mybatis 之 执行流程
Posted better_hui
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mybatis 之 执行流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
一、使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("Configuration.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
GoodsBiLogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(GoodsBiLogMapper.class);
GoodsBiLog goodsBiLog = mapper.selectOne(1);
goodsBiLog.setBatchNo("123123");
mapper.update(goodsBiLog);
System.out.println(goodsBiLog.toString());
}
总结步骤如下:
1、读取配置文件
2、根据配置文件生成SqlSessionFactory
3、生成sqlSession
4、获取mapper
5、执行sql语句
二、实现原理
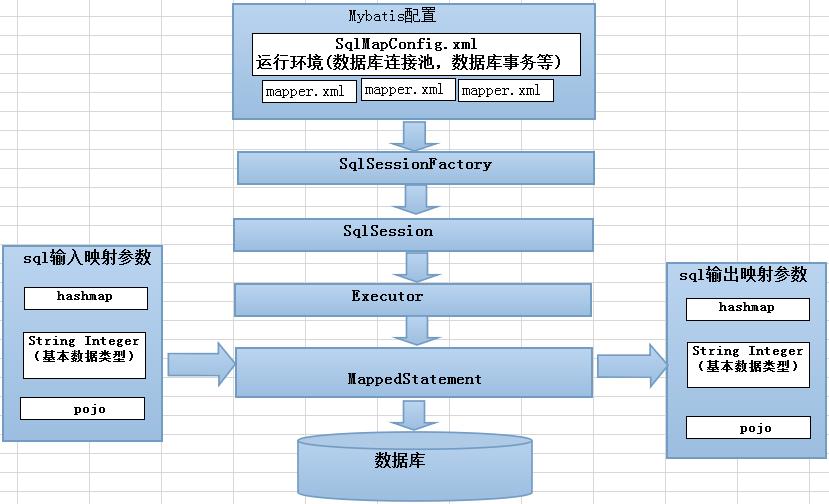
mybatis底层使用的还是原生的jdbc,只是通过各种组件封装了jdbc的执行过程。
原生的jdbc执行步骤
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//注册驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
//获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy","root","westos" ); //(url,user,password)
//获取操作数据库的预处理对象
PreparedStatement pstem = conn.prepareStatement("select * from account");
//执行SQL,得到结果集
ResultSet rs = pstem.executeQuery();
//遍历结果集
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("name"));
}
//释放资源
rs.close();
pstem.close();
conn.close();
}
组件
Configuration
mybatis解析后的配置信息,都保存在这个class里
SqlSessionFactory
mybatis的核心对象,它是单个数据库映射关系经过贬义后的内存镜像,我们可以通过configuration生成sqlSessionFactory对象 。
SqlSession
mybatis底层API , 表示与数据库的一次会话,完成必要数据库增删改查功能
Executor
mybatis的执行器,是mybatis的执行核心,负责sql的执行、缓存的维护
StatementHandler
封装了jdbc statement操作,负责对jdbc statement的操作。
有三个主要实现:
SimpleStatementHandler 简单的通用的
SimpleStatementHandler 预编译的
CallableStatementHandler 存储过程的
ParameterHandler
负责将用户传递的参数转化为jdbc statement所对应的数据类型
默认实现:
DefaultParameterHandler
ResultSetHandler
负责将jdbc返回的resultSet结果集转换为List类型集合
默认实现:
DefaultResultSetHandler
TypeHandler
负责java数据类型和jdbc数据类型之间的映射与转换
默认实现:
BaseTypeHandler
MappedStatement
维护<select|update|delete|insert>节点的封装
SqlSource
负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态的生成sql语句,并转换为boundsql
BoundSql
生成的sql语句以及相应的参数信息
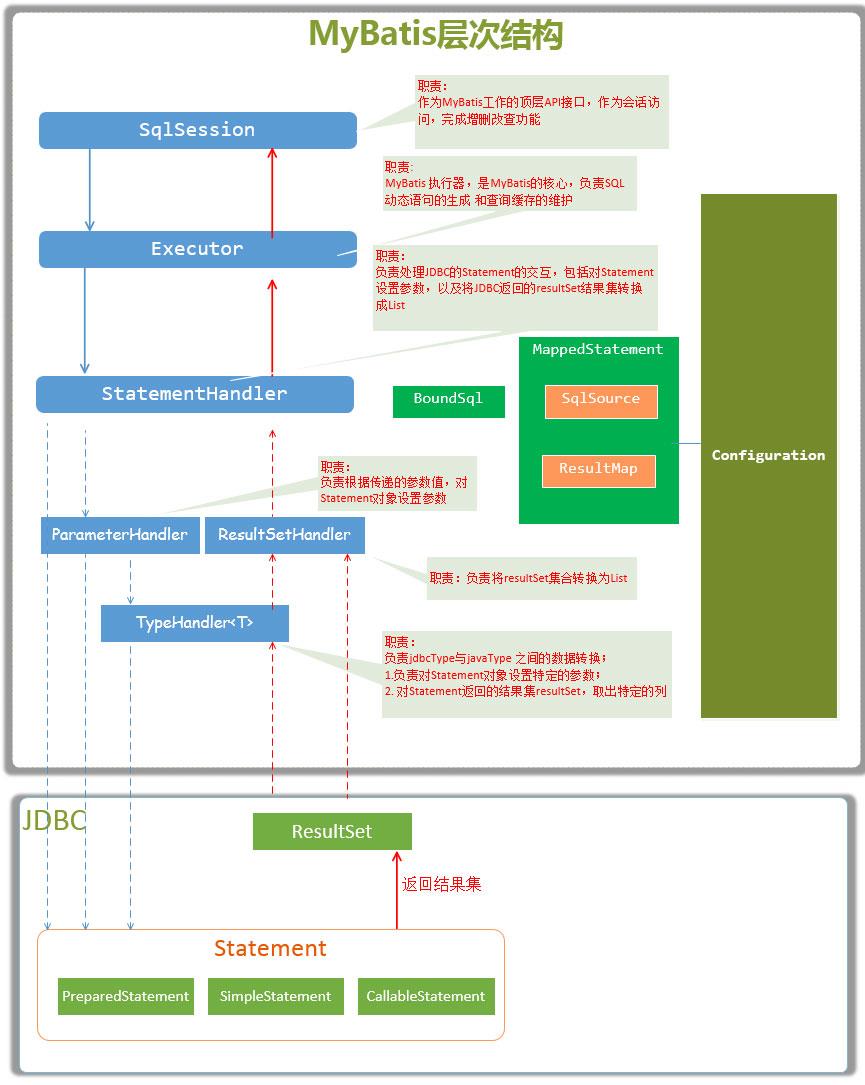
三、具体流程
1、生成sqlSessionFactory
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
// 1、new 一个 xmlConfigBuilder
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
// 2、xmlConfigBuilder.parse() 解析配置文件
// 3、根据解析的configuration对象 , new DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
1.1、解析配置文件
解析后的结果是生成configuration对象
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// properties属性 比如
/**
<properties resource="org/mybatis/example/config.properties">
<property name="username" value="dev_user"/>
<property name="password" value="F2Fa3!33TYyg"/>
</properties>
*/
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); //issue #117 read properties first
// 类型别名 比如
/**
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/>
</typeAliases>
*/
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//插件 也就是拦截器
/**
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="org.mybatis.example.ExamplePlugin">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
*/
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
//对象工厂 public class ExampleObjectFactory extends DefaultObjectFactory
/**
<objectFactory type="org.mybatis.example.ExampleObjectFactory">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
</objectFactory>
*/
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
//对象加工工厂 对指定对象进行特殊加工
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
//各种配置信息
/**
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/>
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/>
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/>
<setting name="autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior" value="WARNING"/>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/>
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25"/>
<setting name="defaultFetchSize" value="100"/>
<setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="false"/>
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode,toString"/>
</settings>
*/
settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
//环境及数据源配置
/**
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="..." value="..."/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
*/
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
//数据库标识,根据这个标识mybatis会映射不同的sql
/**
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR">
<property name="SQL Server" value="sqlserver"/>
<property name="DB2" value="db2"/>
<property name="Oracle" value="oracle" />
</databaseIdProvider>
*/
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
// 类型处理器 public class ExampleTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<String> {
/**
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="org.mybatis.example.ExampleTypeHandler"/>
</typeHandlers>
*/
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// mapper的解析
/**
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/BlogMapper.xml"/>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/>
<package name="org.mybatis.builder"/>
</mappers>
*/
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
2、打开一个sqlSession
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//根据环境信息 获取一个事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//获取一个事务对象,其中包含了数据信息
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//生成一个执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//将执行器包装成一个sqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
2.1、生成执行器
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//根据类型 生成对应的执行器
//依次是 批量的 、 可重用的 、 简单通用的
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//如果开启二级缓存,封装成带缓存的执行器
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//如果有存在对应的插件 ,进行一层层的代理包装
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
3、获取一个mapper
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
//我们一路点啊点啊的 进入到最终核心的逻辑,看到了一个核心的类 MapperProxy , 这就是jdk代理的handler
//我们后续所有的sql执行最终都要在这个方法的invoke方法里
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
}
4、执行 , 我们以query为例
//下面看一下invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
//如果是object的普通方法 ,则直接执行
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
//获取mapperMethod
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//这里就是拦截到了方法 , 并最终调用
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
4.1、mapperMethod.execute
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else {
//查询的方法 最终会走到这里
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
4.2、SqlSession.selectList()
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
sqlSession.selectList()
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//获取sql的节点信息
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
List<E> result = executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
executor.query()
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//根据传入的参数 获取 绑定的sql
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
//生成缓存的key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
//查询
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
以上是关于mybatis 之 执行流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章