CG——Possion Image Editing
Posted Ed_Sheeran
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了CG——Possion Image Editing相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
博主终于正式回来发文了。
之后会写一些学习心得,大学应该不会打ACM了。
目前尝试CG,兴趣使然,希望后面可以坚持吧。
Possion Image Editing
学习资料:https://blog.csdn.net/u011534057/article/details/68922319
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/58867397
这两份讲的比较好,但还是看论文比较好,我按第一篇又是算梯度又是算散度,又在想怎么构造转移矩阵,对自己的数学极度怀疑,差点自闭掉。后来经jdr大佬指点发现按照论文的分析,这实际就是一个解方程组的问题,即 div(h) = div(g), 明显是一个高斯消元的方程,但是图像以像素点储存,复杂度明显爆炸,所以可以用迭代的方式解,因为边界是确定的,最后会收敛,复杂度暴降。
简单概括一下泊松:讲目标图像抽象成一个函数h,背景设为f,融合后的图像设为g,我们所做的就是让g看起来就是f上的一个函数。对策就是边界取f的值,g的变化趋势尽量符合h的变化趋势。即
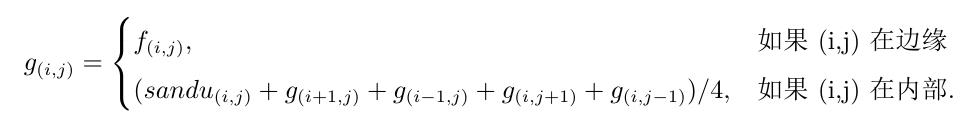
遇到的问题:
1.opencv的c++安装:花了两天都没搞定,按照博客一步步做,但是我下载的文件夹和博客下下来的不一样,最后无法写codevs的路径。(中途又在gcc的编译路径中加了空格,真是佩服我自己)=》最后只有选择Python写。(最后意识到我Python烂到和装环境差不多)
2.算法:按照博客老实按论文公式写,对数学要求太高了,好多人居然用到fft...=》请教jdr获得迭代解方程的算法
3.Python运算太慢,迭代还是T=》只有把数据传到C++来处理,果然还是得C
4.图像坐标轴问题,图像的表示是mat[y][x],这个搞了也挺久的,到处改(顺带一提,Python我用了个for x in,和后面的x变量命名重了,这个bug找的也真的久,写Python真的要注意变量范围,这比C++难多了)
5.多边形选取:最开始搞的ROI是矩形区域,做出来明显有问题,去网上学UI做了一个mask的操作,关于mask要注意区分3个图的坐标表示
6.其他细节:迭代事可能会爆值,结束后判255与0,中间判会增加误差;numpy中array用法不能和list等级,对于array, a[i][j] = [0,0,0]是错误写法,只能写成 a[i][j].all == 0; 对于list, a[i][j] == [0, 0, 0] 返回的是[True, True, True].
算法的局限:
1.背景图像选取应避免边缘截断,目标图像的背景色应和背景的颜色相近
2.使用混合梯度可以使边缘更加圆滑,但是可能会造成颜色变暗,论文后来进行了调色
3.选取图像本身有噪音或者色彩值比较极端经处理后缺陷会放大(网图有些看着正常,但实际颜色和肉眼观察不符,而且网图有很多也是合成的,要注意
原代码及成品:
python处理:

import cv2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import math %matplotlib inline def cv_show(name, img): cv2.imshow(name, img) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() lsPointsChoose = [] tpPointsChoose = [] pointsCount = 0 count = 0 Y, X = 0, 0 pointsMax = 6 lenx, leny = 0, 0 x1, y1, = 0, 0 centerx, centery = 0, 0 flag = esc = False img = cv2.imread(\'ren2.jpg\') #读取图像 dst = cv2.imread("ren1.jpg") # 图像大小处理 h, w = dst.shape[:2] # dst = cv2.resize(dst, (int(w*0.8), int(h*0.8)) ) img = cv2.resize(img, (int(w), int(h)) ) tmp = img.copy() img2 = img.copy() tmp3 = img.copy() tmp2 = dst.copy() fhand = open(\'data.txt\',\'w\') cv2.namedWindow(\'getROI\') cv2.setMouseCallback(\'getROI\',getROI) cv2.namedWindow(\'background\') cv2.imshow(\'background\', dst) cv2.setMouseCallback(\'background\', getcenter) while(1): cv2.imshow(\'getROI\',img) if cv2.waitKey(1)&0xFF==ord("e"): cv2.destroyAllWindows() break fhand.close()

def isout(x, y): if (mask2[x][y][0] == 0) : return True if (mask2[x+1][y][0] == 0): return True if (mask2[x-1][y][0] == 0): return True if (mask2[x][y+1][0] == 0): return True if (mask2[x][y-1][0] == 0): return True return False def handle(mat, x, y, lenx, leny, laparr): global fhand for x__ in laparr: fhand.write(str(x__)) fhand.write(\' \') for i in range(y, leny+y): for j in range(x, x+lenx): fhand.write(str(mat[i][j])+\' \') def getLap(mat, x, y, lenx, leny, t): ans = list() u = 0 print(\'lap\',centerx,centery) for i in range(y, y+leny): for j in range(x, lenx+x): if isout(i, j): pass else: u = (mat[i][j]*4 - mat[i][j-1] - mat[i][j+1] - mat[i-1][j] - mat[i+1][j]) # 混合梯度: # v = (t[i-y+centery][j-x+centerx]*4 - t[i-y+centery][j-1-x+centerx] - t[i-y+centery][j+1-x+centerx] - t[i-1-y+centery][j-x+centerx] - t[i+1-y+centery][j-x+centerx]) # if abs(v) > abs(u): # u = v # print(\'ccc\',u,v) ans.append(u) return ans def display(x, y, lenx, leny): global X, Y X = x Y = y global tmp, tmp2, fhand, mask2, tmp3 fhand.write(str(lenx)) fhand.write(\' \') fhand.write(str(leny)) fhand.write(\'\\n\') for i in range(y, y+leny): for j in range(x, lenx+x): fhand.write(str(mask2[i][j][0]) + \' \') B,G,R = cv2.split(tmp)#imge b,g,r=cv2.split(tmp2)#background B = getLap(B, x, y, lenx, leny, b) G = getLap(G, x, y, lenx, leny, g) R = getLap(R, x, y, lenx, leny, r) # print(\'display\',centerx, centery) handle(b, centerx, centery, lenx, leny, B) handle(g, centerx, centery, lenx, leny, G) handle(r, centerx, centery, lenx, leny, R)
C++迭代处理数据:

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; vector <double> sandu[3], mat[3]; vector <int> mask; int lenx, leny, size; vector <bool> vis; int fix(int x){ //防止爆值 if(x > 255)return 255; if(x < 0)return 0; return x; } bool isout(int x, int y){ // bool fg = 1; int idx = x * lenx + y; // if(mat[0][idx] == 1 && mat[1][idx] == 1 && mat[2][idx] == 1)return 0; // return 1; if(mask[idx] == 0) return 1; int dir[5] = {-1,1,lenx,-lenx}; for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ // fg = 1; int nw = idx + dir[i]; if(nw < 0 || nw >= size)continue; if(mask[idx] == 0)return 1; } return 0; } int main(){ freopen("data.txt","r",stdin); freopen("result1.txt","w",stdout); cin>>lenx>>leny; size=lenx*leny; for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){ int u; scanf("%d", &u); mask.push_back(u); } for(int t = 0; t < 3; t++){ int u; for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++){ scanf("%d", &u); sandu[t].push_back(u*1.0); } for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++){ scanf("%d", &u); mat[t].push_back(u*1.0); } } for(int i = 0; i < leny; i++) for(int j = 0; j < lenx; j++){ bool v = isout(i, j); vis.push_back(v); // if(v) printf("%d %d\\n",i,j); } int cnt=0; for(int t = 0; t < 3; t++){ bool fg = 1; while(fg){ fg = 0;cnt++; for(int i = 0; i < leny; i++) for(int j = 0; j < lenx; j++){ int idx = i * lenx + j; if(vis[idx])continue; double nw = (sandu[t][idx] + mat[t][idx-1] + mat[t][idx+1] + mat[t][idx-lenx] + mat[t][idx+lenx]) / 4; // if(nw > 255) nw = 255; // if(nw < 0) nw = 0; if(abs(nw - mat[t][idx]) > 1e-4)fg = 1; mat[t][idx] = nw; } } } printf("["); for(int i = 0; i < leny; i++){ printf("["); for(int j = 0; j < lenx; j++){ int b = fix(int(mat[0][i*lenx+j])); int g = fix(int(mat[1][i*lenx+j])); int r = fix(int(mat[2][i*lenx+j])); printf("[%d,%d,%d]", b, g, r); if(j != lenx - 1)printf(", "); } printf("]"); if(i != leny - 1)printf(",\\n"); else printf("\\n"); } printf("]"); }
Python处理

def getans(a, b): global dst cnt = 0 cnt2 = 0 centerx, centery = a, b print(a,b) res = open("result.txt","r") w = res.read() res.close() w = eval(w) for i in range(centery, centery + leny): for j in range(centerx, centerx + lenx): if not isout(Y+i-centery, X+j-centerx): dst[i][j] = w[i-centery][j-centerx] cnt2 += 1 else: cnt += 1 print(cnt,cnt2) cv_show(\'ret\',dst) # print(cnt, cnt2) getans(centerx,centery)
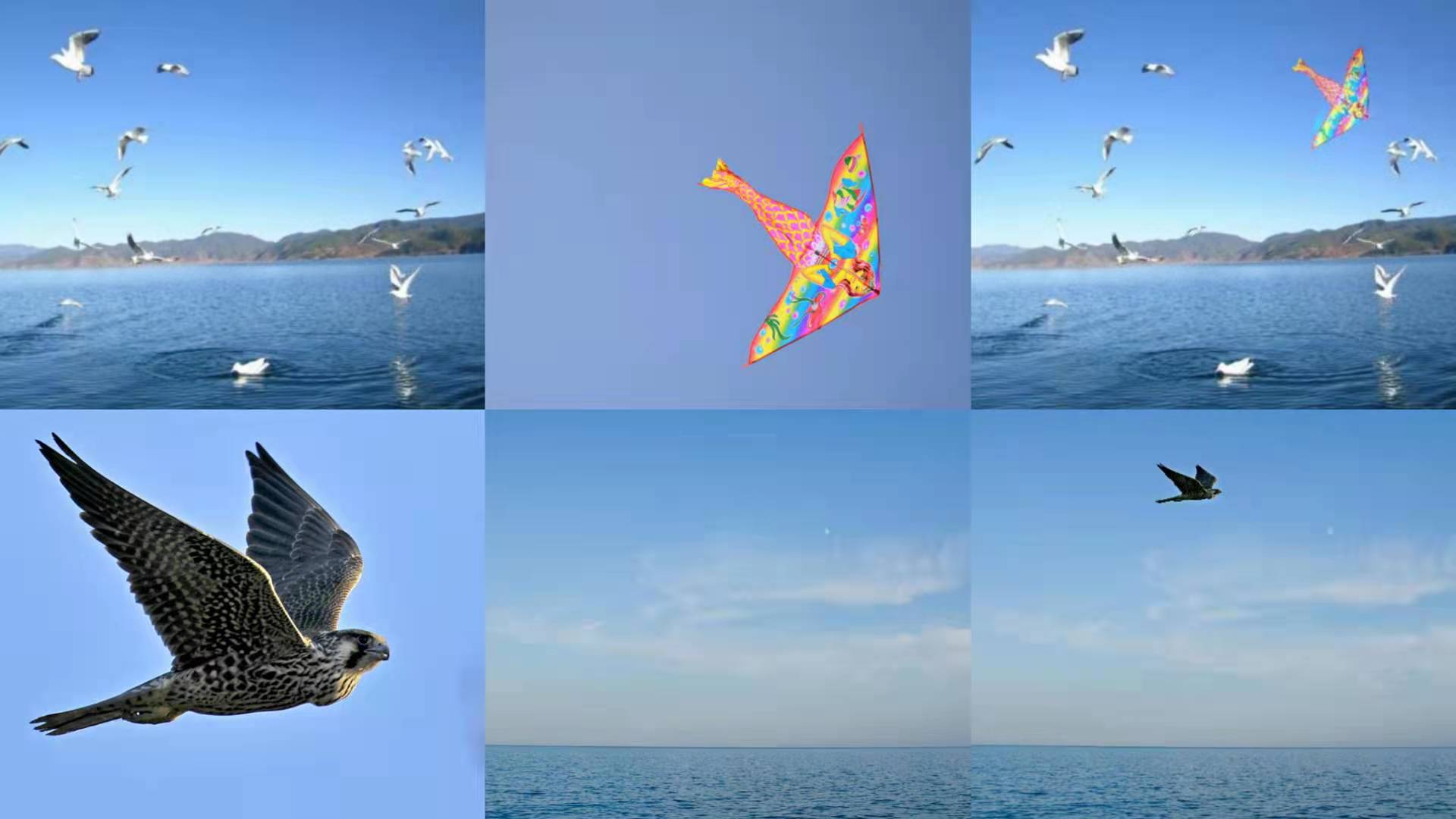
成品:

以上是关于CG——Possion Image Editing的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
