Servlet使用详解
Posted 咖啡加糖
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Servlet使用详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.Servlet 技术
什么是 Servlet
1、Servlet 是 JavaEE 规范之一。规范就是接口
2、Servlet 就 JavaWeb 三大组件之一。三大组件分别是:Servlet 程序、Filter 过滤器、Listener 监听器。
3、Servlet 是运行在服务器上的一个 java 小程序,它可以接收客户端发送过来的请求,并响应数据给客户端。
手动实现 Servlet 程序
1.使用idea创建一个新的模块,如下图

2、编写一个类去实现 Servlet 接口
3、实现 service 方法,处理请求,并响应数据
4、到 web.xml 中去配置 servlet 程序的访问地址
Servlet 程序的示例代码:
package com.atguigu.servlet; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.io.IOException; public class HelloServlet implements Servlet { public HelloServlet() { System.out.println("1 构造器方法"); } @Override public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException { System.out.println("2 init初始化方法"); // 1、可以获取Servlet程序的别名servlet-name的值 System.out.println("HelloServlet程序的别名是:" + servletConfig.getServletName()); // 2、获取初始化参数init-param System.out.println("初始化参数username的值是;" + servletConfig.getInitParameter("username")); System.out.println("初始化参数url的值是;" + servletConfig.getInitParameter("url")); // 3、获取ServletContext对象 System.out.println(servletConfig.getServletContext()); } @Override public ServletConfig getServletConfig() { return null; } /** * service方法是专门用来处理请求和响应的 * @param servletRequest * @param servletResponse * @throws ServletException * @throws IOException */ @Override public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("3 service === Hello Servlet 被访问了"); // 类型转换(因为它有getMethod()方法) HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; // 获取请求的方式 String method = httpServletRequest.getMethod(); if ("GET".equals(method)) { doGet(); } else if ("POST".equals(method)) { doPost(); } } /** * 做get请求的操作 */ public void doGet(){ System.out.println("get请求"); System.out.println("get请求"); } /** * 做post请求的操作 */ public void doPost(){ System.out.println("post请求"); System.out.println("post请求"); } @Override public String getServletInfo() { return null; } @Override public void destroy() { System.out.println("4 . destroy销毁方法"); } }
web.xml 中的配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <!-- servlet 标签给 Tomcat 配置 Servlet 程序 --> <servlet> <!--servlet-name 标签 Servlet 程序起一个别名(一般是类名) --> <servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name> <!--servlet-class 是 Servlet 程序的全类名--> <servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <!--servlet-mapping 标签给 servlet 程序配置访问地址--> <servlet-mapping> <!--servlet-name 标签的作用是告诉服务器,我当前配置的地址给哪个 Servlet 程序使用--> <servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name> <!--url-pattern 标签配置访问地址 <br/> / 斜杠在服务器解析的时候,表示地址为:http://ip:port/工程路径 <br/> /hello 表示地址为:http://ip:port/工程路径/hello <br/> --> <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
访问结果


Servlet 的生命周期
1、执行 Servlet 构造器方法
2、执行 init 初始化方法
3、执行 service 方法
4、执行 destroy 销毁方法
第一、二步,是在第一次访问的时候创建 Servlet 程序会调用。第三步,每次访问都会调用。第四步,在 web 工程停止的时候调用。
通过继承 HttpServlet 实现 Servlet 程序
一般在实际项目开发中,都是使用继承 HttpServlet 类的方式去实现 Servlet 程序。
1、编写一个类去继承 HttpServlet 类
2、根据业务需要重写 doGet 或 doPost 方法
3、到 web.xml 中的配置 Servlet 程序的访问地址
Servlet 类的代码:
package com.atguigu.servlet; import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; public class HelloServlet2 extends HttpServlet { /** * doGet()在get请求的时候调用 * @param req * @param resp * @throws ServletException * @throws IOException */ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("HelloServlet2 的doGet方法"); } /** * doPost()在post请求的时候调用 * @param req * @param resp * @throws ServletException * @throws IOException */ @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("HelloServlet2 的doPost方法"); } }
web.xml 中的配置:
<servlet> <servlet-name>HelloServlet2</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.HelloServlet2</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>HelloServlet2</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello2</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
使用 IDEA 创建 Servlet 程序
菜单:new ->Servlet 程序

配置 Servlet 的信息:

Servlet 类的继承体系
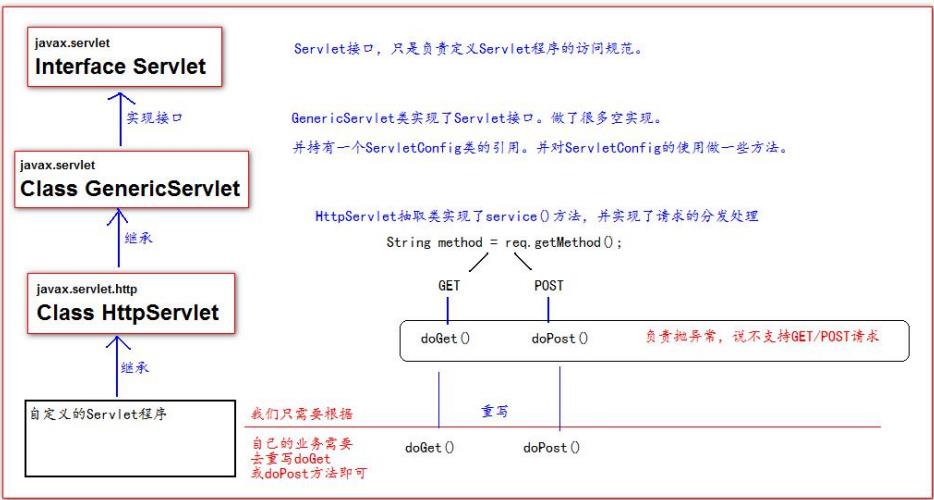
二.ServletConfig 类
ServletConfig 类从类名上来看,就知道是 Servlet 程序的配置信息类。
Servlet 程序和 ServletConfig 对象都是由 Tomcat 负责创建,我们负责使用。
Servlet 程序默认是第一次访问的时候创建,ServletConfig 是每个 Servlet 程序创建时,就创建一个对应的 ServletConfig 对象。
ServletConfig 类的三大作用
1、可以获取 Servlet 程序的别名 servlet-name 的值
2、获取初始化参数 init-param
3、获取 ServletContext 对象
web.xml 中的配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>HelloServlet2</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.HelloServlet2</servlet-class> <!--init-param是初始化参数--> <init-param> <!--是参数名--> <param-name>username</param-name> <!--是参数值--> <param-value>root2</param-value> </init-param> <!--init-param是初始化参数--> <init-param> <!--是参数名--> <param-name>url</param-name> <!--是参数值--> <param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test2</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>HelloServlet2</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello2</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
Servlet 中的代码:
package com.atguigu.servlet; import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; public class HelloServlet2 extends HttpServlet { @Override public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { super.init(config); System.out.println("重写了init初始化方法,做了一些工作"); } /** * doGet()在get请求的时候调用 * @param req * @param resp * @throws ServletException * @throws IOException */ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("HelloServlet2 的doGet方法"); // 也可以使用. ServletConfig servletConfig = getServletConfig(); System.out.println(servletConfig); //1、可以获取Servlet程序的别名servlet-name的值 System.out.println("HelloServlet程序的别名是111:" + servletConfig.getServletName()); //2、获取初始化参数init-param System.out.println("初始化参数username的值是;" + servletConfig.getInitParameter("username")); System.out.println("初始化参数url的值是;" + servletConfig.getInitParameter("url")); } /** * doPost()在post请求的时候调用 * @param req * @param resp * @throws ServletException * @throws IOException */ @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("HelloServlet2 的doPost方法"); } }
访问http://localhost:8080/servlet01/hello2的结果:

三.ServletContext 类
什么是 ServletContext?
1、ServletContext 是一个接口,它表示 Servlet 上下文对象
2、一个 web 工程,只有一个 ServletContext 对象实例。
3、ServletContext 对象是一个域对象。
4、ServletContext 是在 web 工程部署启动的时候创建。在 web 工程停止的时候销毁。
什么是域对象?
域对象,是可以像 Map 一样存取数据的对象,叫域对象。
这里的域指的是存取数据的操作范围,整个 web 工程。
ServletContext 类的四个作用
1、获取 web.xml 中配置的上下文参数 context-param
2、获取当前的工程路径,格式: /工程路径
3、获取工程部署后在服务器硬盘上的绝对路径
4、像 Map 一样存取数据
ServletContext 演示代码:
package com.atguigu.servlet; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; public class ContextServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //1、获取web.xml中配置的上下文参数context-param //ServletContext context = getServletConfig().getServletContext(); ServletContext context = getServletContext(); String username = context.getInitParameter("username"); System.out.println("context-param参数username的值是:" + username); System.out.println("context-param参数password的值是:" + context.getInitParameter("password")); //2、获取当前的工程路径,格式: /工程路径 System.out.println( "当前工程路径:" + context.getContextPath() ); //3、获取工程部署后在服务器硬盘上的绝对路径 /** * / 斜杠被服务器解析地址为:http://ip:port/工程名/ 映射到IDEA代码的web目录<br/> */ System.out.println("工程部署的路径是:" + context.getRealPath("/")); System.out.println("工程下css目录的绝对路径是:" + context.getRealPath("/css")); System.out.println("工程下imgs目录1.jpg的绝对路径是:" + context.getRealPath("/imgs/1.jpg")); // 4.获取ServletContext对象 System.out.println(context); System.out.println("保存之前: Context1 获取 key1的值是:"+ context.getAttribute("key1")); context.setAttribute("key1", "value1"); System.out.println("Context1 中获取域数据key1的值是:"+ context.getAttribute("key1")); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <!--context-param是上下文参数(它属于整个web工程)--> <context-param> <param-name>username</param-name> <param-value>context</param-value> </context-param> <!--context-param是上下文参数(它属于整个web工程)--> <context-param> <param-name>password</param-name> <param-value>root</param-value> </context-param> <servlet> <servlet-name>ContextServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.ContextServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>ContextServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/contextServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
访问http://localhost:8080/servlet01/contextServlet的运行结果:

四.HTTP 协议
什么是 HTTP 协议
协议是指双方,或多方,相互约定好,大家都需要遵守的规则,叫协议。
所谓 HTTP 协议,就是指,客户端和服务器之间通信时,发送的数据,需要遵守的规则,叫 HTTP 协议。
HTTP 协议中的数据又叫报文。
请求的 HTTP 协议格式
客户端给服务器发送数据叫请求。服务器给客户端回传数据叫响应。请求又分为 GET 请求,和 POST 请求两种。
GET 请求:
1、请求行
(1) 请求的方式 GET
(2) 请求的资源路径[+?+请求参数]
(3) 请求的协议的版本号 HTTP/1.1
2、请求头
key : value 组成 不同的键值对,表示不同的含义。

POST 请求:
1、请求行
(1) 请求的方式 POST
(2) 请求的资源路径[+?+请求参数]
(3) 请求的协议的版本号 HTTP/1.1
2、请求头
(1) key : value 不同的请求头,有不同的含义
空行
3、请求体 ===>>> 就是发送给服务器的数据

常用请求头的说明:
Accept: 表示客户端可以接收的数据类型
Accpet-Languege: 表示客户端可以接收的语言类型
User-Agent: 表示客户端浏览器的信息
Host: 表示请求时的服务器 ip 和端口号
哪些是 GET 请求,哪些是 POST 请求:
GET 请求有哪些:
1、form 标签 method=get
2、a 标签
3、link 标签引入 css
4、Script 标签引入 js 文件
5、img 标签引入图片
6、iframe 引入 html 页面
7、在浏览器地址栏中输入地址后敲回车
POST 请求有哪些:
8、form 标签 method=post
响应的 HTTP 协议格式
1、响应行
(1) 响应的协议和版本号
(2) 响应状态码
(3) 响应状态描述符
2、响应头
(1) key : value 不同的响应头,有其不同含义
空行
3、响应体 ---->>> 就是回传给客户端的数据

常用的响应码说明
200 表示请求成功
302 表示请求重定向(明天讲)
404 表示请求服务器已经收到了,但是你要的数据不存在(请求地址错误)
500 表示服务器已经收到请求,但是服务器内部错误(代码错误)
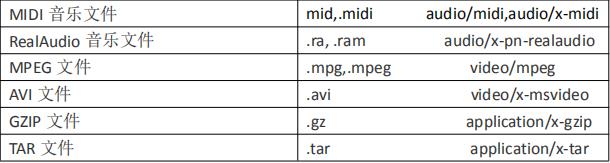
MIME 类型说明
MIME 是 HTTP 协议中数据类型。
MIME 的英文全称是"Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions" 多功能 Internet 邮件扩充服务。MIME 类型的格式是“大类型/小
类型”,并与某一种文件的扩展名相对应。
常见的 MIME 类型:

谷歌浏览器如何查看 HTTP 协议:

火狐浏览器如何查看 HTTP 协议:

五.HttpServletRequest 类
HttpServletRequest 类有什么作用
每次只要有请求进入 Tomcat 服务器,Tomcat 服务器就会把请求过来的 HTTP 协议信息解析好封装到 Request 对象中。然后传递到 service 方法(doGet 和 doPost)中给我们使用。我们可以通过 HttpServletRequest 对象,获取到所有请求的信息。
HttpServletRequest 类的常用方法
| getRequestURI() | 获取请求的资源路径 |
| getRequestURL() | 获取请求的统一资源定位符(绝对路径) |
| getRemoteHost() | 获取客户端的 ip 地址 |
| getHeader() | 获取请求头 |
| getParameter() | 获取请求的参数 |
| getParameterValues() | 获取请求的参数(多个值的时候使用) |
| getMethod() | 获取请求的方式 GET 或 POST |
| setAttribute(key, value) | 设置域数据 |
| getAttribute(key) | 获取域数据 |
| getRequestDispatcher() | 获取请求转发对象 |
常用 API 示例代码:
package com.atguigu.servlet; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Arrays; public class RequestAPIServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("-------------doGet------------"); //1.getRequestURI() 获取请求的资源路径 System.out.println("URI => " + req.getRequestURI()); //2.getRequestURL() 获取请求的统一资源定位符(绝对路径) System.out.println("URL => " + req.getRequestURL()); //3.getRemoteHost() 获取客户端的ip地址 /** * 在IDEA中,使用localhost访问时,得到的客户端 ip 地址是 ===>>> 127.0.0.1<br/> * 在IDEA中,使用127.0.0.1访问时,得到的客户端 ip 地址是 ===>>> 127.0.0.1<br/> * 在IDEA中,使用 真实ip 访问时,得到的客户端 ip 地址是 ===>>> 真实的客户端 ip 地址<br/> */ System.out.println("客户端 ip地址 => " + req.getRemoteHost()); //4.getHeader() 获取请求头 System.out.println("请求头User-Agent ==>> " + req.getHeader("User-Agent")); //5.getMethod() 获取请求的方式GET或POST System.out.println( "请求的方式 ==>> " + req.getMethod() ); // 获取请求参数 String username = req.getParameter("username"); //1 先以iso8859-1进行编码 //2 再以utf-8进行解码 username = new String(username.getBytes("iso-8859-1"), "UTF-8"); String password = req.getParameter("password"); String[] hobby = req.getParameterValues("hobby"); System.out.println("用户名:" + username); System.out.println("密码:" + password); System.out.println("兴趣爱好:" + Arrays.asList(hobby)); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // 设置请求体的字符集为UTF-8,从而解决post请求的中文乱码问题 // 也要在获取请求参数之前调用才有效 req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); System.out.println("-------------doPost------------"); // 获取请求参数 String username = req.getParameter("username"); String password = req.getParameter("password"); String[] hobby = req.getParameterValues("hobby"); System.out.println("用户名:" + username); System.out.println("密码:" + password); System.out.println("兴趣爱好:" + Arrays.asList(hobby)); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>RequestAPIServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.RequestAPIServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>RequestAPIServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/requestAPIServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh_CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <form action="http://localhost:8080/servlet01/requestAPIServlet" method="get"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br/> 密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br/> 兴趣爱好:<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="cpp">C++ <input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="java">Java <input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="js">javascript<br/> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
执行点击下面的提交按钮得到结果如下:
