优化求解t-分布扰动策略和变异策略的花授粉算法matlab源码
Posted 博主企鹅号1575304183
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了优化求解t-分布扰动策略和变异策略的花授粉算法matlab源码相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、花朵授粉算法
花朵授粉算法( Flower Pollination Algorithm,FPA)是由英国剑桥大学学者Yang于2012年提出的,其基本思想来源于对自然界花朵自花授粉、异花授粉的模拟,是一种新的元启发式群智能随机优化技术 。算法中为了简便计算,假设每个植物仅有一朵花,每朵花只有一个配子,我们可以认为每一个配子都是解空间中的一个候选解。
Yang通过对花朵授粉的研究,抽象出以下四大规则:
1) 生物异花授粉被考虑为算法的全局探测行为,并由传粉者通过Levy飞行的机制实现全局授粉;
2)非生物自花授粉被视作算法的局部开采行为,或称局部授粉;
3)花朵的常性可以被认为是繁衍概率,他与两朵参与授粉花朵的相似性成正比例关系;
4)花朵的全局授粉与局部授粉通过转换概率 p∈[0,1]进行调节。 由于物理上的邻近性和风等因素的影响,在整个授粉活动中,转换概率 p是一个非常重要的参数。 文献[1]中对该参数的试验研究认为,取 p =0.8 更利于算法寻优。
直接上步骤(以多元函数寻优为例):
目标函数 : min g = f(x1,x2,x3,x4...........xd)
设置参量:N(候选解的个数),iter(最大迭代次数),p(转换概率),lamda(Levy飞行参数)
初始化花朵,随机设置一个NXd的矩阵;
计算适应度,即函数值;
获取最优解和最优解得位置;
A循环 1 : 1 :iter
B循环
if rand < p
全局授粉;
else
局部授粉;
end if
更新新一代的花朵与适应度(函数变量和函数值);
B循环end
获取新一代的最优解与最优解位置;
A循环end
全局更新公式:xi(t+1) = xi(t) + L(xi(t) - xbest(t)) L服从Levy分布,具体可以搜索布谷鸟算法。
局部更新公式:xi(t+1) = xi(t) + m(xj(t) - xk(t)) m是服从在[0,1]上均匀分布的随机数。其中,xj和xk是两个不同的个体
二、t-分布扰动策略和变异策略的花授粉算法
(1)混沌映射初始化花朵个体位置

(2)基于t-分布扰动策略的全局搜索

(3)基于变异策略的局部搜索

(4)算法实现

二、演示代码
%__________________________________________
% fobj = @YourCostFunction
% dim = number of your variables
% Max_iteration = maximum number of generations
% SearchAgents_no = number of search agents
% lb=[lb1,lb2,...,lbn] where lbn is the lower bound of variable n
% ub=[ub1,ub2,...,ubn] where ubn is the upper bound of variable n
% If all the variables have equal lower bound you can just
% define lb and ub as two single number numbers
% To run ALO: [Best_score,Best_pos,cg_curve]=ALO(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm
function [Leader_score,Leader_pos,Convergence_curve]=WOA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj,handles,value)
% initialize position vector and score for the leader
Leader_pos=zeros(1,dim);
Leader_score=inf; %change this to -inf for maximization problems
%Initialize the positions of search agents
Positions=initialization(SearchAgents_no,dim,ub,lb);
Convergence_curve=zeros(1,Max_iter);
t=0;% Loop counter
% Main loop
while t<Max_iter
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
% Return back the search agents that go beyond the boundaries of the search space
Flag4ub=Positions(i,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=Positions(i,:)<lb;
Positions(i,:)=(Positions(i,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
% Calculate objective function for each search agent
fitness=fobj(Positions(i,:));
All_fitness(1,i)=fitness;
% Update the leader
if fitness<Leader_score % Change this to > for maximization problem
Leader_score=fitness; % Update alpha
Leader_pos=Positions(i,:);
end
end
a=2-t*((2)/Max_iter); % a decreases linearly fron 2 to 0 in Eq. (2.3)
% a2 linearly dicreases from -1 to -2 to calculate t in Eq. (3.12)
a2=-1+t*((-1)/Max_iter);
% Update the Position of search agents
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
r1=rand(); % r1 is a random number in [0,1]
r2=rand(); % r2 is a random number in [0,1]
A=2*a*r1-a; % Eq. (2.3) in the paper
C=2*r2; % Eq. (2.4) in the paper
b=1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
l=(a2-1)*rand+1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
p = rand(); % p in Eq. (2.6)
for j=1:size(Positions,2)
if p<0.5
if abs(A)>=1
rand_leader_index = floor(SearchAgents_no*rand()+1);
X_rand = Positions(rand_leader_index, :);
D_X_rand=abs(C*X_rand(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.7)
Positions(i,j)=X_rand(j)-A*D_X_rand; % Eq. (2.8)
elseif abs(A)<1
D_Leader=abs(C*Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.1)
Positions(i,j)=Leader_pos(j)-A*D_Leader; % Eq. (2.2)
end
elseif p>=0.5
distance2Leader=abs(Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));
% Eq. (2.5)
Positions(i,j)=distance2Leader*exp(b.*l).*cos(l.*2*pi)+Leader_pos(j);
end
end
end
t=t+1;
Convergence_curve(t)=Leader_score;
if t>2
line([t-1 t], [Convergence_curve(t-1) Convergence_curve(t)],'Color','b')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best score obtained so far');
drawnow
end
set(handles.itertext,'String', ['The current iteration is ', num2str(t)])
set(handles.optimumtext,'String', ['The current optimal value is ', num2str(Leader_score)])
if value==1
hold on
scatter(t*ones(1,SearchAgents_no),All_fitness,'.','k')
end
end
四、仿真结果
表1 测试函数基本信息
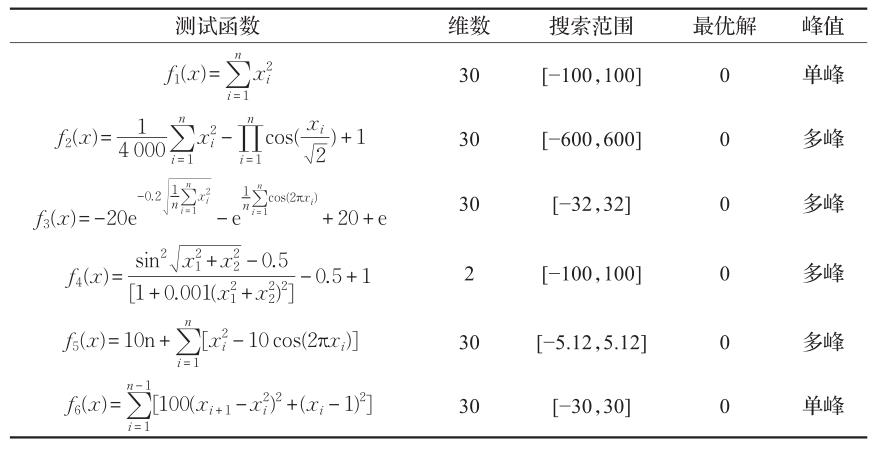
为了验证本文提出的tMFPA算法的性能,仿真实验的每种算法独立运行30次,最大迭代次数设为2000次,以30维为例。
结果显示如下: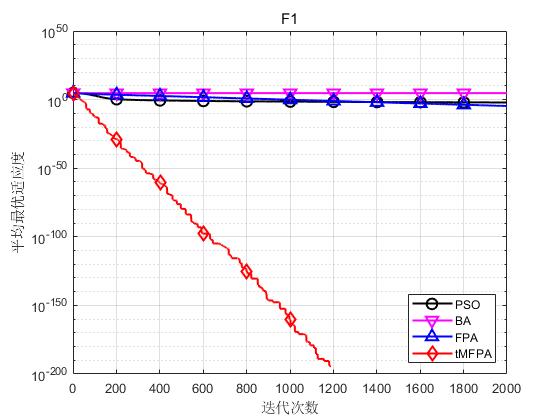
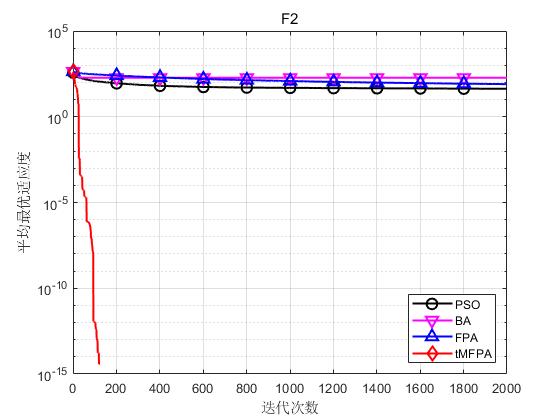
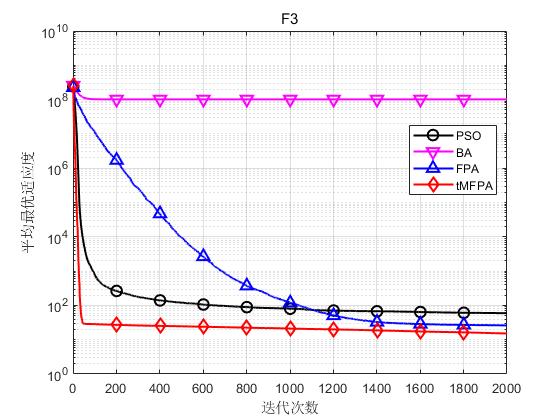
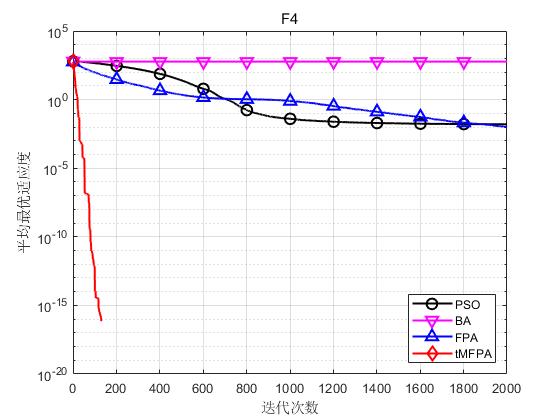
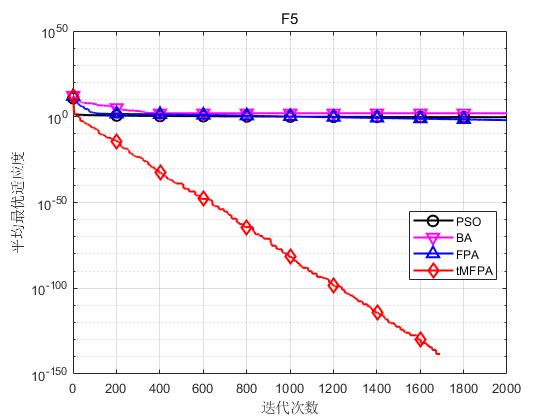
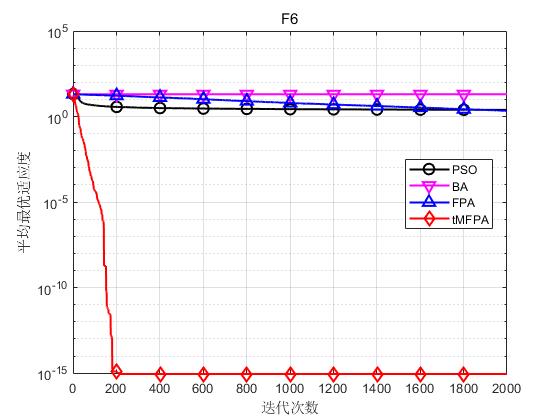
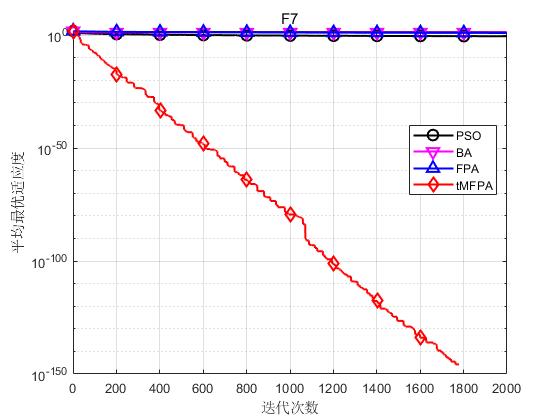
结果表明,tMFPA相比于FPA和其他启发式智能算法具有更好的寻优精度和收敛速度。
五、参考文献及代码私信博主
[1] 宁杰琼,何庆. t-分布扰动策略和变异策略的花授粉算法[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2021, 42(1): 64-70.

以上是关于优化求解t-分布扰动策略和变异策略的花授粉算法matlab源码的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
优化求解基于动态全局搜索和柯西变异改进的花授粉算法matlab源码
优化算法贪婪策略和变异策略的混合蚁群算法含Matlab源码 1521期