openmp 并行编程探秘
Posted qianbo_insist
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了openmp 并行编程探秘相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
openmp debug下
int64_t taketime()
{
int64_t a = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
a++;
return a;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int64_t tmp;
clock_t t1 = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
tmp = taketime();
clock_t t2 = clock();
cout << tmp << endl;
std::cout << "Serial time: " << t2 - t1 << std::endl;
t1 = clock();
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp for
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
tmp = taketime();
}
t2 = clock();
cout << tmp << endl;
std::cout << "Parallel time: " << t2 - t1 << std::endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
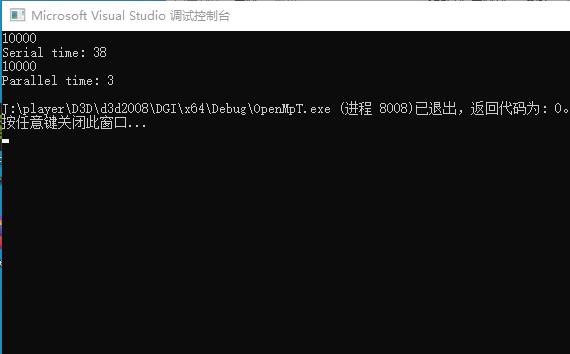
在debug openmp下,程序效率好像大大提升,结果正确,我们接下来变成release代码
openmp release下
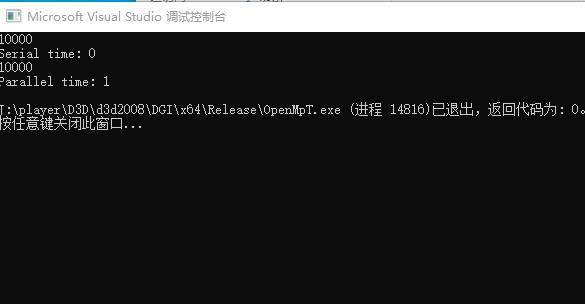
release状态下,非openmp 优化比openmp 并行下快了不止一点吧,我们提升以下clock
class TicToc
{
public:
TicToc()
{
tic();
}
void tic()
{
start = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
}
double toc()
{
end = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
std::chrono::duration<double> elapsed_seconds = end - start;
return elapsed_seconds.count();
}
private:
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock> start, end;
};
我们改成 elapsed_seconds.count(),也就是返回double的秒数
这下返回的不是毫秒,是秒了,下面就是
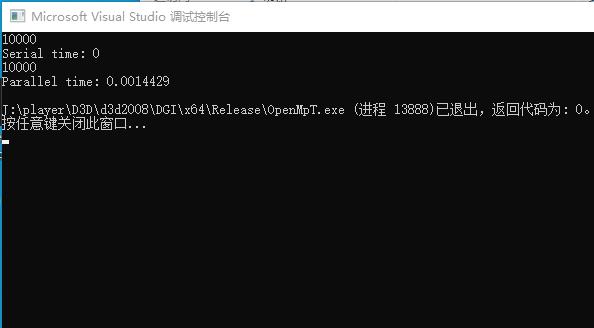
这下奇怪了吧,openmp的效率反而慢了,我们再做一个测试
openmp 遇到真耗时
比如耗时为查询数据库,写文件,网络发送,这时候编译器无法优化的操作时,我们看看发生了什么
#include <thread>
void real_taketime2()
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(20));
}
我们增加一个函数 ,在里面模拟损耗时间20毫秒,再次执行
void real_taketime2()
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(20));
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int64_t tmp;
clock_t t1 = clock();
TicToc tt;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
real_taketime2();
clock_t t2 = clock();
double c = tt.toc();
//cout << tmp << endl;
std::cout << "Serial time: " << t2-t1<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Serial time: " << c << std::endl;
t1 = clock();
tt.tic();
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp for
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
real_taketime2();
}
t2 = clock();
c = tt.toc();
//cout << tmp << endl;
std::cout << "Parallel time: " <<t2-t1<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Parallel time: " << c << std::endl;
return 0;
}
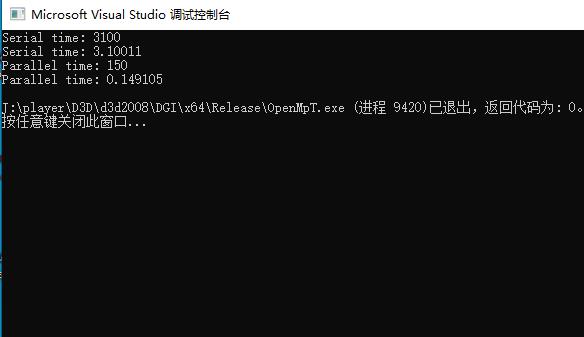
可以看出,for循环失去了release版本的优惠,无法优化,本来2秒的操作编程了3秒多,而openmp 行为因为真实的耗时操作,使用了多cpu并发,时间消耗优化了几倍。
其他openmp 函数
返回当前可用的处理器个数
int omp_get_num_procs(void)
返回当前并行区域中的活动线程个数
int omp_get_num_threads(void)
返回当前的线程号
int omp_get_thread_num(void)
设置要创建的并行线程个数
int omp_set_num_threads(void)
现在我们限制并发为2:
omp_set_num_threads(2);
t1 = clock();
tt.tic();
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp for
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
real_taketime2();
}
t2 = clock();
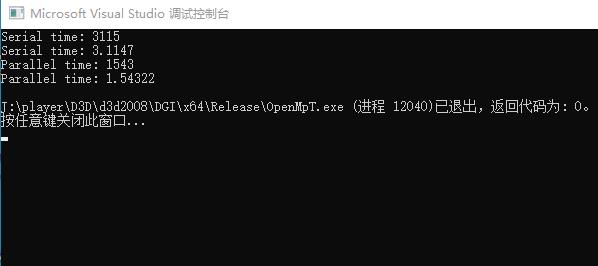
现在并发核数为2,并发时间基本就是串行的一半,结论应该有了吧。我们真正要使用openmp,一定时要用在真正耗时的操作上,避免和release 编译优化混淆,否则得不偿失。
以上是关于openmp 并行编程探秘的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章