C++中STL常用算法
Posted 不倒翁*
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++中STL常用算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.常用的遍历算法
(1)for_each
将仿函数f施行于[first, last)区间内每一个元素身上。f不可以改变元素内容,因为first和last都是InputIterator,不保证接受赋值行为。如果想要修改内容,应该使用算法transform(),f可以返回一个值,但该值会被忽略。f可以是仿函数,也可以是普通函数.使用该算法要包含#include < algorithm >头文件

include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
//普通函数
void print1(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
//仿函数
class Print2
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
};
void test()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(50);
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print1); //遍历容器,并按照给定函数输出
cout << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print2());
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
上面代码中的print1和print2两个函数都是打印出当前值的意思,就是在使用for_each遍历v容器时,打印当前v容器对应的值.下面是程序运行的结果.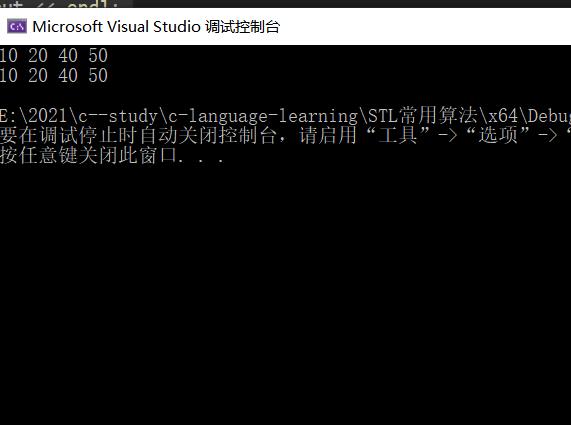
(2)transform
transform的主要用法是,遍历一个原容器的值,并把原容器中的值,以一个仿函数的形式,来将原容器中的值按照仿函数里的实现来改变,并将改变后的值放入到新的目标容器中去.注意这里的改变并不会将原容器的值改变,只是在传送时来改变,然后将改变的值放入新容器中.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
class Transform
{
public:
int operator()(int val)
{
return val-5; //将原容器的值做一个减5的操作
}
};
//仿函数
class Print2
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
};
void test()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(50);
vector<int>vTarget;
vTarget.resize(v.size());//要先将目标容器开辟一个空间来存放Tranform后的值
transform(v.begin(), v.end(),vTarget.begin(),Transform());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print2()); //遍历原容器并打印出值
cout << endl;
for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), Print2());//遍历transform后的目标容器,并打印出该容器中的值
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
下面看程序执行的结果:
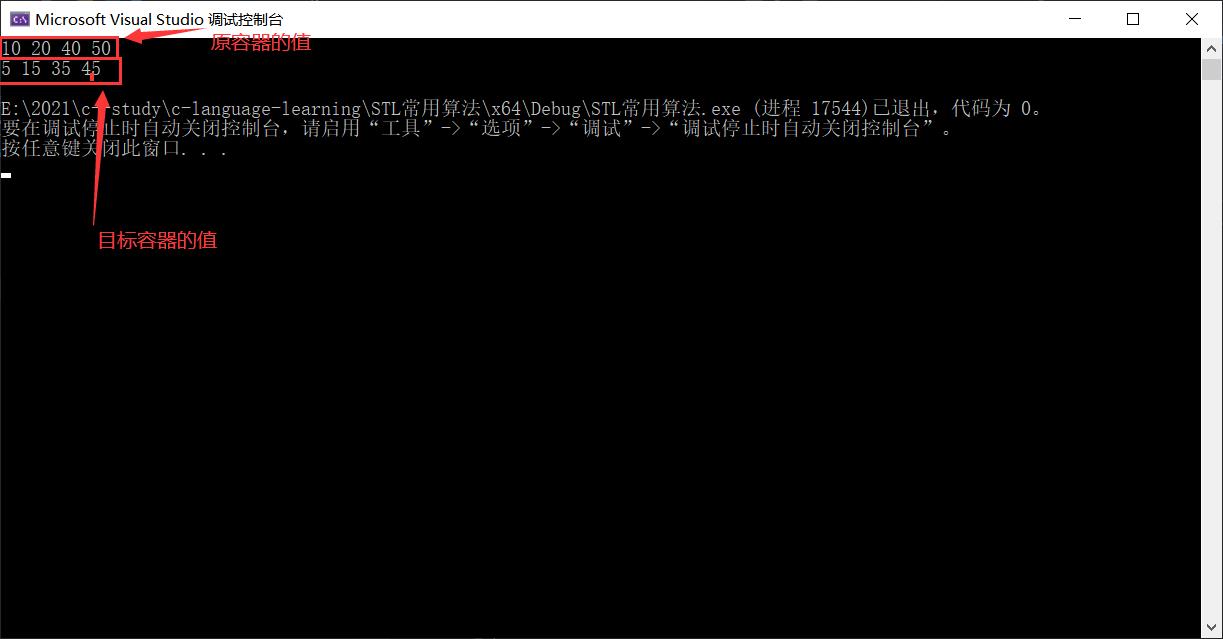
这里可以看到目标容器的值都做了减5的操作,而原容器的值不会改变.
2.常用的查找算法
(1)find
运用equality操作符,循序查找[first, last)区间内的每一个元素,找出满足第一个匹配等同条件的元素,并返回该元素的迭代器,否则,返回last。下面看具体例子
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
void test()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(60);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(10);
//在提供的区间内查找
vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 20);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了!" << endl;
cout << *it << endl;
}
}
//自定义数据类型的查找
class Person //定义一个Person的类
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p) //判断年龄和姓名是否相同,相同返回为真,否则返回为假
{
if (p.m_Name == this->m_Name && p.m_Age == this->m_Age)
return true;
else
return false;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test2()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("aaa", 20);
Person p2("bbb", 50);
Person p3("ccc", 40);
Person p5("sss", 30);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p5);
Person pp("bbb", 50); //给定查找条件
vector<Person>::iterator it=find(v.begin(), v.end(), pp);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了!" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test();
test2();
return 0;
}
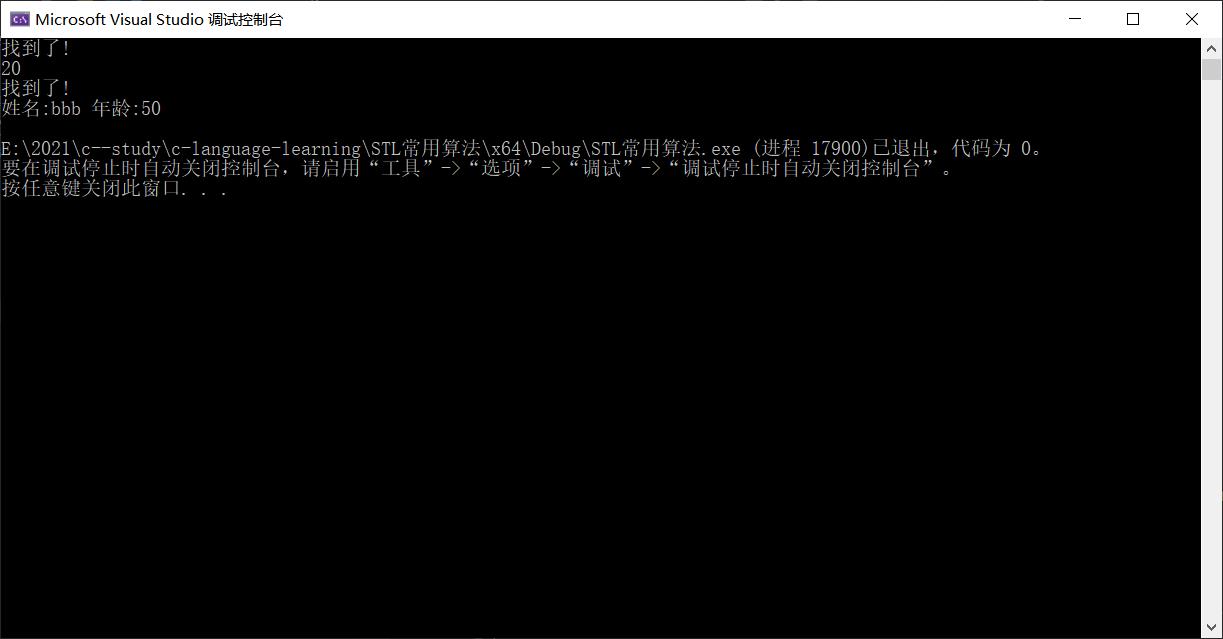
下面是程序运行的结果,找到后,打印出需要信息.
(2)find_if
find_if是按条件查找,使用方法跟find差不多
根据指定的pred运算条件,循序查找[first, last)区间内的每一个元素,找出第一个运算结果为true的元素,并返回该元素的迭代器,否则,返回last。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
class Geratf
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 50;//给定判定条件
}
};
void test()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(10);
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Geratf());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了!" << endl; //如果找到返回区间内第一个大于50的值
cout << *it << endl;
}
}
//自定义数据类型查找
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p)
{
if (p.m_Name == this->m_Name && p.m_Age == this->m_Age)
return true;
else
return false;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
class GreatAge //仿函数
{
public:
bool operator()(Person& p)
{
return p.m_Age > 30;
}
};
void test2()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("aaa", 20);
Person p2("bbb", 60);
Person p3("ccc", 40);
Person p5("sss", 30);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p5);
vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreatAge());//按照给定条件查找
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了!" << endl;//返回第一个年龄大于30的位置
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test();
test2();
return 0;
}
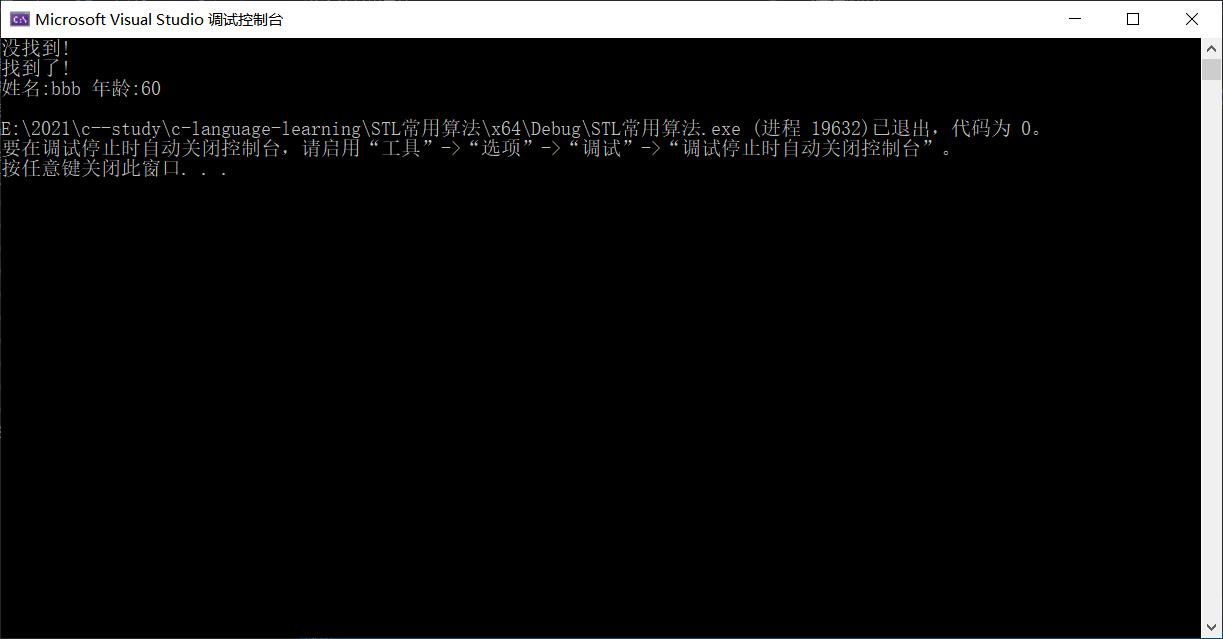
下面看程序运行的结果:第一个容器v中没有大于50的值,所以输出的是没找到,第二个中,虽然有两个人的年龄大于30,但返回的只是第一个大于30 的人的信息
(3)count
运用equality操作符,将[first, last)区间内的每一个元素拿来和指定值value比较,并返回与value相等的元素个数。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
void test()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(10);
int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 10);
cout << num << endl;
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p) //重载== 年龄相等
{
if ( p.m_Age == this->m_Age)
return true;
else
return false;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
//自定义数据类型
void test2()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("aaa", 20);
Person p2("bbb", 60);
Person p3("ccc", 40);
Person p5("sss", 30);
Person p4("ooo", 60);
Person p6("ppb", 60);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p5);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p6);
Person p("qqq", 60);
int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p); //统计年龄相同的人个数
cout << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
test2();
return 0;
}
上面代码运行的结果都是3,第一个容器中有3个10,第二个里面有3个年龄为60岁的.
(4)count_if
将指定操作pred实施于[first, last)区间内的每一个元素上,并返回“造成pred计算结果为true”的所有元素的个数,即返回满足pred条件的所有元素的个数。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
class Geratf
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 50;
}
};
void test()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(100);
v.push_back(90);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(10);
int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Geratf());
cout << num << endl;
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p) //重载== 年龄相等
{
if (p.m_Age == this->m_Age)
return true;
else
return false;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
class compareAge
{
public:
bool operator()(const Person& p)
{
return p.m_Age > 40;
}
};
//自定义数据类型
void test2()
{
vector<Person>v;
Person p1("aaa", 20);
Person p2("bbb", 60);
Person p3("ccc", 40);
Person p5以上是关于C++中STL常用算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章