MySQL数据库高阶语句之查询视图NULL值
Posted 28线不知名云架构师
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL数据库高阶语句之查询视图NULL值相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
准备工作
1.mysql安装
2.实验准备,数据表配置
mysql -uroot -p
show databases;
create database ky11;
use ky11;
create table www (id int,name varchar(10) primary key not null ,score decimal(5,2),address varchar(20),hobbid int(5));
insert into www values(1,'lilei',90,'nanjing',1);
insert into www values(2,'hanmeimei',90,'shanghai',2);
insert into www values(3,'wangwu',70,'shanghai',3);
insert into www values(4,'zhangsan',99,'xuzhou',5);
insert into www values(5,'lili',98,'xuzhou',4);
insert into www values(6,'wangsan',10,'wuxi',3);
insert into www values(7,'tianqi',11,'wuxi',5);
mysql> select * from www;一、MySQL的高阶查询

1.1 排序
1.1.1 按照关键字排序
①语法
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name ORDER BY column1, column2, ...
②ASC 是按照升序进行排序的,是默认的排序方式,即 ASC 可以省略。SELECT 语句中如果没有指定具体的排序方式,则默认按 ASC方式进行排序。
③DESC 是按降序方式进 行排列。当然 ORDER BY 前面也可以使用 WHERE 子句对查询结果进一步过滤。
创建一个表格:
数据库有一张www表,记录了学生的id,姓名,分数,地址和班级
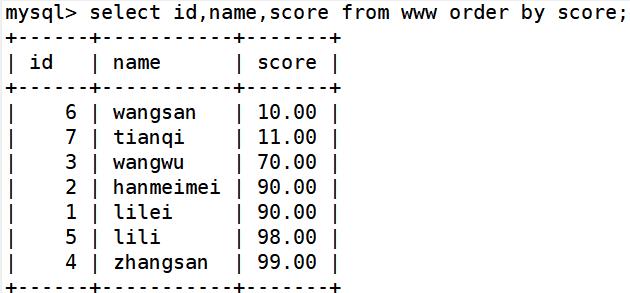
①按照分数升序排列
select id,name,score from www order by score;
②按照分数降序排列
select id,name,score from www order by score desc;

③order by还可以结合where进行条件过滤
select name,score from www where hobbid='3' order by score desc; ##筛选爱好是4的学生按分数降序排列
1.1.2 多字段排序
ORDER BY 语句也可以使用多个字段来进行排序,当排序的第一个字段相同的记录有多条的情况下,这些多条的记录再按照第二个字段进行排序,ORDER BY 后面跟多个字段时,字段之间使用英文逗号隔开,优先级是按先后顺序而定
但order by 之后的第一个参数只有在出现相同值时,第二个字段才有意义
select id,name,hobbid from www order by hobbid desc,id desc; ##查询学生信息先按兴趣id降序排列,相同分数的,id也按降序排列
从www表内查询id、name、hobbid进行多字段的组合排序
hobbid进行降序排序,再在相同hobbid中的id进行降序

select id,name,hobbid from www order by id desc,hobbid desc; ##这里的id值没有重复的,所以此种排序没有意义

1.2区间判断及查询不重复记录
1.2.1AND/OR ——且/或
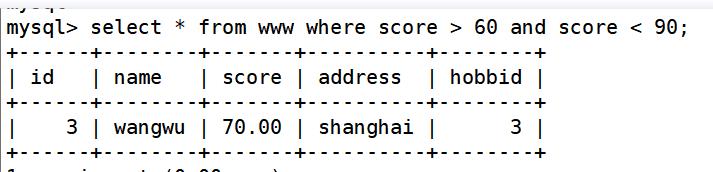
and:同时满足
select * from www where score > 60 and score < 90; ##查询www表内分数大于60且小于90分
or:两者满足一个即可
select * from www where score > 60 or score < 90; ##查询www表内分数大于60或小于90分

1.2.2嵌套/多条件
select * from www where score > 70 or (score > 75 and score < 90); ##筛选出来的是大于70的所有分数

1.2.3添加-distinct
distinct 查询不重复记录
语法
select distinct 字段 from 表名;
实例
select distinct hobbid from www; ##查询数据表www内不重复的数据

多字段去重没有意义了,所以更多用于单字段的去重
select distinct hobbid,id from www;

1.3对结果进行分组

语法
SELECT column_name, aggregate_function(column_name)FROM table_name WHERE column_name operator valueGROUP BY column_name;
实例
按hobbid相同的分组,计算相同分数的学生个数(按照name计数,同时基于hobbid分组)
select count(name),hobbid from www where score>=80 group by hobbid;

结合where语句,筛选分数大于等于80的分组,计算学生个数
select count(name),hobbid from www where score>=80 group by hobbid;
 结合order by把计算出的学生个数按升序排列
结合order by把计算出的学生个数按升序排列
select count(name),score,hobbid from www where score>=80 group by hobbid order by count(name) asc;

1.4限制结果条目-limit

语法
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name LIMIT [offset,] number
LIMIT 的第一个参数是位置偏移量(可选参数),是设置 MySQL 从哪一行开始显示。 如果不设定第一个参数,将会从表中的第一条记录开始显示。需要注意的是,第一条记录的 位置偏移量是 0,第二条是 1,以此类推。第二个参数是设置返回记录行的最大数目。
实例:
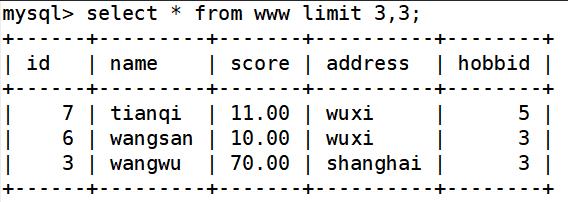
select * from www limit 3; ##查询所有信息显示前四行记录

select * from www limit 3,3; ##从第4行开始,往后显示3行内容
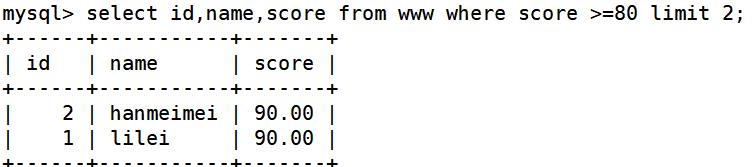
select id,name,score from www where score >=80 limit 2; ##成绩大于80的且显示前两条记录
select id,name,score from www where score >=80 limit 2,2; ##成绩大于80的且显示第三行开始的后两条记录
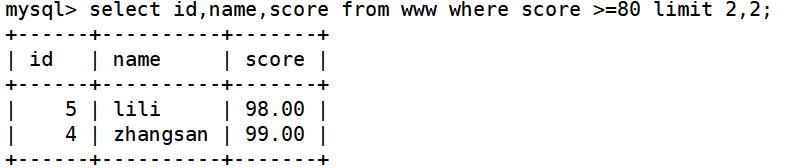
select id,name from www order by id limit 3; ##结合order by语句,按id的大小升序排列显示前三行

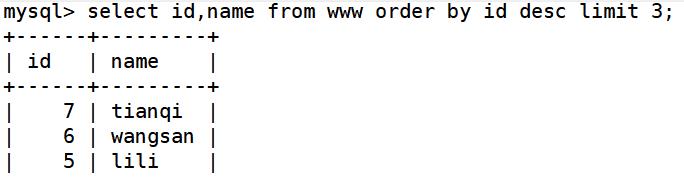
select id,name from www order by id desc limit 3; ##输出最后三行需要结合到order by语句
1.5设置别名-alias
在 MySQL 查询时,当表的名字比较长或者表内某些字段比较长时,为了方便书写或者 多次使用相同的表,可以给字段列或表设置别名。使用的时候直接使用别名,简洁明了,增强可读性
对于列的别名:SELECT column_name AS alias_name FROM table_name;
对于表的别名:SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name AS alias_name;
s:代表多个列明
在使用 AS 后,可以用 alias_name 代替 table_name,其中 AS 语句是可选的。AS 之后的别名,主要是为表内的列或者表提供临时的名称,在查询过程中使用,库内实际的表名 或字段名是不会被改变的
实例
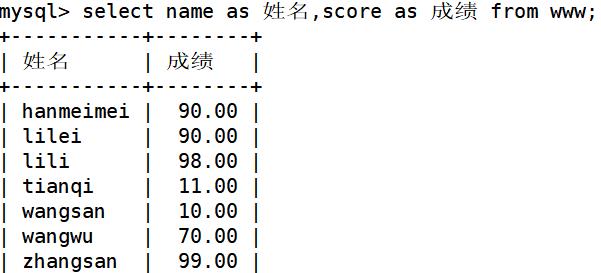
select name as 姓名,score as 成绩 from www;
如果表的长度比较长,可以使用 AS 给表设置别名,在查询的过程中直接使用别名
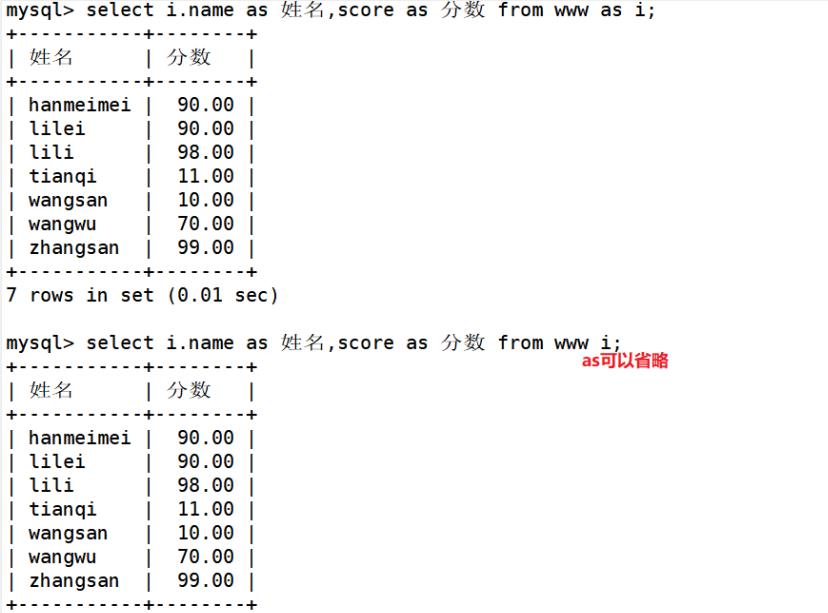
临时设置www的别名为i
select i.name as 姓名,i.score as 成绩 from info as i;
查询info表的字段数量,以number显示
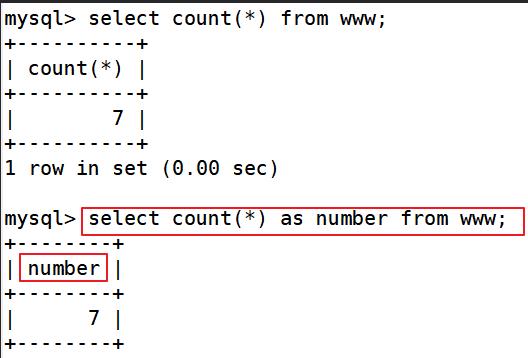
好处:
- 对复杂的表进行查询的时候,别名可以缩短查询语句的长度
- 多表相连查询的时候(通俗易懂、减短sql语句)
此外,AS 还可以作为连接语句的操作符。
create table www1 as select * from www; ##创建www1表,将www表的查询记录全部插入www1表

1.6通配符

实例
select id,name from www where name like '%n%'; ##查询名字中间有n的记录

select id,name from www where name like 'w__g__'; ##查询名字w和g中间有2个字符的记录

select id,name from www where name like 'wan___'; ##查询wang后面3个字符的名字记录

通配符“%”和“_”不仅可以单独使用,也可以组合使用
select id,name from www where name like 'l%_'; ##查询名字以l开头的记录

1.7子查询

1.7.1select语句使用
相同表实例
select name,score from info where id in (select id from info where score >80);
in: 将主表和子表关联/连接的语法;从主语句的结果集中过滤条件
主语句:select name,score from info where id
子语句(集合): select id from info where score >80
子语句中的sql语句是为了,最后过滤出一个结果集,用于主语句的判断条件
不同表实例
create table qqq (id int); ##创建数据表qqq
insert into qqq values(1),(2),(3),(4);

select id,name,score from www where id in (select * from qqq); ##多表查询

1.7.2子查询的多层嵌套

- 多层嵌套–子查询结合SELECT
select name,score from www where id in (select id from www where score > 80); ##查询分数大于80的记录

- 多层嵌套–子查询结合INSERT
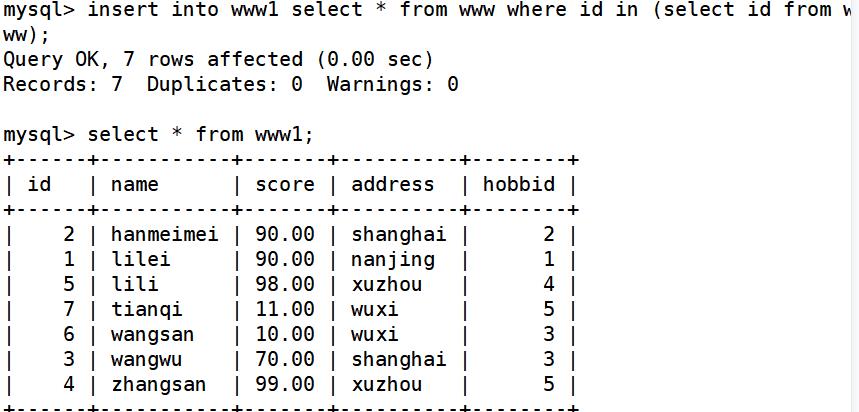
子查询还可以用在 INSERT 语句中。子查询的结果集可以通过 INSERT 语句插入到其他的表中
delete from www1; ##将t1里的记录全部删除,重新插入info表的记录
insert into www1 select * from www where id in (select id from wwww);
- 多层嵌套–子查询结合UPDATE
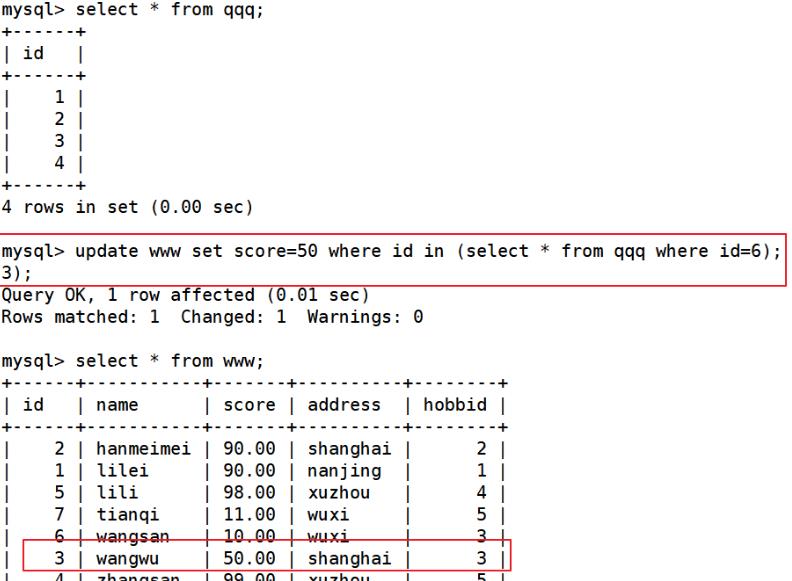
UPDATE 语句也可以使用子查询
UPDATE 内的子查询,在 set 更新内容时,可以是单独的一列,也可以是多列
update www set score=50 where id in (select * from qqq where id=3);
- 在 IN 前面还可以添加 NOT,其作用与 IN 相反,表示否定(即不在子查询的结果集里面)
update www set score=100 where id not in (select * from qqq where id > 1);
select * form member where id >1 ##选择出id大于1的
not in:不在范围内
表示 先匹配出qqq表内的id字段为基础匹配的结果集(2,3,4)
然后再执行主语句,以主语句的id为基础 进行where 条件判断/过滤,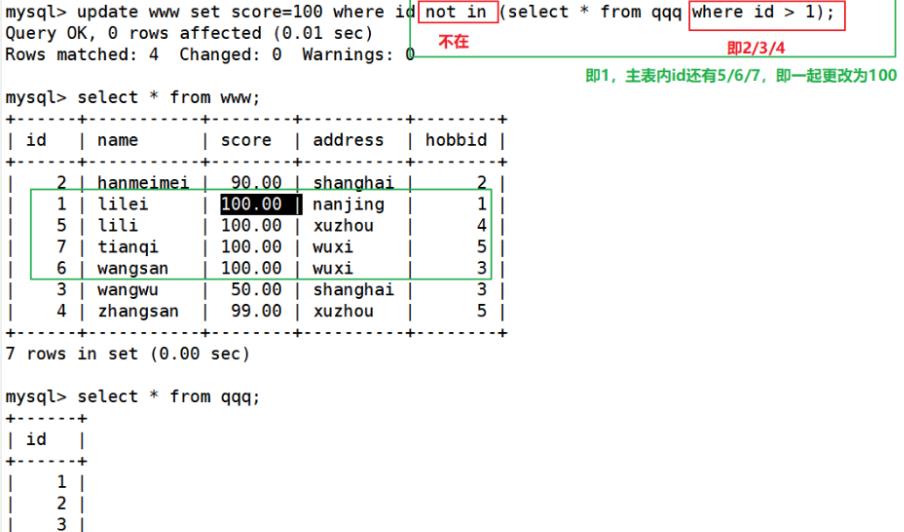
- 多层嵌套–子查询结合DELETE
delete from www where id in ( select id where score > 80); ##删除大于80分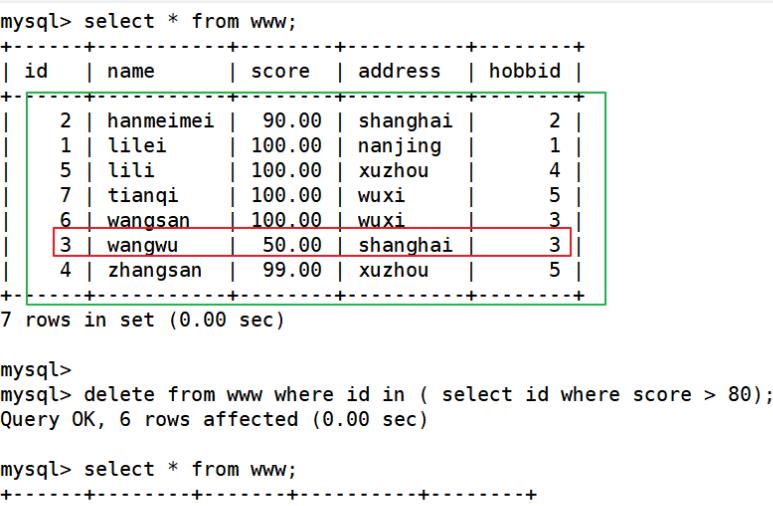
- 多层嵌套–子查询结合EXISTS
EXISTS 这个关键字在子查询时,主要用于判断子查询的结果集是否为空。如果不为空, 则返回 TRUE;反之,则返回 FALSE
select count(*) from www where exists(select id from www where score=90); ##有满足分数是90的则计数
select count(*) from www where exists(select id from www where score>100); ##没有满足分数是100的则直接返回0

二、MySQL数据库-视图


2.1 单表创建视图
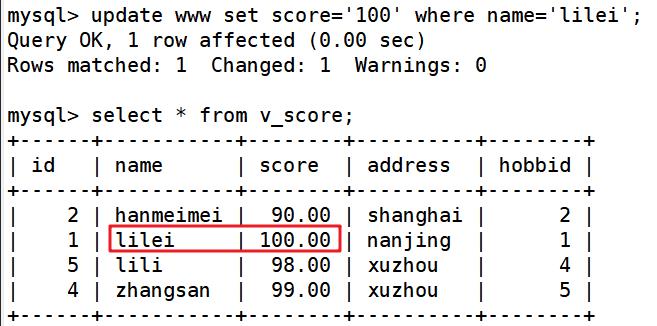
create view v_score as select * from www where score>=80; ##创建视图
select * from v_score; ##查看视图
update www set score='100' where name='lilei';
2.2多表创建视图
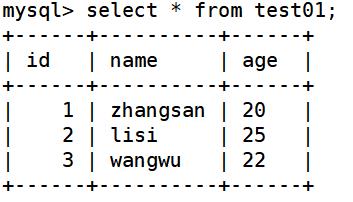
create table test01 (id int,name varchar(10),age char(10));
insert into test01 values(1,'zhangsan',20),(2,'lisi',25),(3,'wangwu',22);
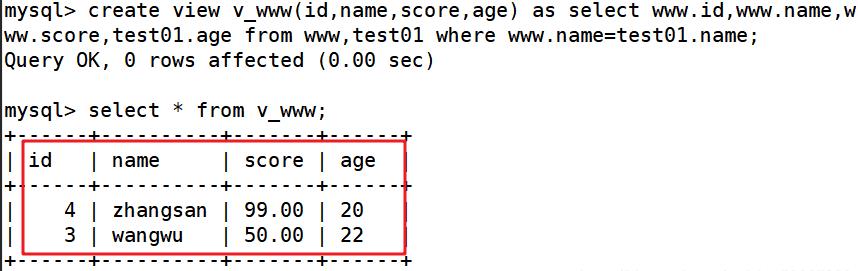
create view v_www(id,name,score,age) as select www.id,www.name,www.score,test01.age from www,test01 where www.name=test01.name; ##需要创建一个表需要输出id、姓名、成绩、年龄
创建视图 视图叫v_组合,字段是id、name、score、test01.age来源于www.id、www.name、www.score、test01.age,来自于www和test01表,同时where判断www表中的name等于test01表内的name字段
select * from v_www;
2.3修改表-update

update www set score=100 where name='zhangsan'; ##修改zhangsan成绩为100
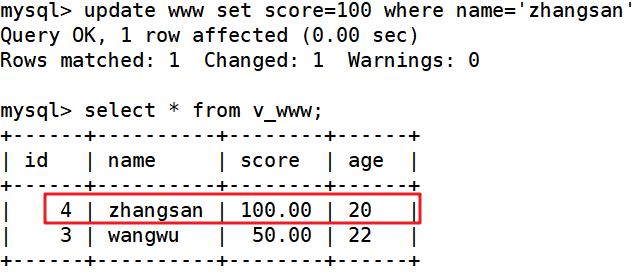
更改视图会影响原本文件
select * from www; ##查询源文件发现zhangsan成绩已更改
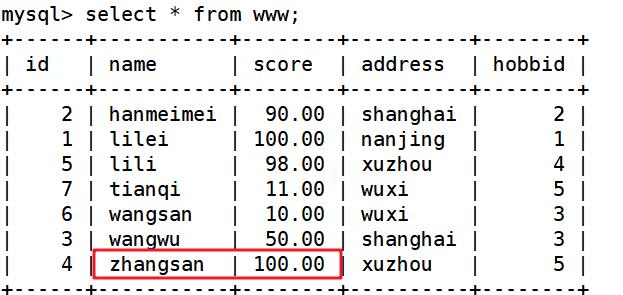
三、NULL值

实例:
alter table www add column addr varchar(50); ##插入一条记录,显示出来就是null
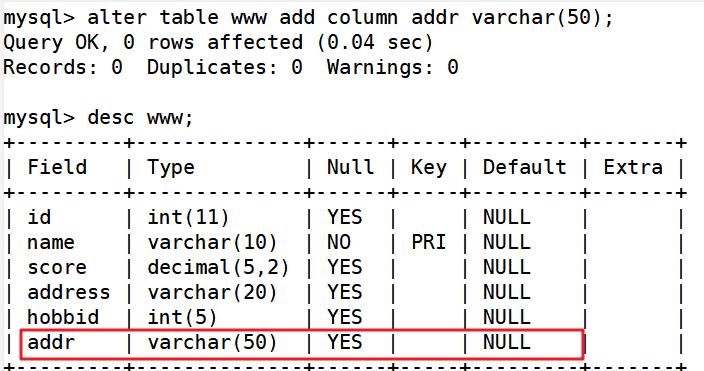
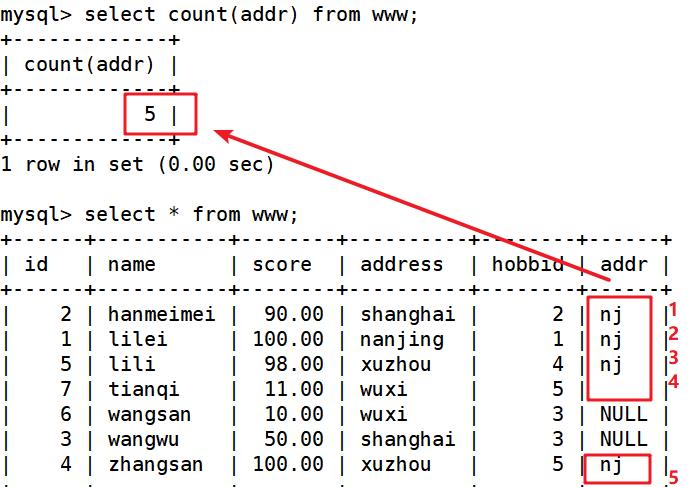
update www set addr='nj' where score >=70; ##分数≥70的更改地址为nj

select count(addr) from www; ##统计数量:检测null不会加入统计中

update www set addr='' where name ='tianqi'; ##www表中其中name等于tianqi修改为空值
select count(addr) from www; ##统计数量,检测空值反而会会被添加到统计中
select * from www where addr is null; ##查询空值的判断方法
select * from www where addr is not null; ##查询不是空值的判断方法
以上是关于MySQL数据库高阶语句之查询视图NULL值的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
