mysql高阶语句一
Posted 遙遙背影暖暖流星
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mysql高阶语句一相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
高阶语句一
1、按关键字排序
模板表:
数据库有一张info2表,记录了学生的id,姓名,分数,地址和爱好
create table info2 (id int,name varchar(10) primary key not null ,score decimal(5,2),address varchar(20),hobbid int(5));
insert into info2 values(1,'liuyi',80,'beijing',2);
insert into info2 values(2,'wangwu',90,'shengzheng',2);
insert into info2 values(3,'lisi',60,'shanghai',4);
insert into info2 values(4,'tianqi',99,'hangzhou',5);
insert into info2 values(5,'jiaoshou',98,'laowo',3);
insert into info2 values(6,'hanmeimei',10,'nanjing',3);
insert into info2 values(7,'lilei',11,'nanjing',5);
insert into info2 values(10,'liujie',100,'guangzhou',5);
mysql> select * from info2;

(1)按一个字段排序:
语法: select 列名1,列名2 from 表名 order by 列名;
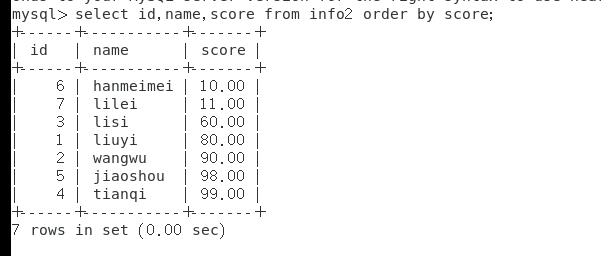
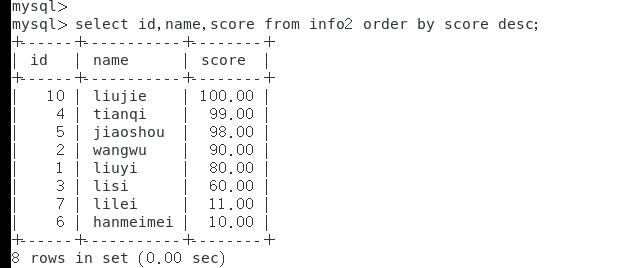
select id,name,score from info order by score; #按照score这一列排序,默认正序
select id,name,score from info order by score asc; #按照score正序排序
select id,name,score from info order by score desc; #安装倒序排序
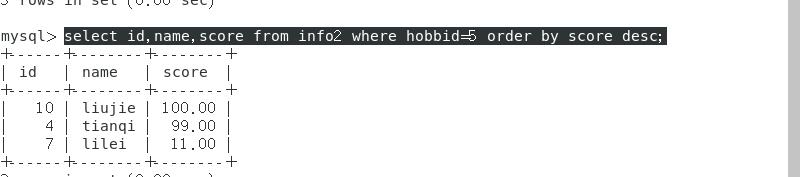
还可以结合where进行进一步筛选
select id,name,score from info2 where hobbid=5 order by score desc;
(2)多字段排序
当排序的第一个字段有相同的多条的情况下,再把写记录这按照第二个字段进行排序
select id,name,hobbid from info2 order by hobbid desc,id desc; #先按hobbid降序排序,中间有相同条目按照id降序
select id,name,hobbid from info2 order by hobbid desc,id; #先按hobbid降序排序,中间有相同条目按照id正序排序


2、区间判断及查询不重复记录
2.1 AND/OR ——且/或
select * from info where score >70 and score <=90;
select * from info where score >70 or score <=50;
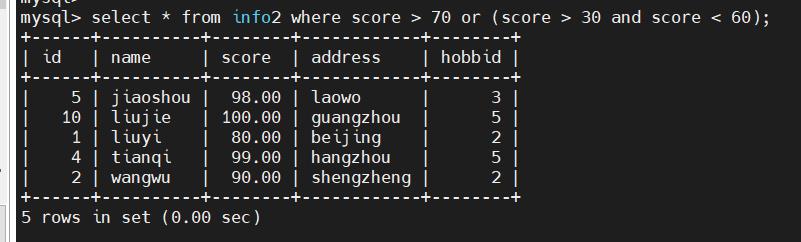
select * from info2 where score > 70 or (score > 30 and score < 60); #嵌套/多条件
② distinct 查询不重复记录
语法:
select distinct 字段 from 表名﹔
mysql> select distinct hobbid from info2;
+--------+
| hobbid |
+--------+
| 3 |
| 5 |
| 4 |
| 2 |
+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.2、对结果进行分组统计
语法:select count(被计算的字段名),字段名1 from 表名 group by 作为标准分组的字段名;
mysql> select count(name),hobbid from info2 group by hobbid;
+-------------+--------+
| count(name) | hobbid |
+-------------+--------+
| 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 3 | 5 |
+-------------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(name),hobbid from info2 where score>=80 group by hobbid; #结合where
+-------------+--------+
| count(name) | hobbid |
+-------------+--------+
| 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 5 |
+-------------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(name),score,hobbid from info2 where score >=80 group by hobbid order by count(name);
+-------------+--------+--------+
| count(name) | score | hobbid |
+-------------+--------+--------+
| 1 | 98.00 | 3 |
| 2 | 100.00 | 5 |
| 2 | 80.00 | 2 |
+-------------+--------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3、限制结果条目
利用limit 限制输出的结果记录
select * from info2 limit 3; #输出前三行
select * from info limit 3,3; #输出第三以下的的三行
select id,name from info order by id limit 3; #通过倒序,输出最后的三行
4、设置别名(alias ——或as)
4.1当表中的字段名过长等情况,可以设置别名增加select可阅读性(库内实际的表名 或字段名是不会被改变的)
select name as 姓名,score as 成绩 from info2; #对列名
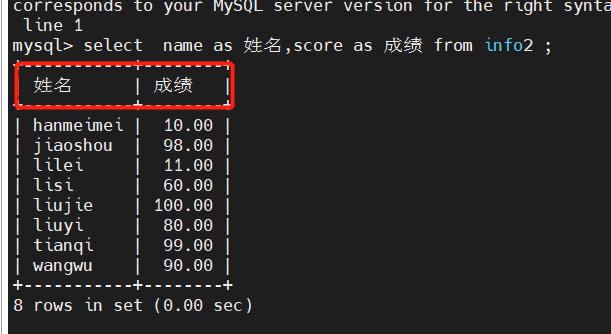
mysql> select i.name as 姓名,i.score as 成绩 from info2 as i; #对列名和表名
+-----------+--------+
| 姓名 | 成绩 |
+-----------+--------+
| hanmeimei | 10.00 |
| jiaoshou | 98.00 |
| lilei | 11.00 |
| lisi | 60.00 |
| liujie | 100.00 |
| liuyi | 80.00 |
| tianqi | 99.00 |
| wangwu | 90.00 |
+-----------+--------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) as 记录 from info2; #查询info表的记录数量,显示
+--------+
| 记录 |
+--------+
| 8 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) 记录 from info2; #省略as也可以
+--------+
| 记录 |
+--------+
| 8 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
4.2 as作为连接语句的操作符。
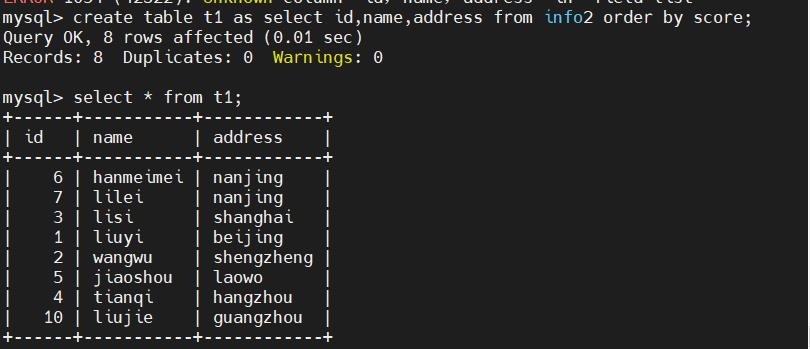
create table t1 as select id,name,address from info2 order by score;
#将后面的语句的结果输出成一张新表t1,区别于like的只能全部复制
create table t1 (select * from info);
#克隆、复制表结构,约束等没有复制,但是如果原表设置了主键,那么附表的:default字段会默认设置一个0
create table test1 as select * from info where score >=60;
#也可以加入where 语句判断
4.3 as的注意事项
#将结果集做为一张表进行查询的时候,我们也需要用到别名,示例:
需求:从info表中的id和name字段的内容做为"内容" 输出id的部分
mysql> select id from (select id,name from info);
ERROR 1248 (42000): Every derived table must have its own alias
#此时会报错,原因为:
select * from 表名 此为标准格式,而以上的查询语句,"表名"的位置其实是一个结果集,mysql并不能直接识别,而此时给与结果集设置一个别名,以”select a.id from a“的方式查询将此结果集是为一张"表",就可以正常查询数据了,如下:
select a.id from (select id,name from info) a;
5、通配符用法
通常通配符都是跟 LIKE 一起使用的,并协同 WHERE 子句共同来完成查询任务。常用的通配符有两个,分别是:
%:百分号表示零个、一个或多个字符,类似linux正则的*
_:下划线表示单个字符 ,两个_则表示两个字符
mysql> select id,name from info2 where name like 'liu%'; #查找以liu开头的
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 10 | liujie |
| 1 | liuyi |
+------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select id,name from info2 where name like '%jie'; #查找以jie结尾的
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 10 | liujie |
+------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select id,name from info where name like 'c_ic_i'; #查询名字里是c和i中间有一个字符的记录
+----+--------+
| id | name |
+----+--------+
| 7 | caicai |
+----+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
6、子查询
子查询也被称作内查询或者嵌套查询,是指在一个查询语句里面还嵌套着另一个查询语 句。子查询语句是先于主查询语句被执行的,其结果作为外层的条件返回给主查询进行下一 步的查询过滤。
PS: 子语句可以与主语句所查询的表相同,也可以是不同表
select name,score from info2 where id in (select id from info2 where score>80);
#in: 将主语句和子语句(括号内容)关联/连接的语法
+----------+--------+
| name | score |
+----------+--------+
| jiaoshou | 98.00 |
| liujie | 100.00 |
| tianqi | 99.00 |
| wangwu | 90.00 |
+----------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into t1 select * from info where id in (select id from info);
#将子查询的结果插入到表中
6.1、DELETE 也适用于子查询
mysql> delete from info where id in (select id where score>80);
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select id,name,score from t1;
+----+-----------+-------+
| id | name | score |
+----+-----------+-------+
| 2 | shangzhen | 80.00 |
| 7 | caicai | 50.00 |
| 8 | zhaokun | 80.00 |
| 9 | xiawenjie | 80.00 |
+----+-----------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
6.2 exists判断
EXISTS 这个关键字在子查询时,主要用于判断子查询的结果集是否为空。如果不为空, 则返回 TRUE;反之,则返回 FALSE
mysql> select count(*) from info2 where exists(select id from info2 where score=80);
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 8 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
#exists 这个关键字在子查询时,主要用于判断子查询的结果集是否为空。如果不为空, 则返回 TRUE;反之,则返回 FALSE
查询如果存在分数大于500的记录则计算info的字段数,info表没有大于500的,所以返回0
mysql> select count(*) from info2 where exists(select id from info2 where score>500);
#进行判断,子语句为则进行统计,否则为零
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 0 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
7、视图
数据库中的虚拟表,这张虚拟表中不包含真实数据,只是做了映射
视图我们可以定义展示的条件
这个结果会动态变化,同时可以给不同的人群(例如权限范围)展示不同的视图
创建视图
create view v_score as select * from info where score>=80;
show table status\\G
#查看视图
select * from v_score;
#修改原表数据
update info set score='60' where name='wangwu';
#查看视图
select * from v_score;
8、null值与空值
null值与空值的区别:
空值长度为0,不占空间,NULL值的长度为null,占用空间
is null无法判断空值
空值使用=''或者”<>"来处理(!=)
count()计算时,NULL会忽略,空值会加入计算
alter table info add column addr varchar(50);
update info set addr='nj' where score >=70;
#统计数量:检测null是否会加入统计中
select count(addr) from info;
#将info表中其中一条数据修改为空值''
update info set addr='' where name='wangwu';
#统计数量,检测空值是不会被添加到统计中
select count(addr) from info;
#查询null值
select * from info where is null;
#查询不为空的值
select * from info where is not null;
以上是关于mysql高阶语句一的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章