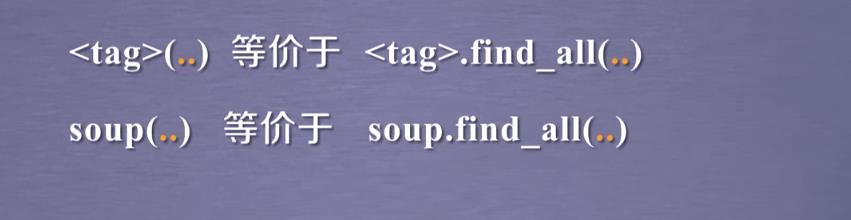python爬虫入门
Posted 临风而眠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python爬虫入门相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
python爬虫入门(4)
bs4库实践
一.信息组织与提取方法
1.三种主要的信息组织形式
XML JSON YAML



2.信息提取的一般方法
从标记过的信息中提取所关注的内容



实例:提取html中所有URL链接
方法:
(1)搜索到所有<a>标签
(2)解析<a>标签格式,提取href后的链接内容
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo =r.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,"html.parser")
for link in soup.find_all('a'):
print(link.get('href'))
运行结果
http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001
http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001
3.基于bs4库的HTML内容查找方法
find_all方法
name参数
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo =r.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,"html.parser")
print(soup.find_all('a'))
print(soup.find_all(['a','b']))
运行结果
[<a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">Basic Python</a>, <a class="py2" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" id="link2">Advanced Python</a>]
[<b>The demo python introduces several python courses.</b>, <a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">Basic Python</a>, <a class="py2" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" id="link2">Advanced Python</a>]
for tag in soup.find_all(True):
print(tag.name)
运行结果
html
head
title
body
p
b
p
a
a
attrs参数
print(soup.find_all('p','course'))
print(soup.find_all(id='link1'))
运行结果
[<p class="course">Python is a wonderful general-purpose programming language. You can learn Python from novice to professional by tracking the following courses:
<a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">Basic Python</a> and <a class="py2" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" id="link2">Advanced Python</a>.</p>]
[<a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">Basic Python</a>]
import re
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get("http://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo =r.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,"html.parser")
print(soup.find_all(id=re.compile('link')))
这里用到了正则表达式,会输出id以link开头的信息
运行结果
[<a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">Basic
Python</a>, <a class="py2" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" id="link2">Advanced Python</a>]
recursive参数
默认
True,若想只搜索儿子节点,就设置为False
print(soup.find_all('a'))
print(soup.find_all('a',recursive=False))#仅搜索儿子节点
string参数
print(soup.find_all(string="Basic Python"))
print(soup.find_all(string=re.compile("python")))#正则表达式
运行结果
['Basic Python']
['This is a python demo page', 'The demo python introduces several python courses.']
由于find_all很常用,故提供了两种简单的等价形式
二.实例:爬取菜价
爬取北京新发地市场上的菜价信息
1.查看网页源代码
查看源代码,看源代码中是否直接显示需要爬取的信息

发现有,进行下一步
2.检验状态码
import requests
url="http://www.xinfadi.com.cn/marketanalysis/0/list/1.shtml"
resp=requests.get(url)
print(resp.status_code)
返回值为200,可以正常访问
爬取网页源代码
print(resp.text)
中文可以正常显示,字符集没有问题
3.生成Beautiful对象
不要忘记解释器
#指定html解析器
page=BeautifulSoup(resp.text,"html.parser")
4.查找数据(菜价表)
方法:
find(标签,属性=属性值) (find只找一个)
find_all
所找内容在一个表格里面,先找
<table>有很多
<table>标签,他们的不同就是class属性的属性值不同
#find方法
table=page.find("table",class_="hq_table")
因为class是python的关键字,所以易混淆,bs4提供了加一个下划线的方法来区分
另一种写法:
table=page.find("table",attrs={"class":"hq_table"})
此写法避免class问题
5.在菜价表里找具体数据
<tr>代表行
<td>代表列
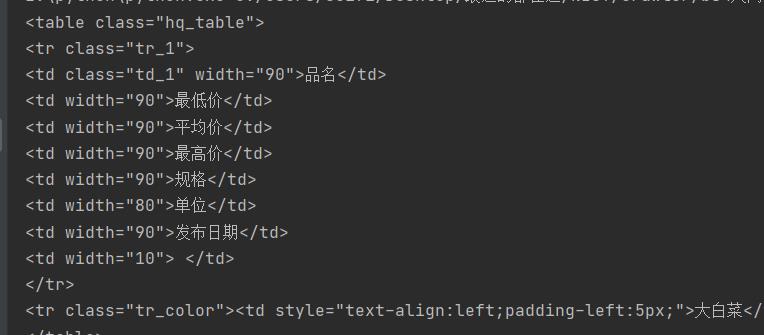
图中所显示的是第一个<tr>标签出现的地方
而后面第二个<tr>标签开始才是正式的所要提取的内容
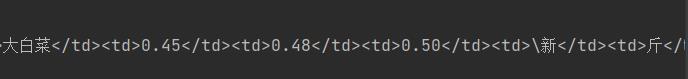
要在每个<tr>标签里找到所有<td>标签,分别对应品名,最低价,平均价,最高价,规格,单位,发布日期
具体代码如下:
trs=table.find_all("tr")[1:]#第一行表头先不提取
for tr in trs:#每一行
tds=tr.find_all("td")
# .text表示拿到被标签标记的内容
name =tds[0].text #品名
lowest =tds[1].text #最低价
mean =tds[2].text #平均价
highest=tds[3].text #最高价
guige =tds[4].text #规格
unit =tds[5].text #单位
date =tds[6].text #发布日期
print(name,lowest,mean,highest,guige,unit,date)
python语法没过关, 🌵🐶,去搜了个python切片的教程
6.写入文件
import csv
f=open("菜价.csv",mode="w")
csvwriter = csv.writer(f)
7.完整代码
#爬取菜价
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
url="http://www.xinfadi.com.cn/marketanalysis/0/list/1.shtml"
resp=requests.get(url)
#指定html解析器
page=BeautifulSoup(resp.text,"html.parser")
# table=page.find("table",class_="hq_table")
f=open("菜价.csv",mode="w")
csvwriter = csv.writer(f)
table=page.find("table",attrs={"class":"hq_table"})
#拿到每一行的数据
trs=table.find_all("tr")[1:]#第一行表头先不提取
for tr in trs:#每一行
tds=tr.find_all("td")
# .text表示拿到被标签标记的内容
name =tds[0].text #品名
lowest =tds[1].text #最低价
mean =tds[2].text #平均价
highest=tds[3].text #最高价
guige =tds[4].text #规格
unit =tds[5].text #单位
date =tds[6].text #发布日期
csvwriter.writerow([name,lowest,mean,highest,guige,unit,date])
f.close()
print("done!")
resp.close()
三.实例:爬取图片
目标,在优美图库网站上爬取动画图片
1.查看网页源码
所要爬取的是具体的图片,首先看所需爬取内容是否在源码中有体现
比如第一张双刀索隆,是有的,那就可以继续了
2.查看状态码,编码
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
url = "https://umei.net/katongdongman/"
resp = requests.get(url)
print(resp.status_code)
print(resp.apparent_encoding)
print(resp.encoding)
状态码是200
resp.apparent_encoding是utf-8
resp.encoding是ISO-8859-1
所以需要修改编码
resp.encoding=resp.apparent_encoding
检验编码除了上面那种打印两种编码对比是否相同的方法,还可以先print(resp.text),然后看是否有乱码,有乱码就去看charset里面写的编码,然后把resp.encoding改为那种编码即可
3.生成Beautiful对象
mainpage = BeautifulSoup(resp.text, "html.parser")
4.在主页面找到分区

找到有辨识度网页源码,ctrl+F搜索发现网页源码中只有这一处有
TypeList,所以可以选择这个
ChildPages = mainpage.find("div", attrs={"class": "TypeList"})
5.拿到各个所需图片的所在网址的url
childs = ChildPages.find_all("a")#find_all方法会返回一个列表
for child in childs:
# 从BeautifulSoup对象拿到里面的href属性的值,直接用get
print(child.get("href"))

发现不是完整的域名,要拼接一下
for child in childs:
# 从BeautifulSoup对象拿到里面的href属性的值,直接用get
# print(child.get("href"))
child_page_resp = requests.get("https://umei.net/"+child.get("href"))
child_page_resp.encoding = 'utf-8'
child_page_text = child_page_resp.text
6.在各个子页面找图片的下载地址
以双刀索隆那张图为例,在那个子页面找辨识度高的源代码

for child in childs:
# 从BeautifulSoup对象拿到里面的href属性的值,直接用get
# print(child.get("href"))
child_page_resp = requests.get("https://umei.net/"+child.get("href"))
child_page_resp.encoding = 'utf-8'
child_page_text = child_page_resp.text
child_page = BeautifulSoup(child_page_text,"html.parser")
p=child_page.find("p",align="center")
img =p.find("img")
print(img)
break
#先试一下效果,所以加一个break
成功!

实际需要的是src属性
在标签里面拿到属性,用.get()方法
print(img.get("src"))
7.下载图片
请求图片的地址即可
img = p.find("img")
src = img.get("src")
# 下载图片
img_resp = requests.get(src)
img_name = src.split("/")[-1]
# 拿到url中的最后一个/后面的内容
with open("picture/"+img_name, mode="wb")as f: # 放 在提前建好的picture文件夹里面
# 图片内容写入文件
f.write(img_resp.content) # img_resp.content是字节
time.sleep(1)
为了了解进度,可以加入提示语
#如:
print('done')
防止ip被封
import time
#在for循环中:
time.sleep(1)
mode='rb'

done!
8.完整代码
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
url = "https://umei.net/katongdongman/"
resp = requests.get(url)
resp.encoding = resp.apparent_encoding
mainpage = BeautifulSoup(resp.text, "html.parser")
# 在主页面找到分区
ChildPages = mainpage.find("div", attrs={"class": "TypeList"})
# print(ChildPages)
childs = ChildPages.find_all("a")
for child in childs:
# 从BeautifulSoup对象拿到里面的href属性的值,直接用get
# print(child.get("href"))
child_page_resp = requests.get("https://umei.net/"+child.get("href"))
child_page_resp.encoding = 'utf-8'
child_page_text = child_page_resp.text
child_page = BeautifulSoup(child_page_text, "html.parser")
p = child_page.find("p", align="center")
img = p.find("img")
src = img.get("src")
# 下载图片
img_resp = requests.get(src)
img_name = src.split("/")[-1]
# 拿到url中的最后一个/后面的内容
with open("picture/"+img_name, mode="wb")as f: # 放在提前建好的picture文件夹里面
# 图片内容写入文件
f.write(img_resp.content) # img_resp.content是字节
time.sleep(1)
print('done',img_name)
print('all done!')
resp.close()
四.遇到的问题
1.writerow

一开始csvwriter.writerow([name,lowest,mean,highest,guige,unit,date])写成了csvwriter.writerow(name,lowest,mean,highest,guige,unit,date)
以上是关于python爬虫入门的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章