Spring知识总结
Posted scanner小霸王
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring知识总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.IOC:反转控制
1)DI:依赖注入
2)IOC在spring容器的实现:
a).通过IOC容器读取Bean的实例之前,需要先将IOC容器本身实例化
b)Spring提供了IOC容器的两种实现方式.
BeanFactory:IOC容器的基本实现,是Spring内部的基础设施,是面向Spring本身的,不是提供给开发人员使用的。
ApplicationContext:BeanFactory的子接口,提供了更多高级特性。面向Spring的使用者,几乎所有场合都使用ApplicationContext而不是底层的BeanFactory。
3)ApplicationContext有两个主要实现类:
a) ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:对应类路径下的XML格式的配置文件
b) FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:对应文件系统中的XML格式的配置文件
4)bean:
同一个类型的bean在XML文件中配置了多个,则获取时会抛出异常,所以同一个类型的bean在容器中必须是唯一的。
a)通过setXXX()方式赋值:
XML配置
<!-- 使用bean元素定义一个由IOC容器创建的对象 -->
<!-- class属性指定用于创建bean的全类名 -->
<!-- id属性指定用于引用bean实例的标识 -->
<bean id="student" class="first.bean.Student">
<!-- 使用property子元素为bean的属性赋值 -->
<property name="studentId" value="1001"/>
<property name="stuName" value="Tom2015"/>
<property name="age" value="20"/>
</bean>
代码实现:
//1创建IOC容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("helloWorld.xml");
//2根据id值得到bean实例
Student student = (Student) classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student);
b)通过构造的方式赋值
XML
<bean id="student1" class="first.bean.Student">
<constructor-arg value="007" index="0" type="java.lang.Integer"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="名字" index="1" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="18" index="2" type="java.lang.Integer"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="student11" class="first.bean.Student">
<constructor-arg name="studentId" value="007" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="名字" name="stuName"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="18" name="age"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
代码实现:
@Test
public void test(){
//1创建IOC容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("helloWorld.xml");
//2根据id值得到bean实例
Student student = (Student) classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("student1");
System.out.println(student);
//2根据id值得到bean实例
Student student11 = (Student) classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("student11");
System.out.println(student11);
}
c)bean给属性赋null值,ref标签赋值以及属性里面有对象,集合,map,properties等属性;
xml
<bean id="student2" class="first.bean.Student">
<!-- 使用property子元素为bean的属性赋值 -->
<property name="stuName">
<null></null>
</property>
<!--list集合里面存一个对象-->
<!--对象实体-->
<property name="dog">
<bean class="first.bean.Dog">
<property name="name" value="大黄"></property>
</bean>
</property>
<property name="bookList">
<list>
<bean class="first.bean.Session">
<constructor-arg name="classId" value="001"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="className" value="计算机"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean class="first.bean.Session">
<constructor-arg name="classId" value="002"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="className" value="高数"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</list>
</property>
<!--map-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry>
<key>
<value>
map01
</value>
</key>
<bean class="first.bean.Dog">
<property name="name" value="my dog"></property>
</bean>
</entry>
<entry>
<key>
<value>
map02
</value>
</key>
<ref bean="secondog"></ref>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--properties-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">root</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="secondog" class="first.bean.Dog">
<property name="name" value="大黄"></property>
</bean>
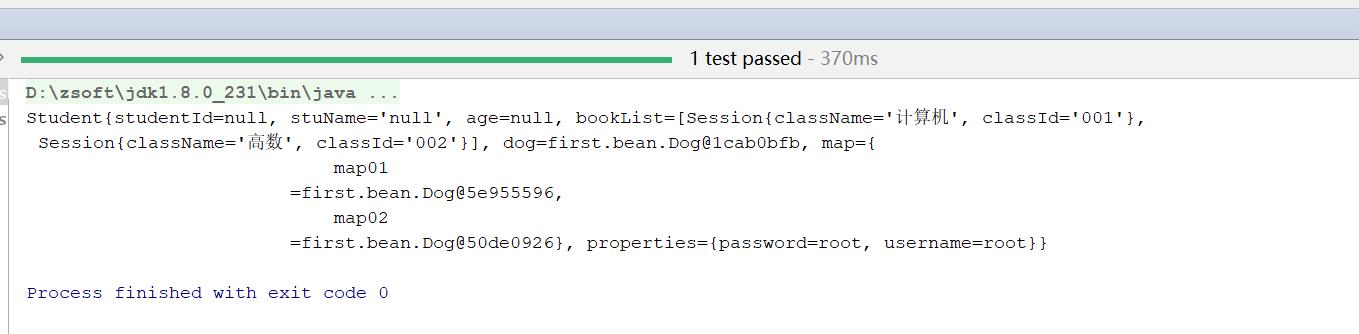
代码:
@Test
public void test01(){
//1创建IOC容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("helloWorld.xml");
//2根据id值得到bean实例
Student student = (Student) classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("student2");
System.out.println(student);
}
输出:
d)级联赋值:为对象的对象的属性赋值
xml
<!--级联赋值-->
<bean id="student3" class="first.bean.Student">
<property name="dog" ref="secondog">
</property>
<property name="dog.name" value="新的大黄"></property>
</bean>
e)通过继承实现bean配置信息的重用
(指的是配置信息的继承,并非类的继承)
加了一个parent的属性;
当加了一个abstract的属性的时候,就意味着只能继承,不能被调用获取数据
<bean id="student4" class="first.bean.Student" parent="student2">
<property name="dog" ref="secondog">
</property>
<property name="dog.name" value="新的大黄吗"></property>
</bean>
f)bean的创建顺序默认就是配置文件的配置顺序
,可以通过depends-on改变创建顺序
意思是等bean容器secondog,student3执行完成再执行student1
<bean id="student1" class="first.bean.Student" depends-on="secondog,student3">
<constructor-arg value="007" index="0" type="java.lang.Integer"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="名字" index="1" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="18" index="2" type="java.lang.Integer"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
f) bean的作用域,指定bean是否单实例,默认是单实例
scope属性:有四种值:
prototype:多实例:当获取bean实例时候才会被创建,且每一次获取将得到一个新的实例。
singleton:单实例,单实例在容器启动完成就已经创建好对象,保存在容器中,构造器只调一次。
request:在web环境同一次请求创建一个bean实例(通常没用)
session:在web环境同一次会话创建一个bean实例(通常没用)
g)配置通过静态工厂方法创建bean,实例工厂创建bean、FactoryBean
bean的创建默认就是框架通过反射new出来的bean实例,
工厂模式:工厂帮我们创建对象
静态工厂:工厂本身不用创建对象,通过静态方法调用,对象=工厂类.工厂方法名();
实例工厂:工厂本身需要创建对象,工厂类 对象 = new 工厂类,工程类.getAirPlane();
静态工厂XML:
这里并非要创建AirPlaneStaitcFactory实例,所以指定factory-method属性表名是个工厂,返回的不是工厂的对象而是该方法的对象
<!--这里并非要创建AirPlaneStaitcFactory实例,所以指定factory-method属性表名是个工厂,返回的不是工厂的对象而是该方法的对象-->
<bean id="staitcAirPlane" class="first.bean.AirPlaneStaitcFactory" factory-method="getAirPlane">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="歼20">
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
java代码:
package first.bean;
public class AirPlaneStaitcFactory {
public static AirPlane getAirPlane(String name){
AirPlane airPlane = new AirPlane();
airPlane.setName(name);
airPlane.setDriverName("机长名字");
airPlane.setLength("100m");
return airPlane;
}
}
实例工厂:
xml:
ii)先创建InstancePlaneFactory bean实例
ii)配置我们要创建的AirPlane使用哪个工厂
factory-bean指定哪个工厂实例
factory-method使用哪个工厂方法
<!--先创建实例工厂-->
<bean id="InstancePlaneFactory" class="first.bean.AirPlaneInstanceFactory">
</bean>
<bean id="InstancePlane" class="first.bean.AirPlane"
factory-bean="InstancePlaneFactory"
factory-method="getAirPlane">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="实例飞机"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
java
public void test2(){
//1创建IOC容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
AirPlaneInstanceFactory airPlaneInstanceFactory = (AirPlaneInstanceFactory)classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("InstancePlaneFactory");
AirPlane AirPlane = airPlaneInstanceFactory.getAirPlane("实例机长");
System.out.println(AirPlane);
}
FactoryBean*(是spring规定的接口)
这个接口的实现类都是工厂类
xml:
<bean id="myFactoryBeanImple" class="first.bean.MyFactoryBeanImple">
</bean>
实现类:
getObject相当于工厂方法;
getObjectType返回工厂类型
isSingleton:是否单例;false不是单例
package first.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
public class MyFactoryBeanImple implements FactoryBean<AirPlane>{
/**\\
* 返回创建的对象
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public AirPlane getObject() throws Exception {
System.out.println("进来getObject方法。。。");
AirPlane airPlane = new AirPlane();
airPlane.setName("自带工厂方法的名字");
return airPlane;
}
/**
* 返回对象的类型
* spring会自带调用,来确定创建对象的类型
* @return
*/
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
System.out.println("进来getObjectType方法" +
"。。。");
return null;
}
/**
* false为单例
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
测试结果:
因为该工厂是spring认识的工厂,当容器一被创建的时候,
当isSingleton()方法返回false的时候,为多例,
当isSingleton()方法返回值为true时候,为单例子,;
不管是单实例还是多实例,只有bean被调用才创建。
h)创建带有生命周期方法的bean
生命周期:bean的创建到销毁
ioc容器中注册bean:
ii)、单例bean,容器启动的时候创建好,容器关闭时候销毁;
ii)多例bean,获取的时候才创建;
可以为bean自定义一些生命周期方法,在创建和销毁就可以自动调用;
bean里面可以指定destroy-method(销毁),和init-method(创建)属性

i)bean的后置处理器BeanPostProcessor,在bean的初始化前后调用方法
xml:
<bean id="airPlane" class="first.bean.AirPlane" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestroy">
<property name="name" value="歼击机"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="processor" class="first.bean.MyBeanPostProcessor">
</bean>
java:
@Test
public void test3(){
//1创建IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
classPathXmlApplicationContext.close();
// System.out.println(AirPlane);
}
运行结果:
before和after方法分别在初始化之前和后初始化之后调用
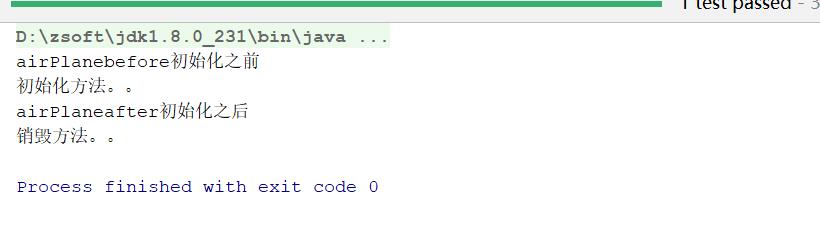
执行顺序:
构造器—》后置处理器before—》初始化方法–》后置处理器after–》初始化完成
无论bean是否有初始化方法,后置处理器都会默认有,还有继续工作
j)引用外部属性文件
数据库连接池作为单实例是最好的,一个项目就一个连接池,连接池里面有很多连接,可以让spring帮忙创建
xml
方式一:直接在xml配置;
方式二:引入外部的配置文件
<context:property-placeholder location=“classpath:dbconfig.properties”/>
并加上命名空间:
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
,为了防止和spring的属性重复,通常在配置的时候,加个前缀。eg:jdbc.username
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="hhh"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.10.**:3306/xx?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"></property>
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="processor" class="first.bean.MyBeanPostProcessor">
</bean>
<!--加载外部配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:dbconfig.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource2" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
java可以根据类型拿或者根据id去拿取;
根据类型拿到连接池,可以获得该类型的所有实现子类等等
@Test
public void test4(){
//1创建IOC容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
//拿到连接池
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("dataSource");
//根据类型拿到连接池,可以获得该类型的所有实现子类等等
DataSource dataSource11 = (DataSource)classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean(DataSource.class);
DataSource dataSource2 = (DataSource)classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("dataSource2");
}
k)基于xml的自动装配
autowire=“defaut/no”
三种规则自动装配:
在bean中加入autowire的属性;
例如:
