图像配准基于matlab GUI Powell+蚁群算法图像配准含Matlab源码 928期
Posted 紫极神光
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了图像配准基于matlab GUI Powell+蚁群算法图像配准含Matlab源码 928期相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、简介
1 蚁群算法(ant colony algorithm,ACA)起源和发展历程
Marco Dorigo等人在研究新型算法的过程中,发现蚁群在寻找食物时,通过分泌一种称为信息素的生物激素交流觅食信息从而能快速的找到目标,于是在1991年在其博士论文中首次系统地提出一种基于蚂蚁种群的新型智能优化算法“蚂蚁系统(Ant system,简称AS)”,后来,提出者及许多研究者对该算法作了各种改进,将其应用于更为广泛的领域,如图着色问题、二次分配问题、工件排序问题、车辆路径问题、车间作业调度问题、网络路由问题、大规模集成电路设计等。近些年来,M.Dorigo等人把蚂蚁算法进一步发展成一种通用的优化技术“蚁群优化(Ant Colony Optimization,简称ACO)”,并将所有符合ACO框架的算法称为“蚁群优化算法(ACO algorithm)”。
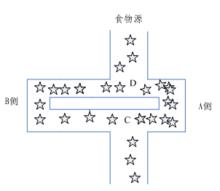
具体来说,各个蚂蚁在没有事先告知食物在什么地方的前提下开始寻找食物。当一只找到食物以后,它会向环境释放一种挥发性分泌物pheromone (称为信息素,该物质随着时间的推移会逐渐挥发消失,信息素浓度的大小表征路径的远近)信息素能够让其他蚂蚁感知从而起到一个引导的作用。通常多个路径上均有信息素时,蚂蚁会优先选择信息素浓度高的路径,从而使浓度高的路径信息素浓度更高,形成一个正反馈。有些蚂蚁并没有像其它蚂蚁一样总重复同样的路,他们会另辟蹊径,如果另开辟的道路比原来的其他道路更短,那么,渐渐地,更多的蚂蚁被吸引到这条较短的路上来。最后,经过一段时间运行,可能会出现一条最短的路径被大多数蚂蚁重复着。最终,信息素浓度最高的路径即是最终被蚂蚁选中的最优路径。
与其他算法相比,蚁群算法是一种比较年轻的算法,具有分布式计算、无中心控制、个体之间异步间接通信等特点,并且易于与其他优化算法相结合,经过不少仁人志士的不断探索,到今天已经发展出了各式各样的改进蚁群算法,不过蚁群算法的原理仍是主干。
2 蚁群算法的求解原理
基于上述对蚁群觅食行为的描述,该算法主要对觅食行为进行以下几个方面模拟:
(1)模拟的图场景中包含了两种信息素,一种表示家,一种表示食物的地点,并且这两种信息素都在以一定的速率进行挥发。
(2)每个蚂蚁只能感知它周围的小部分地方的信息。蚂蚁在寻找食物的时候,如果在感知范围内,就可以直接过去,如果不在感知范围内,就要朝着信息素多的地方走,蚂蚁可以有一个小概率不往信息素多的地方走,而另辟蹊径,这个小概率事件很重要,代表了一种找路的创新,对于找到更优的解很重要。
(3)蚂蚁回窝的规则与找食物的规则相同。
(4)蚂蚁在移动时候首先会根据信息素的指引,如果没有信息素的指引,会按照自己的移动方向惯性走下去,但也有一定的机率改变方向,蚂蚁还可以记住已经走过的路,避免重复走一个地方。
(5)蚂蚁在找到食物时留下的信息素最多,然后距离食物越远的地方留下的信息素越少。找到窝的信息素留下的量的规则跟食物相同。蚁群算法有以下几个特点:正反馈算法、并发性算法、较强的鲁棒性、概率型全局搜索、不依赖严格的数学性质、搜索时间长,易出现停止现象。
蚂蚁转移概率公式:
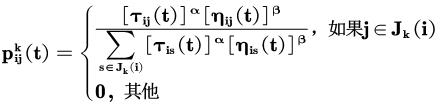
公式中:是蚂蚁k从城市i转移到j的概率;α,β分别为信息素和启发式因子的相对重要程度;为边(i,j)上的信息素量;为启发式因子;为蚂蚁k下步允许选择的城市。上述公式即为蚂蚁系统中的信息素更新公式,是边(i,j)上的信息素量;ρ是信息素蒸发系数,0<ρ<1;为第k只蚂蚁在本次迭代中留在边(i,j)上的信息素量;Q为一正常系数;为第k只蚂蚁在本次周游中的路径长度。
在蚂蚁系统中,信息素更新公式为:
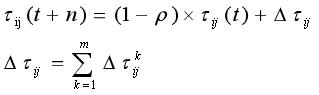
3 蚁群算法的求解步骤:
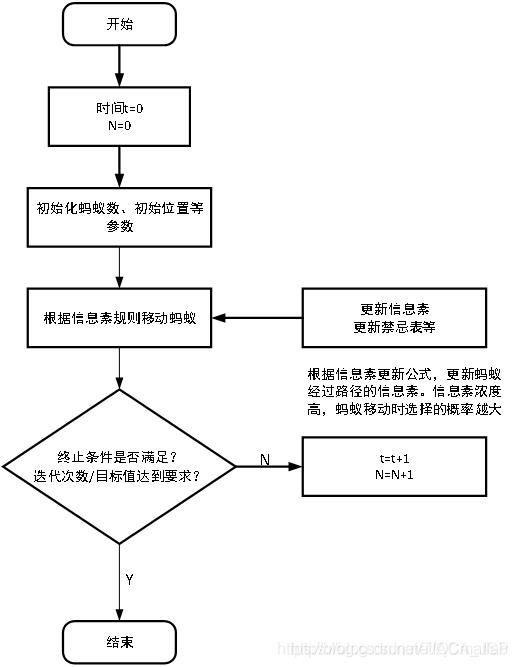
(1)初始化参数在计算之初,需要对相关参数进行初始化,如蚁群规模(蚂蚁数量)m、信息素重要程度因子α、启发函数重要程度因子β、信息素会发银子ρ、信息素释放总量Q、最大迭代次数iter_max、迭代次数初值iter=1。
(2)构建解空间将各个蚂蚁随机地置于不同的出发点,对每个蚂蚁k(k=1,2,3…m),按照(2-1)计算其下一个待访问城市,直到所有蚂蚁访问完所有城市。
(3)更新信息苏计算每个蚂蚁经过路径长度Lk(k=1,2,…,m),记录当前迭代次数中的最优解(最短路径)。同时,根据式(2-2)和(2-3)对各个城市连接路径上信息素浓度进行更新。
(4) 判断是否终止若iter<iter_max,则令iter=iter+1,清空蚂蚁经过路径的记录表,并返回步骤2;否则,终止计算,输出最优解。
(5)判断是否终止若iter<iter_max,则令iter=iter+1,清空蚂蚁经过路径的记录表,并返回步骤2;否则,终止计算,输出最优解。3. 判断是否终止若iter<iter_max,则令iter=iter+1,清空蚂蚁经过路径的记录表,并返回步骤2;否则,终止计算,输出最优解。
二、源代码
function varargout = ImageRegistration(varargin)
% IMAGEREGISTRATION M-file for ImageRegistration.fig
% IMAGEREGISTRATION, by itself, creates a new IMAGEREGISTRATION or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = IMAGEREGISTRATION returns the handle to a new IMAGEREGISTRATION or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% IMAGEREGISTRATION(\'CALLBACK\',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in IMAGEREGISTRATION.M with the given input arguments.
%
% IMAGEREGISTRATION(\'Property\',\'Value\',...) creates a new IMAGEREGISTRATION or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before ImageRegistration_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property
% application
% stop. All inputs are passed to ImageRegistration_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE\'s Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help ImageRegistration
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 24-May-2021 17:01:50
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct(\'gui_Name\', mfilename, ...
\'gui_Singleton\', gui_Singleton, ...
\'gui_OpeningFcn\', @ImageRegistration_OpeningFcn, ...
\'gui_OutputFcn\', @ImageRegistration_OutputFcn, ...
\'gui_LayoutFcn\', [] , ...
\'gui_Callback\', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
addpath(pwd);
% --- Executes just before ImageRegistration is made visible.
function ImageRegistration_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to ImageRegistration (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for ImageRegistration
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes ImageRegistration wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = ImageRegistration_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
clc
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%调用OpenImage.m读入参考图像并获取文件名、图像大小%%%%%%%%%%%%
[fname,pname,index]=uigetfile({\'*.jpg;*.bmp;*.png;*.tif;*.gif;*.jpeg\'},\'选择参考图像\');
if index
name=[pname fname];
temp=imread(name);
[m,n]=size(temp);
m=num2str(m);
n=num2str(n);
imsize=[\' \',m,\'*\',n];
handles.ImsizeI=imsize;
handles.filenameI=name;
handles.names_dispI=[fname,imsize];
end
set(handles.text2,\'String\',handles.names_dispI);
guidata(hObject,handles);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%显示参考图像%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
axes(handles.axes1)
I=imread(handles.filenameI);
save I;
imshow(I)
figure(5)
imshow(I)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
clc
%%%%%%%%%%%调用OpenImage.m读入浮动图像并获取并获取文件名、图像大小%%%%%%%%%%
[fname,pname,index]=uigetfile({\'*.jpg;*.bmp;*.png;*.tif;*.gif;*.jpeg\'},\'选择浮动图像\');
if index
name=[pname fname];
temp=imread(name);
[m,n]=size(temp);
m=num2str(m);
n=num2str(n);
imsize=[\' \',m,\'*\',n];
handles.ImsizeJ=imsize;
handles.filenameJ=name;
handles.names_dispJ=[fname,imsize];
end
set(handles.text3,\'String\',handles.names_dispJ);
guidata(hObject,handles);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%显示浮动图像%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
axes(handles.axes2)
J=imread(handles.filenameJ);
imshow(J)
figure(6)
imshow(J)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
clc
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%检测是否已输入参考图像与浮动图像%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
axesIbox=get(handles.axes1,\'box\');
axesJbox=get(handles.axes2,\'box\');
if strcmp(axesIbox,\'off\')||strcmp(axesJbox,\'off\')
errordlg(\'Please select Image for Registration\',\'Error\')
error(\'NO Image!\')
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%检测参考图像与浮动图像大小是否相同%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
handles.isSameSizeIJ=strcmp(handles.ImsizeI,handles.ImsizeJ);
if handles.isSameSizeIJ~=1
errordlg(\'Please select the Same Size Image\',\'Error\')
error(\'Image Size doesn"t match!\')
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%读入并复制图像,一幅用于配准过程,另一幅用于配准后输出%%%%%%%%%
I1=imread(handles.filenameI);
J1=imread(handles.filenameJ);
handles.Old_I=I1;
handles.Old_J=J1;
I=I1;
J=J1;
handles.I=I;
handles.J=J;
guidata(hObject,handles);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%显示配准前参考图像与浮动图像的“融合"效果图%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
axes(handles.axes4)
imshow(uint8(I+J))
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%调用函数GLPF.m(高斯低通滤波器),完成高斯低通预处理%%%%%%%%%%%%%
[I,J]=GLPF(handles);
handles.I=I;
handles.J=J;
guidata(hObject,handles);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%调用函数Powell.m,实现图像配准%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
tic
RegistrationParameters=Powell(handles);
%RegistrationParameters=AntColony(handles);
%RegistrationParameters=AntColonyimprove(handles);
toc
ElapsedTime=toc;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%显示配准结果%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
handles.RegistrationParameters=RegistrationParameters;
y=RegistrationParameters(1);
x=RegistrationParameters(2);
ang=RegistrationParameters(3);
RegistrationResult=sprintf(\'X,Y,Angle=[%.5f][%.5f][%.5f]\',x,y,ang);
MI_Value=RegistrationParameters(4);
MI_Value=sprintf(\'MI_Value=[%.4f]\',MI_Value);
ElapsedTime=sprintf(\'Elapsed Time=[%.3f]\',ElapsedTime);
axes(handles.axes5)
[FusionImage,RegistrationImage]=Fusion(handles);
imshow(FusionImage)
axes(handles.axes3)
imshow(RegistrationImage)
figure(7)
imshow(RegistrationImage)
set(handles.text8,\'string\',RegistrationResult);
set(handles.text9,\'string\',MI_Value);
set(handles.text10,\'string\',ElapsedTime);
三、运行结果
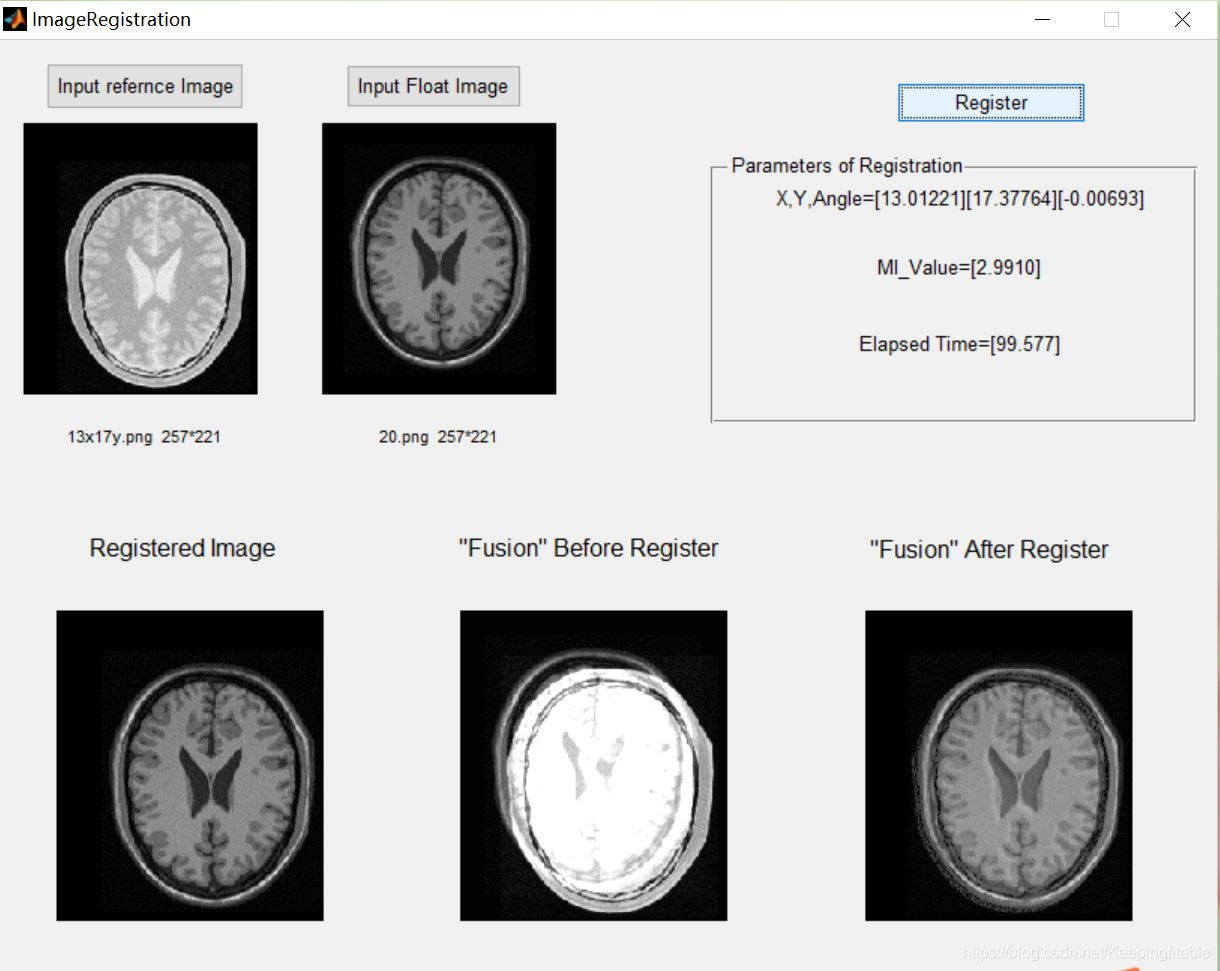
四、备注
版本:2014a
完整代码或代写加1564658423
以上是关于图像配准基于matlab GUI Powell+蚁群算法图像配准含Matlab源码 928期的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
图像配准基于Powell+蚁群算法实现图像配准matlab源码含 GUI
图像配准基于Horn-Schunck和Lucas-Kanade等光流场实现图像配准matlab源码含GUI界面