剑指offer 1.实现赋值运算符函数 2.数组中重复的数字
Posted 蚍蜉撼树谈何易
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了剑指offer 1.实现赋值运算符函数 2.数组中重复的数字相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.实现赋值运算符函数
注意事项:
1.必须将引用作为返回值。目的:实现连续赋值
2.传入的参数为常量引用 目的:省去了一次构造、保护了原有数据
3.确保释放自身原本占有的内存。目的:避免内存泄露
4.判断传入的参数与自身是不是一个实例。如果是的话,就直接return *this。
//1.首先将引用作为返回值 2.传入参数为常量引用
CMyString&CMyString::operator=(const CMyString &str)
{
//4.判断传入的参数与自身是不是一个实例。
if(this!=&str)
{
CMyString strtemp(str);//若构造函数中有new运算符,如果内存不足抛出异常,不会对原来已有的数据产生影响
char*ptemp=strtemp.m_pData;
strtemp.m_pData=m_pData;
m_pData=pTemp;//交换临时对象和this指针所指对象。
}
return *this;
}
因为临时变量在栈上开辟的,所以在函数结束时会调用析构函数自动去释放这部分空间,避免了内存泄露的问题。
拓展:
构造,拷贝,析构,赋值运算符的重载、现代化写法
class String
{
public:
String(const char* str = "")
{
if (nullptr == str)
{
str = "";
}
// 无论如何str都有一个合法的指针--str肯定是一个合法的字符串
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
// 深拷贝方式:拷贝构造
String(const String& s)
: _str(nullptr)//必须将原本的值置为nullptr,因为free()null值是不会报错的。
{
String temp(s._str);
swap(_str, temp._str);
}
String& operator=(String s)
{
swap(_str, s._str);
return *this;
}
~String()
{
if (_str)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
数组中重复的数字
剑指offer 03 --数组中重复数字
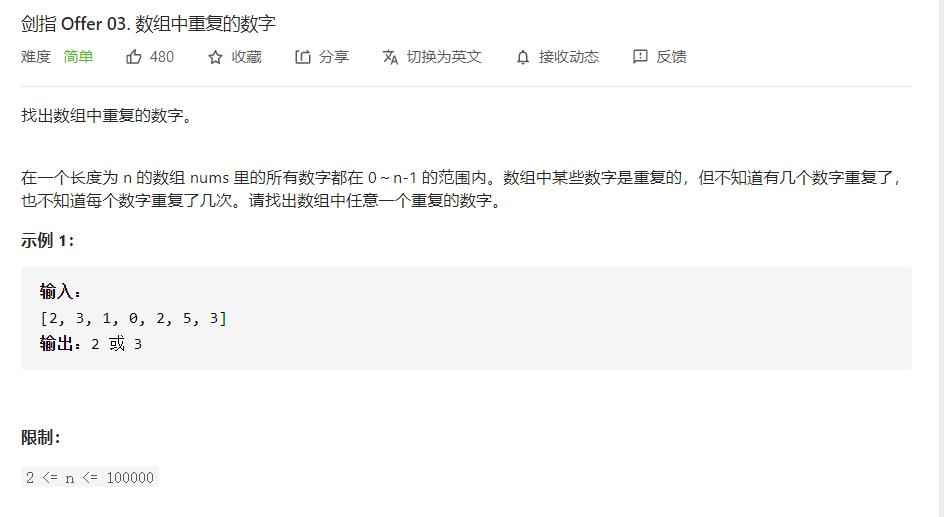
因为长度为n的数组的数字在0~n-1范围内,所以可以采用计数的思想来做。
class Solution {
public:
int findRepeatNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int>v1;
int size=nums.size();
v1.resize(size,0);
for(auto e:nums)
{
++v1[e];
if(v1[e]==2)
{
return e;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
空间复杂度O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)
原地交换的思想:
class Solution {
public:
int findRepeatNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int size=nums.size();
int temp;
for(int i=0;i<size;++i)
{
if(nums[i]!=i)
{
if(nums[i]==nums[nums[i]])
{
return nums[i];
}
}
temp=nums[i];
nums[i]=nums[temp];
nums[temp]=temp;
}
return 0;
}
};
空间复杂度O(1)时间复杂度O(n)
以上是关于剑指offer 1.实现赋值运算符函数 2.数组中重复的数字的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章