基于随机定位的地图信息获取方式
Posted Narule
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于随机定位的地图信息获取方式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基于随机定位的地图信息获取方式
基本定义
场景
一个应用要用到地图,地图拖动时,要填补新的版图上的地理信息
目的
快速获取屏幕内需要的地图信息,不获取多余无用的地图信息
功能要点
1.确定地图范围,获取的信息不超出显示屏过多
(比如屏幕地图查询100平方米的信息,服务返回的信息不能超过130平米的地图信息)
2.动态快速获取信息,通过定位快速获取周围地理信息,第一时间从缓存获取或者数据库获取,且不要有复杂查询和大量查询。
绝对定位:坐标,传人任何一个点,都能通过角色定位知道这个点在哪,以及其他延伸计算
通过地图的中心定位,优先快速确定要获取那些位置的地理信息,快速获取对应的图块。
3.根据维度调整信息获取范围和格式
粒度:通过两个点确定查询信息的范围,同时确定粒度(地图缩放级别)
(4).原先有的信息短时间不重复获取
(拖动地图导致50%地图位置换了,还有50%地图不变,不用再次请求)
确定地图范围
通过两个点,或者中心定位+范围,要快速得出在范围内地图信息
地图切割
分块
将地图切割均等大小
块级别
地图显示可以是世界地图,也可以是城镇地图,缩放差距很大,地图块也要级别表示具体缩放场景
坐标
一个绝对坐标,作为参考
每一个切割的分块地图都有一个坐标,坐标唯一
确定分块坐标唯一依据:分块级别,经纬度,
分块地图表示方法
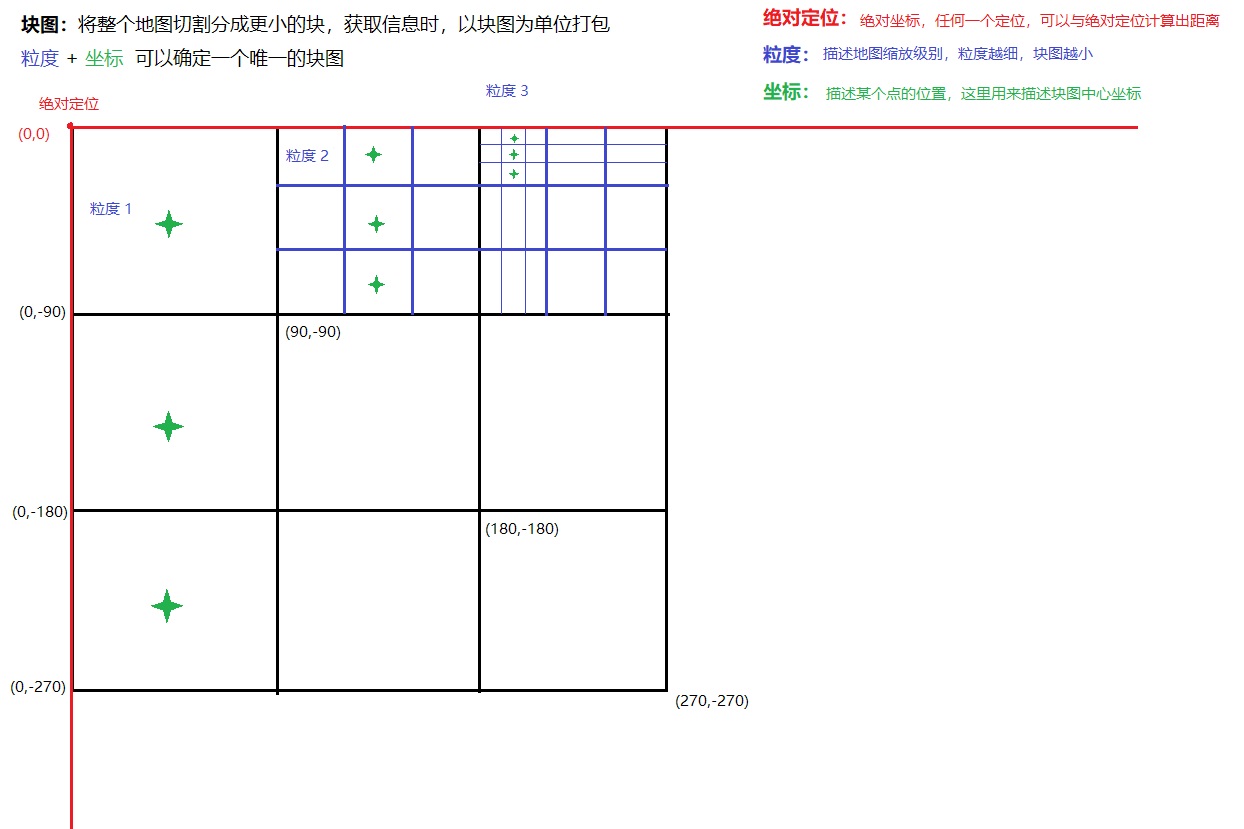
获取范围内的分块地图
矩形对角线两个点,可以确定范围
入参:坐标1,坐标2,粒度(地图缩放级别)
返回:分块地图坐标
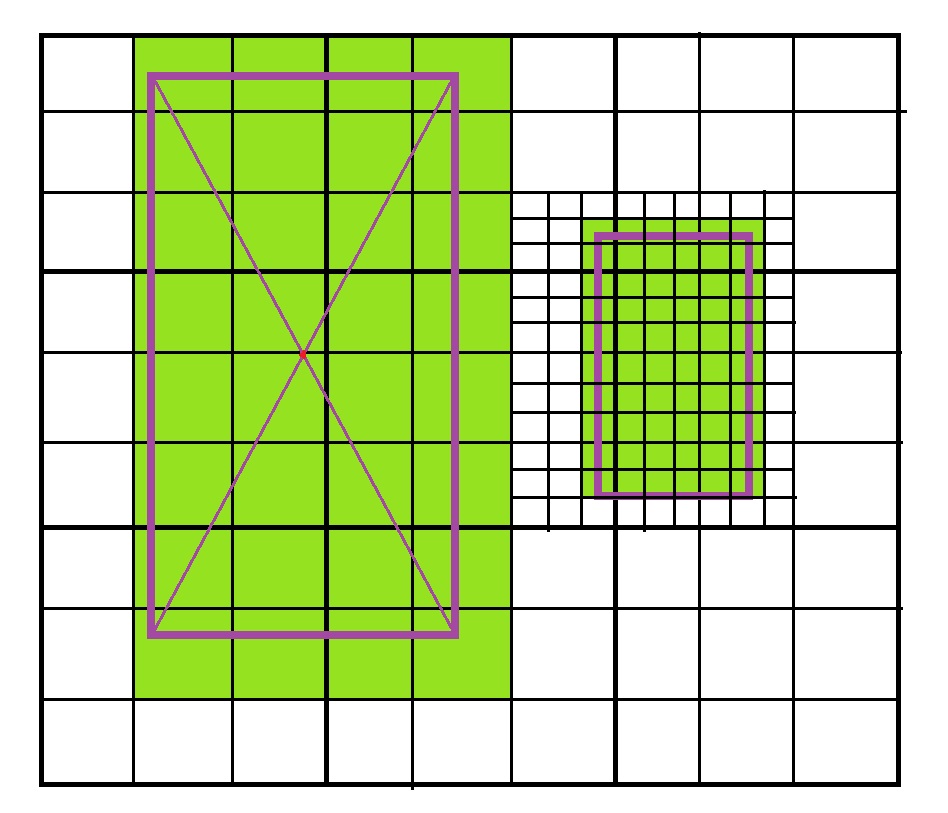
将问题细分化,可以分解为,先求所有图块的x坐标,在求x坐标,然后数组相乘,或多所有图块的二维坐标(x,y)
输入:点A,点B,地图扩展系数
返回:两个点覆盖的范围
Fun(coordinate c1,coordinate c2,granularity g) return Array(Map-Coordinate)
public static DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#0.0000");
/**
* -求两个点包含图块坐标范围
* @param x1 点A
* @param x2 点B
* @param granularity 地图扩展系数
* @return A,B两点包含的图块的一维坐标
*/
public static double[] range_position(double x1,double x2,double granularity) {
double minX = Math.min(x1, x2);
double maxX = Math.max(x1, x2);
//左边界
double left = Math.floor(minX/granularity) * granularity;
//右边界
double right = Math.ceil(maxX/granularity) * granularity;
//相差
double difference = right - left;
double d_pointNumber = difference/granularity;
//一维坐标数
int pointNumber = (int) (int)Math.ceil(Double.valueOf(df.format(d_pointNumber)));
double[] points = new double[pointNumber];
points[0] = Double.valueOf(df.format(left + granularity/2));
for(int i = 1; i<pointNumber; i++) {
points[i] = Double.valueOf(df.format(points[i-1] + granularity));
}
return points;
}
调用上面方法两次,分别传入 x坐标 和 y坐标,求出(x,y) 集合,得到所有图块二维坐标。
快速获取图块信息
地图信息要快速获取,上面返回坐标,通过坐标和扩展级别能确定唯一性,因此可以通过唯一key对应一个图块
//图块唯一key
//参数 x y 坐标 扩展系数 图块边长
public static String getMpk(double x,double y, int gly,double mapLength) {
return MapBlock.head + gly + "-"+ df.format(mapLength) + "(" +x + ","+ y + ")";
}
首先应该是初始化的时候,将地图分块信息读取,放入缓存,或者数据库
如果传入两个点,就能获得对应的图块唯一key,直接从缓存获取或者数据库查询
code-动态获取屏幕内地图
传入矩形对角线两个坐标,返回矩形内所有图块
实现类:
MapRangePosition
package net.narule.algorithm.map;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* -地图范围定位
* @author Narule
*
*/
public class MapRangePosition {
/**
* -给定一个矩形,返回矩形接触的区域
* @param c1
* @param c2
* @return
*/
public static List<MapBlock> getRangeMapBlock(Coordinate c1,Coordinate c2){
//扩展系数
int calculateGly = Granularity.calculateGly(c1, c2);
//图块边长
double mapSideLength = calculateGly * Granularity.unit_length;
double z = c1.getZ();
double[] range_position_x = range_position(c1.getX(),c2.getX(), mapSideLength);
double[] range_position_y = range_position(c1.getY(),c2.getY(), mapSideLength);
ArrayList<MapBlock> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (double x : range_position_x) {
for (double y : range_position_y) {
Coordinate coordinate = new Coordinate(x,y,z);
MapBlock mapBlock = new MapBlock(coordinate,getMpk(x, y, calculateGly, mapSideLength),calculateGly);
list.add(mapBlock);
}
}
return list;
}
public static String getMpk(Coordinate c,int gly,double mapLength) {
return MapBlock.head + gly + "_"+ mapLength + "(" +c.getX() + ","+ c.getY() + ")";
}
public static String getMpk(double x,double y, int gly,double mapLength) {
return MapBlock.head + gly + "-"+ df.format(mapLength) + "(" +x + ","+ y + ")";
}
public static DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#0.0000");
/**
* -求两个点包含图块坐标范围
* @param x1 点A
* @param x2 点B
* @param granularity 地图扩展系数
* @return A,B两点包含的图块的一维坐标
*/
public static double[] range_position(double x1,double x2,double granularity) {
double minX = Math.min(x1, x2);
double maxX = Math.max(x1, x2);
//左边界
double left = Math.floor(minX/granularity) * granularity;
//右边界
double right = Math.ceil(maxX/granularity) * granularity;
//相差
double difference = right - left;
double d_pointNumber = difference/granularity;
//一维坐标数
int pointNumber = (int) (int)Math.ceil(Double.valueOf(df.format(d_pointNumber)));
double[] points = new double[pointNumber];
points[0] = Double.valueOf(df.format(left + granularity/2));
for(int i = 1; i<pointNumber; i++) {
points[i] = Double.valueOf(df.format(points[i-1] + granularity));
}
return points;
}
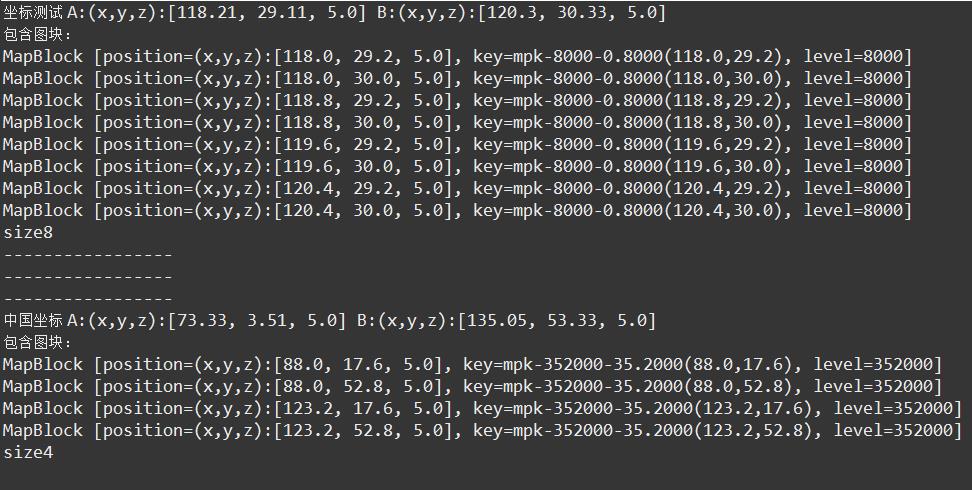
public static void main(String[] args) {
Coordinate A = new Coordinate(118.21,29.11,5);
Coordinate B = new Coordinate(120.30,30.33,5);
List<MapBlock> rangeMapBlock = getRangeMapBlock(A, B);
System.out.println("坐标测试 A:" + A + " B:" + B);
System.out.println("包含图块:");
for (MapBlock mapBlock : rangeMapBlock) {
System.out.println(mapBlock);
}
System.out.println("size" + rangeMapBlock.size());
Coordinate CNA = new Coordinate(73.33,3.51,5);
Coordinate CNB = new Coordinate(135.05,53.33,5);
System.out.println("-----------------");
System.out.println("-----------------");
System.out.println("-----------------");
List<MapBlock> chineseMapBlock = getRangeMapBlock(CNA,CNB);
System.out.println("中国坐标 A:" + CNA + " B:" + CNB);
System.out.println("包含图块:");
for (MapBlock mapBlock : chineseMapBlock) {
System.out.println(mapBlock);
}
System.out.println("size" + chineseMapBlock.size());
}
}
描述对象
Coordinate 坐标
表示在地图上的位置
package net.narule.algorithm.map;
/**
* -coordinate 定位对象
* @author Narule
*
*/
public class Coordinate {
private double x;
private double y;
private double z;
public Coordinate() {
super();
}
public Coordinate(double x, double y, double z) {
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getZ() {
return z;
}
public void setZ(double z) {
this.z = z;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Coordinate [x=" + x + ", y=" + y + ", z=" + z + "]";
}
}
Granularity 缩放系数
地图缩放大小,标尺
package net.narule.algorithm.map;
/**
* -granularity 粒度
* @author Narule
*
*/
public class Granularity {
/**
* -缩放级别
*/
private static int gly;
/**
* -最小单位
* 地球赤道40075千米
* 经纬度中 0.01有 1.1 千米
* 0.001 100m
* 0.0001 10m
* 10m
*/
public static final double unit_length = 0.0001;
public static double unit_granularity = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(unit_length, 2)*2);
/**
* -块图边长
*/
private static double mapSideLength;
/**
* -计算缩放级别
* @param c1
* @param c2
* @return
*/
public static int calculateGly(Coordinate c1,Coordinate c2) {
double x = Math.abs(c1.getX() - c2.getX());
double y = Math.abs(c1.getY() - c2.getY());
double minL = Math.min(x, y);
gly = (int) Math.ceil(
minL/unit_granularity
);
if(gly <= 10) gly = 10;
else if(gly > 10 && gly < 100) gly = gly / 10 * 10;
else if(gly > 100 && gly < 1000) gly = gly / 100 * 100;
else if(gly > 1000) gly = gly / 1000 * 1000;
return gly;
}
public static double getGly() {
return gly;
}
public double getMapSideLength() {
return mapSideLength;
}
}
MapBlock 图块
将地图分割成更小的图块,每一块都包含坐标和缩放系数,通过坐标和缩放系数能确定唯一
package net.narule.algorithm.map;
import java.io.Serializable;
/*
* -地图块
*/
public class MapBlock implements Serializable{
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public static final String head = "mpk-";
private Coordinate position;
private String key;
private int level;
public MapBlock(Coordinate coordinate){
this.position = coordinate;
}
public MapBlock(Coordinate coordinate,String key,int level){
this.position = coordinate;
this.key = key;
this.level = level;
}
public Coordinate getPosition() {
return position;
}
public void setPosition(Coordinate position) {
this.position = position;
}
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MapBlock [position=" + position + ", key=" + key + ", level=" + level + "]";
}
public int getLevel() {
return level;
}
public void setLevel(int level) {
this.level = level;
}
}
以上是关于基于随机定位的地图信息获取方式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章