿到方法返回值以后,用视图解析器进行拼串得到完整的页面地址
8.拿到页面地址,前段控制器帮我妈转发到页面
@RequestMapping分析
作用:就是告诉SpringMvc这个方法用来处理什么请求
这里@RequestMapping("/hello")里面的/可以省略,即使省略了,也是默认从当前项目下开始,最好加上
如果不在web.xml中指定配置文件位置的解决办法


url-pattern的配置
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<!--
/和/*都是拦截所有请求,但是/*的范围更大,还会拦截到*.jsp这些请求
一旦拦截jsp页面就不会显示了
/会拦截所有请求,但是不会拦截*.jsp,能保证jsp访问正常
处理*.jsp是tomcat做的事情
DefaultServlet是tomcat中处理静态资源的
除了jsp和servlet外,剩下的都是静态资源
index.html:静态资源,tomcat会在服务器下找到这个资源并返回
我们前端控制器的/禁用了tomcat服务器中的DefaultServlet(相当于子类重写了父类的配置,那么就会隐藏父类的配置)
1.服务器的大Web.xml中有一个DefaultServlet的url-pattern=/
2.我们配置的前端控制器url-pattern=/
静态资源会来到DefaultServlet(前端控制器)来看哪个方法的RequestMapping是这个index.html
3.我们没有覆盖服务器中的JspServlet的配置
4./*直接就是拦截所有请求,我们写/是为了迎合后来的Rest风格的URL地址
-->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
使用@RequestMapping映射请求

一个方法处理一个请求,不能两个方法处理一个请求,不然报错
类上加上注解,访问时的路径需要多加一层
/*
* 为当前类的所有的方法的请求地址指定了一个基准路径
* */
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/haha")
public class userController {
/*
* /代表从当前项目开始
* 处理当前项目下的hello请求
* 请求映射
* */
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
@RequestMapping注解的相关属性
method限定请求方式

@Controller
public class userController {
/*
* /代表从当前项目开始
* 处理当前项目下的hello请求
* 请求映射
* */
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
params规定请求参数
建议看下面的这篇链接文章
@RequestMapping中的params(请求参数映射限定)
headers规定请求头
@RequestMapping中的headers(请求头数据映射限定)
/*
* 为当前类的所有的方法的请求地址指定了一个基准路径
* */
@Controller
public class userController {
/*
* user-agent: 浏览器信息
* 实现让谷歌不能访问,火狐能访问
* */
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",headers =
{"User-Agent=User-Agent:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:2.0.1) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/4.0.1"})
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
consumes:只接收内容类型是哪种的请求,规定请求头中的content-type
produces:告诉浏览器返回的内容类型是什么,给响应头中加上Content-Type:text/html;char
@RequestMapping中的consumes属性和produces属性
ant风格的URL----URL地址可以写模糊的通配符



*号优先级比?号低
模糊和精确多个匹配情况下,精确优先
?代替一个字符:
/*
* 为当前类的所有的方法的请求地址指定了一个基准路径
* */
@Controller
public class userController {
@RequestMapping("/antTest0?")
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
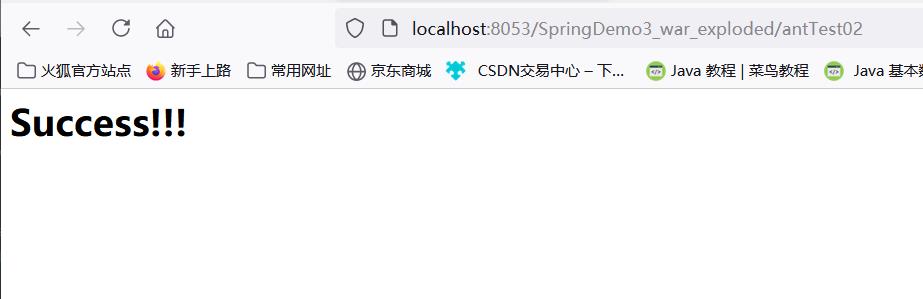
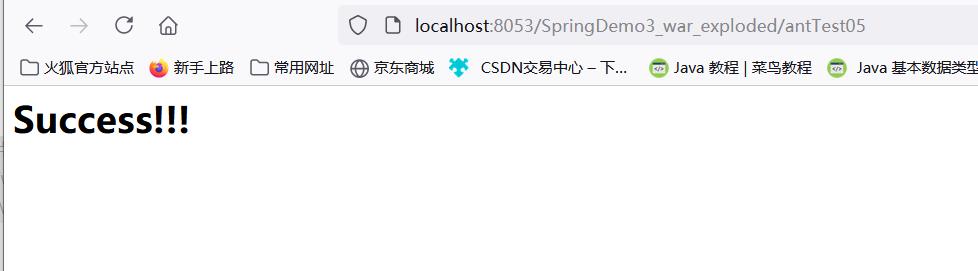
*号匹配任意多个字符
@Controller
public class userController {
@RequestMapping("/antTest0*")
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
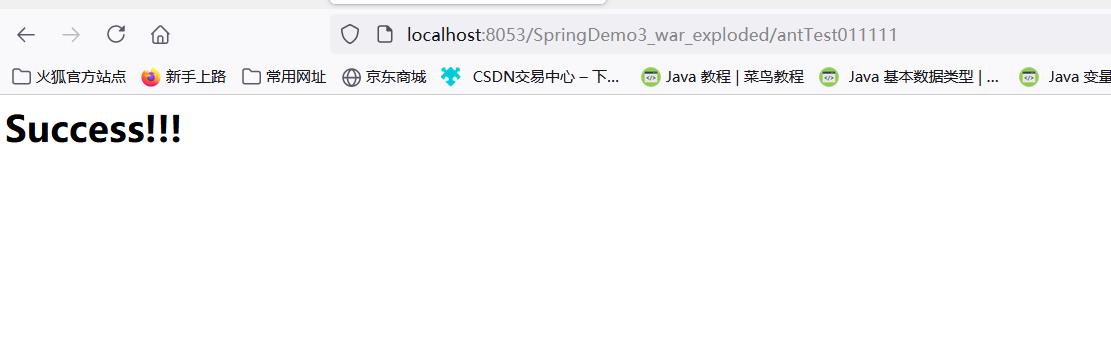
*号代替一层路径,只能代替一层路径
@Controller
public class userController {
@RequestMapping("/*/antTest01")
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
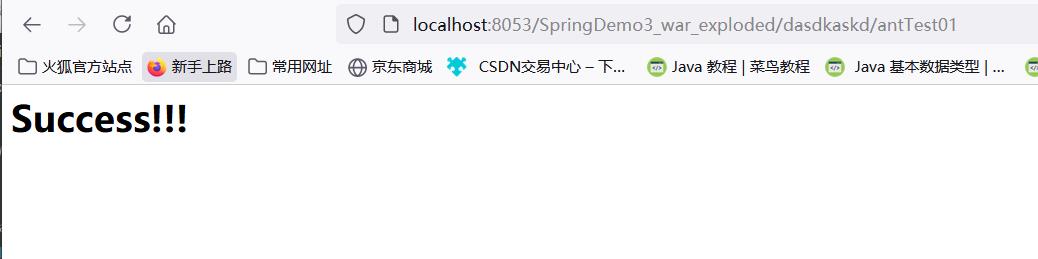
只能代替一层路径
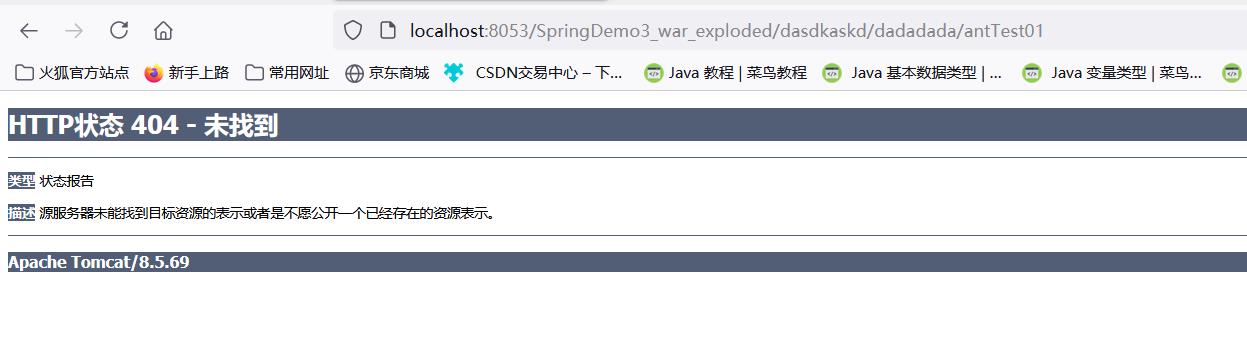
**代替多层路径
@Controller
public class userController {
@RequestMapping("/**/antTest01")
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
路径上可以有占位符,占位符语法就是在任意路径的地方上写一个{变量名}
路径上的占位符只能占掉一层路径
@Controller
public class userController {
@RequestMapping("/antTest01/{id}")
public String show()
{
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
获取路径上的占位符-----@PathVariable()
获取路径中的参数值——@PathVariable中的value
@Controller
public class userController {
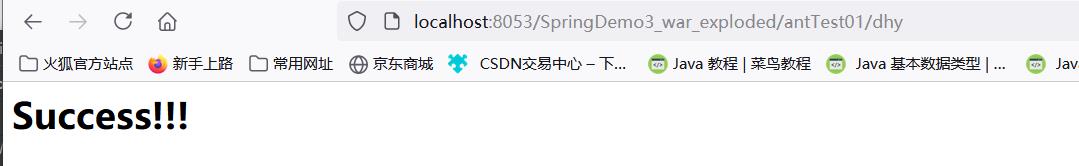
@RequestMapping("/antTest01/{id}")
public String show(@PathVariable("id")String id)
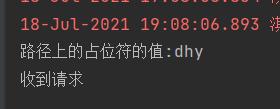
{
System.out.println("路径上的占位符的值:"+id);
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
获取路径上的多层占位符
@Controller
public class userController {
@RequestMapping("/ant/{id1}/{id2}")
public String show(@PathVariable("id1")String id1,@PathVariable("id2")String id2)
{
System.out.println("路径上的占位符的值1:"+id1);
System.out.println("路径上的占位符值2:"+id2);
System.out.println("收到请求");
//视图解析器自动拼串
//前缀+返回值+后缀
return "Success";
}
}
REST风格的URL地址约束





Rest风格增删改查搭建