Codeforces Round #725 (Div. 3) A~G 题解记录
Posted tags: 篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Codeforces Round #725 (Div. 3) A~G 题解记录相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。 补题链接:Here 数组 \\(a\\) 的大小为 \\(n\\) ,请问每次可以删除最左和最右侧的元素,请问最少执行多少次能删除掉数组中的最大值和最小值 (\\(1\\le a_i\\le n\\)) 在输入的时候确定最大值和最小值的下标, 4种情况 比较从左边删除和右边删除的情况即可 Polycarp 要对他的 \\(n\\) 个朋友的蛋糕数量重新分配,使得每个人的蛋糕数量相同。 找到最小的 \\(k\\) \\(a_{i1} + a_{i2}+...+a_{ik}\\) 进行分配 数学题, 首先如果总的蛋糕数不是 \\(n\\) 的倍数,直接输出 \\(-1\\) ,接下来在统计大于平均值的人数即可 在数组 \\(a\\) 中寻找最大对数的 \\((i,j) (1\\le i < j \\le n)\\) 使得 \\(l \\le a_i + a_j \\le r\\) 简单来说要统计两种情况 二分上面两种情况,然后相减就是合适的区间长度了。 但要注意如果本身 \\(a_i * 2\\) 就符合情况的话会重复计算一次,要减去一 最后输出 \\(ans / 2\\) 给与 \\(a\\) 和 \\(b\\) 两个整数,在一回合操作里, 请问是否能在 \\(k\\) 个回合结束后使得 \\(a=b\\) 看样例想到是质因数个数的问题, 但试了下先欧拉素数筛晒出 \\(1e9\\) 的数据还是 TLE了(常数太大了),然后尝试直接统计因子个数,注意使用 没看懂题意,以后补 這道題比賽沒寫出來虧了一個億 给定两个整数 \\(l\\) 和 \\(r\\),其中 \\(l<r\\)。 我们将向 \\(l\\) 加 1,直到结果等于 \\(r\\)。 因此,将执行 \\(r-l\\) 次加法。 对于每个这样的加法,让我们看看在它之后将更改的位数。 累加不同位数的情况下 \\(r - l\\) ,直到 \\(l = 0\\) 和 \\(r= 0\\) 如果这算数位DP, 那么算是我见过最简单的数位DP了. Polycarp 有 x 个红色糖果和 y 个蓝色糖果。 使用它们,他想制作礼品套装。 每个礼品套装包含一个红色糖果和 b 个蓝色糖果,或一个蓝色糖果和 b 个红色糖果。 任何糖果最多只能属于一个礼品套装。 帮助 Polycarp 找到他可以创造的最大数量的礼品套装。 例如,如果 \\(x=10,y=12,a=5,b=2\\),那么 Polycarp 可以制作三套礼物: 思路来自 Arctic_Clam 考虑二分可分的集合的数量。 不妨设 \\(x < y,a < b\\) 记 \\(n\\) 为要验证的集合数量,\\(s\\) 为第 一种集合数量,\\(t\\)为 第二种集合数量。 变形可以得到 也就是说,给定n,我们可以求出s的取值区间。再判定下该区间是否合法即可。 似乎本题也可以三分做,dalao也对三分做了正确性证明(tql 二分的正确性是显然的,但是三分的正确性并不那么显然。 以上是关于Codeforces Round #725 (Div. 3) A~G 题解记录的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
1538A. Stone Game
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
int id1, id2;
for (int i = 1, x; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> x;
if (x == 1)id1 = i;
if (x == n)id2 = i;
}
if (id1 > id2) swap(id1, id2);
int cnt1 = (id1 + min(n - id2 + 1, id2 - id1));
int cnt2 = (n - id2 + 1 + min(id1, id2 - id1));
cout << min(cnt1, cnt2) << "\\n";
}
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n);
for (int &x : a)cin >> x;
int maxPos = max_element(a.begin(), a.end()) - a.begin();
int minPos = min_element(a.begin(), a.end()) - a.begin();
cout << min({
max(maxPos, minPos) + 1,
(n - 1) - min(maxPos, minPos) + 1,
(n - 1) - maxPos + minPos + 2,
(n - 1) - minPos + maxPos + 2
}) << "\\n";
}
1538B. Friends and Candies
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
ll cnt = 0;
vector<int>a(n);
for (int &x : a)cin >> x, cnt += x;
if (cnt % n != 0) {cout << -1 << "\\n"; return ;}
int c = 0;
cnt /= n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (a[i] > cnt)c++;
}
cout << c << "\\n";
}
1538C. Number of Pairs
双指针写法
void solve() {
int n; ll L, R;
cin >> n >> L >> R;
vector<ll>a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)cin >> a[i];
sort(a.begin() + 1, a.end());
int l = 2, r = n;
ll cnt = 0;
while (l <= n and a[1] + a[1] <= L)l++;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
while (l > 1 and a[l - 1] + a[i] >= L)l--;
while (r > i and a[r] + a[i] > R)r--;
if (r >= max(l, i)) {
if (l > i)cnt += (r - l + 1);
else cnt += r - i;
}
}
cout << cnt << \'\\n\';
}
二分写法
void solve() {
int n, l, r ;
cin >> n >> l >> r;
vector<int>a(n);
for (int &x : a)cin >> x;
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ans += upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), r - a[i]) - a.begin();
ans -= lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), l - a[i]) - a.begin();
if (2 * a[i] >= l && a[i] * 2 <= r)ans--;
}
cout << ans / 2 << "\\n";
}
1538D. Another Problem About Dividing Numbers
scanf 而不是 cin)void solve() {
int a, b, k;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &k);
if (k == 1) {
puts(a != b && (a % b == 0 || b % a == 0) ? "YES" : "NO");
return ;
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= b; ++i) {
while (b % i == 0) {
b /= i; cnt++;
}
}
if (b != 1)cnt++;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= a; ++i) {
while (a % i == 0) {
a /= i;
cnt++;
}
}
if (a != 1)cnt++;
puts(cnt >= k ? "YES" : "NO");
}
1538E. Funny Substrings
1538F. Interesting Function
void solve() {
ll l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
ll ans = 0;
while (l != 0 || r != 0) {
ans += (r - l);
l /= 10, r /= 10;
}
cout << ans << "\\n";
}
ll dp[20];
void init(int n) {
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)dp[i] = dp[i - 1] * 10 + 1;
}
int cnt(ll x) {
int a[20] = {0}, Cnt = 0;
while (x) {
a[Cnt++] = x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = Cnt - 1; i >= 0; --i)ans += dp[i + 1] * a[i];
return ans;
}
void solve() {
ll l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
cout << cnt(r) - cnt(l) << "\\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr);
init(15);
int _; for (cin >> _; _--;) solve();
return 0;
}
1538G. Gift Set
如何 \\(O(1)\\) 求给定的某个集合可行与否?
于是我们有
\\(eg:\\) \\(s\\) 取值区间的左界应该是向下取整,但是 \\(x−nb\\) 和 \\(a − b\\) 都是负数,而 C++默认是趋零取整,所以要特判。ll x, y, a, b;
bool check(ll n) {
ll l = (x - n * b) / (a - b);
if ((x - n * b) < 0 and (-(x - n * b)) % (b - a) != 0)l++;
ll r = (y - n * a) / (b - a);
return l <= r and r >= 0 and l <= n;
}
void solve() {
cin >> x >> y >> a >> b;
if (x > y) swap(x, y);
if (a > b) swap(a, b);
if (a == b) {
cout << (x /= a) << "\\n";
return ;
}
ll l = 0, r = x;
while (l < r) {
if (l == r - 1) {
if (check(r)) l = r;
break;
}
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << l << \'\\n\';
}
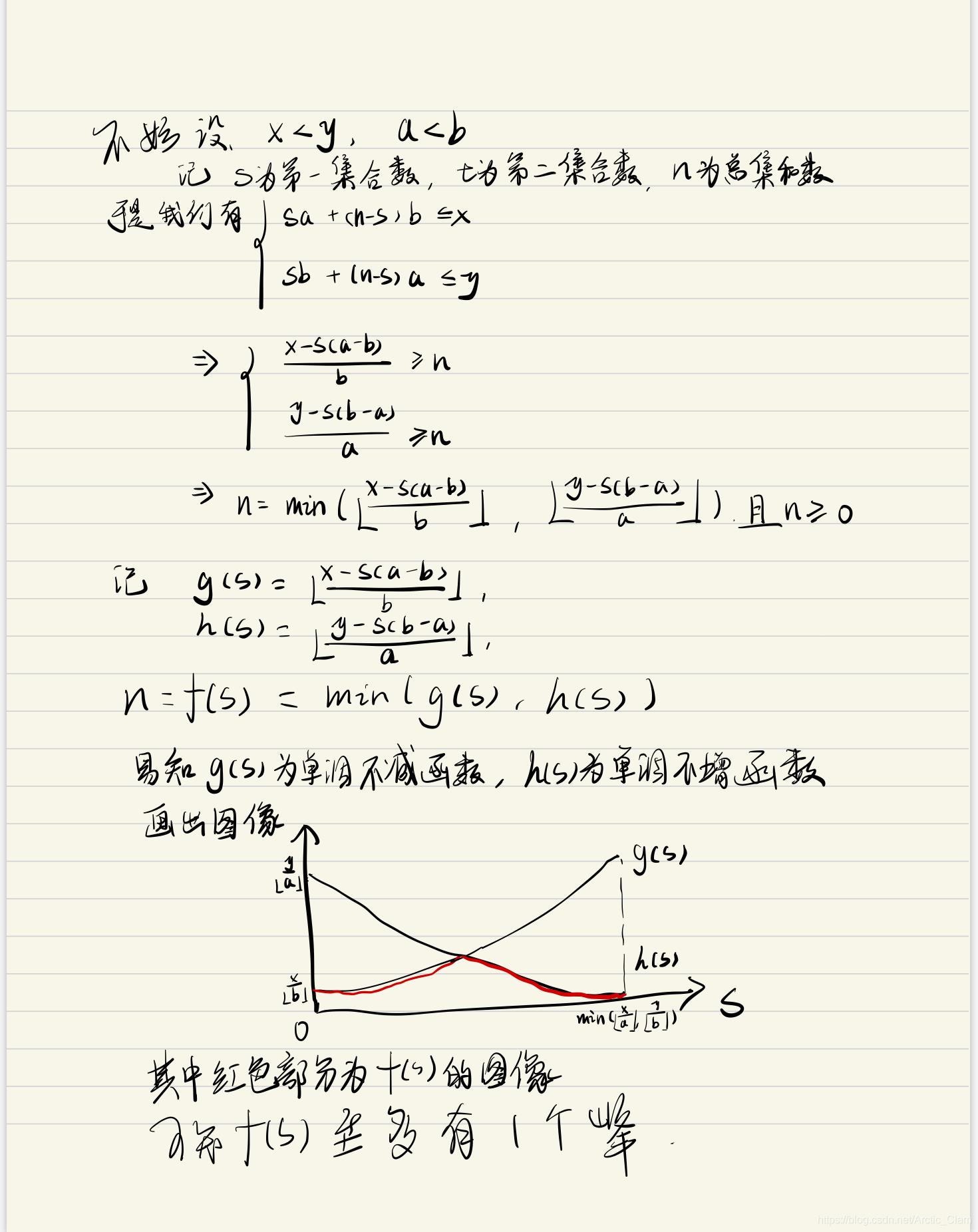
为了证明三分的正确性,我们需要证明集合总数n是第一集合数s的函数,且该函数至多有一个峰。
下面给出证明: