HashMap 简析
Posted 乌龟王八蛋
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HashMap 简析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
HashMap 简析
基本使用
对于 HashMap 的使用,主要是演示不同的操作方式,区别于 List 列表容器
具体的初始化、元素添加,会直接结合源码分析
对于更多的 API 使用,请参考官方提供的 API 手册
// 创建 HashMap 对象
HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
// 添加元素
hashMap.put(0,"A");
hashMap.put(1,"B");
hashMap.put(2,"C");
hashMap.put(4,"D");
// 容器是否为空
System.out.println(hashMap.isEmpty());
// 取出元素
System.out.println(hashMap.get(2));
// 删除元素
hashMap.remove(3);
// 获取所有的键 K
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hashMap.keySet().toArray()))
初始化
无参初始化
public HashMap() {
// 负载因子的值默认为加载因子的值,0.75f
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
}
HashMap 的初始化容量也是空,再次声明,源码的阅读需结合具体的 JDK 版本
有参构造函数
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
// 指定初始容量、负载因子
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
transient Node<K,V>[] table;:负责存储键值对,以数组的形式
final float loadFactor;:负载因子
负载因子的大小,是 table 已经使用的容量的百分比
负载因子,在无参初始化时,设置为 0.75 加载因子,即负载因子默认为 0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;:加载因子
int threshold;:容量阙值, 计算公式 : table * loadFactor = threshold
节点类
HashMap 的哈希表,是由数组、单向链表组成
table 中直接存储一组数组,而数组中的每个元素可以拓展为一个单向链表
在 HashMap 中,存在两个节点类 Node、TreeNode
数组、单向链表中的元素,都是一个 Node 类,table 是 Node 类型的数组
当单向链表长度为 8 时,会转换为树形结构,此时会用到 TreeNode
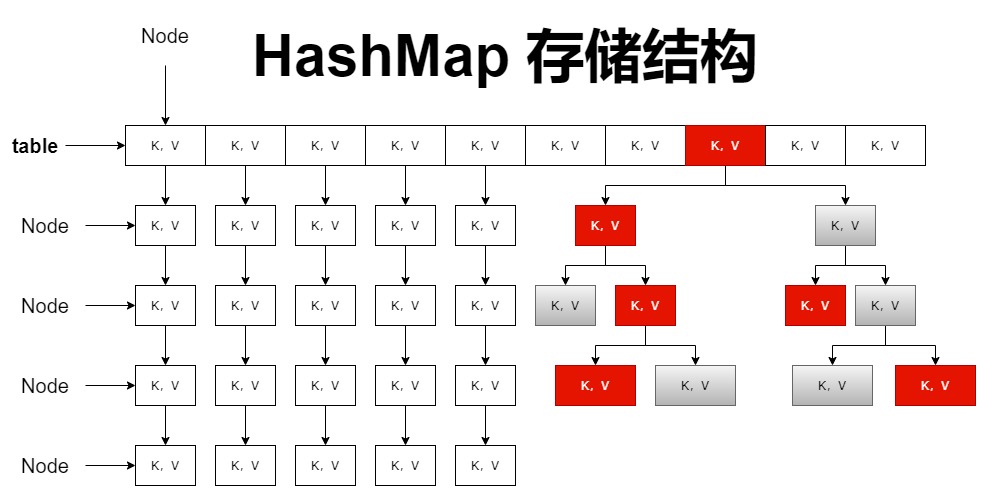
源码分析,自此之后,会精简代码,完全版请直接参考 JDK 源码
// Node 节点类,以 K,V 键值对的形式存储元素
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
// hash:该 Node 类在内存中的地址值
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
// next:指向下一个可能存在的 Node 节点
Node<K,V> next;
// 判断节点类对象是否相同
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
// 父节点
TreeNode<K,V> parent;
// 左节点
TreeNode<K,V> left;
// 右节点
TreeNode<K,V> right;
// 下一节点
TreeNode<K,V> prev;
// true 为红树;false 为黑树
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
}
为空扩容
HashMap 初始化时,默认 Node 数组为空,在添加第一个键值对时,存在默认扩容
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 若table数组为空,则该分支执行,默认扩容,核心为
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
}
}
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
// 此时数组为空,获得的是 0
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
}
else if (oldThr > 0)
// 初始阙值为零,即 table 为 null,该分支执行
// DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4
else {
// 此次扩容为 16
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
// 负载因子为 12
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
// 数组扩容完毕
table = newTab;
return newTab;
}
在首次添加键值对时,将 table 的容量扩充为 16,负载因子占比 7.5,值为 12
计算 hash 值
每一个数组中的 Node 节点,都存在一个唯一的 hash 值
此数组所代表的单向链表中的Node节点,具有相同的hash值
// 添加元素,其中的 key 作为哈希值运算
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
// 将 key 通过一系列的运算,转换为 hash 值返回
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
// 若 key 为 0,则放置在数组 Node 节点的首位
// hash 值的计算,具体涉及到 hashCode()、按位异或、无符号右移
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
以下是按位异或的使用,对于这二者,可以参考 语言基础
// 按位异或 `^`:相同为 0,不同为 1
System.out.println(16 ^ 7);
/*
原码 16:00000000 00000000 00000000 00010000
原码 7:00000000 00000000 00000000 00000111
按位异或:00000000 00000000 00000000 00010111
*/
简单的理解,hashMap 的为空扩容,容量是 16,那么 hash 值就是 hashCode% 数组长度
hash 值可能存在重复,重复的键值对以单向链表的结构存储
元素添加
// 第一步:放入键值对 K,V
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
// 第二步:确定存储位置
/*
hash:key 的哈希值
key:键
value:值
onlyIfAbsent:若为 true,则不更改原有值
evict:若为 false,table 处于创建模式
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
// tab:接收 table 数组;
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 判断 table 数组中的某个位置是否为空,根据 hash 值选定
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
// newNode.. 创建常规的数组 Node 节点类
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 若当前数组位置已存在元素,则向单向链表追加
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 判断键是否相同
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 判断该节点是否是树节点,即由单向链表转为红黑树
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 添加为树节点
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 依旧为单向链表,循环添加至链表的末尾位置
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// 将传入的键值对存储为下一个节点
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 若键重复,则覆盖 Value 值
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
}
链表转树
在一定的条件下,单向链表会被转换为红黑树结构
之后,新的键值对会以树节点的形式存储
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
else {
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// 创建新的节点,此处已完成元素添加
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 判断当前是否满足单向链表转树的条件
// TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
// 单向链表转为树结构,必须使得 table 长度大于 64,否则继续扩容
// MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
单向链表转为红黑树结构,必须满足两点
- 常规数组节点下的单向链表,长度必须大于等于 7
- 数组 table 的长度必须大于等于 64,即存在 63 个常规数组节点
数组扩容
table 的为空扩容,默认长度是 16
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
// 数组 table 是否为 null,即为空扩容
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
// 扩容至极限 Integer.MAX_VALUE
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
// 扩容为原来的二倍
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1;
}
else if (oldThr > 0)
newCap = oldThr;
// 数组的为空扩容
else {
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
// 新、老数组元素的拷贝迁移
}
}
// 返回扩容后的新数组
return newTab;
}
对于 HashMap 容器的扩容,存在三点
- 为空扩容,扩容至 16
- 非空扩容,每次 扩容二倍
- 极限扩容,扩容至最大 Integer.MAX_VALUE
红黑自平衡
以上是关于HashMap 简析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章