Prism框架中的DelagateCommand(下)
Posted Hello 寻梦者!
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Prism框架中的DelagateCommand(下)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
背景
在上篇中我们主要分析了2个问题并带着一个疑问来到了这里,我们先来看上一篇中提到的那个场景就是我们如果我们在View中定义了两个Button,代表上一页和下一页总共只有两页的数据,一般情况是我们希望这两个按钮有这样的功能如果当前页是第一页,那么我们界面上的上一页的Button就会灰掉,只有我们点击了下一页的按钮之后这个上一页的按钮就又恢复成可以点击的状态,同样如果当前页面是第二页那么下一页的按钮也应该灰掉知道界面上面点击了上一页的按钮,这个时候我们该如何实现,其实通过命令绑定的方法很容易实现就是后台在定义这个DelegateCommand传入的两个参数,其中第二个参数就能够控制当前命令是否可以响应,进而影响绑定的Button的显示状态,如果这样还不够,我通过下面的一个例子来进行说明。
internal class TestViewModel
{
private const int _startPage = 1;
private const int _totalPage = 2;
public TestViewModel()
{
SwitchPrevious = new DelegateCommand(DoSwithPrevious, CanSwitchPrevious);
SwitchNext = new DelegateCommand(DoSwitchNext, CanSwitchNext);
}
private int _currentPage = _startPage;
public int CurrentPage
{
get { return _currentPage; }
private set { _currentPage = value; }
}
private ICommand _switchPrevious;
public ICommand SwitchPrevious
{
get { return _switchPrevious; }
set { _switchPrevious = value; }
}
private bool CanSwitchPrevious()
{
return CurrentPage == _totalPage;
}
private void DoSwithPrevious()
{
CurrentPage--;
}
private ICommand _switchNext;
public ICommand SwitchNext
{
get { return _switchNext; }
set { _switchNext = value; }
}
private bool CanSwitchNext()
{
return CurrentPage == _startPage;
}
private void DoSwitchNext()
{
CurrentPage++;
}
}
上面的例子足够简单,我们发现每次点击按钮的时候我们会改变CurrentPage的值,但同时这个值又会反过来影响CanSwitchNext和CanSwitchPrevious的返回值,这两个返回值又会进而影响到两个定义的Command,这两个Command的变化又会影响到两个Button的状态,但是现在的问题是如果我们只是简单继承一下ICommand接口中定义的CanExecuteChanged事件的时候,我们会发现当我们点击界面上一页和下一页的时候并没有达到我们想要的效果,我们发现只有在构造这两个Command的构造函数中才会Raise这个CanExecuteChanged事件,其它情况下是不会触发这个事件,所以内部的绑定机制是不会更新Button的状态的,所以Prism中在DelegateCommand定义了这两个方法用来监控每个属性的变化,当这个属性发生变化的时候能够自动的触发CanExecuteChanged事件从而使整个界面得到反馈,就像上面列举这个这个例子我们在创建DelegateCommand的时候还需要监控这个TestViewModel中的CurrentPage这个属性(而不是字段)的状态,从而达到通知这个DelegateCommand的目的。
过程分析
有了上面的过程了解你应该很清楚为什么要加这两个方法,下面就将整个过程进行分析。
1 ObservesCanExecute方法
[Fact]
public void NonGenericDelegateCommandShouldObserveCanExecute()
{
bool canExecuteChangedRaised = false;
ICommand command = new DelegateCommand(() => { }).ObservesCanExecute(() => BoolProperty);
command.CanExecuteChanged += delegate { canExecuteChangedRaised = true; };
Assert.False(canExecuteChangedRaised);
Assert.False(command.CanExecute(null));
BoolProperty = true;
Assert.True(canExecuteChangedRaised);
Assert.True(command.CanExecute(null));
}
我们来看看上面的这个单元测试程序,这里我们使用了使用ObservesCanExecute来监控了一个BoolProperty这个属性,在BoolProperty赋值前,canExecuteChangedRaised和command.CanExecute都是false,但是当我们赋值true之后就能监控到当前属性值变化,然后触发command的CanExecuteChanged事件,然后改变两个值,结果我们知道了我们再来看看ObservesCanExecute这个方法的实现。
/// <summary>
/// Observes a property that is used to determine if this command can execute, and if it implements INotifyPropertyChanged it will automatically call DelegateCommandBase.RaiseCanExecuteChanged on property changed notifications.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="canExecuteExpression">The property expression. Example: ObservesCanExecute(() => PropertyName).</param>
/// <returns>The current instance of DelegateCommand</returns>
public DelegateCommand ObservesCanExecute(Expression<Func<bool>> canExecuteExpression)
{
_canExecuteMethod = canExecuteExpression.Compile();
ObservesPropertyInternal(canExecuteExpression);
return this;
}
这里需要注意我们上面的测试用例中并没有为DelegateCommand创建第二个参数,所以初始化完成后_canExecuteMethod是空的,当我们执行上面的方法之后会将当前的Expression(() => BoolProperty)解析成方法传给_canExecuteMethod方法,后面就是调用ObservesPropertyInternal方法并将当前的表达式传入到方法的内部,我们再来看ObservesPropertyInternal的内部实现。
/// <summary>
/// Observes a property that implements INotifyPropertyChanged, and automatically calls DelegateCommandBase.RaiseCanExecuteChanged on property changed notifications.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">The object type containing the property specified in the expression.</typeparam>
/// <param name="propertyExpression">The property expression. Example: ObservesProperty(() => PropertyName).</param>
protected internal void ObservesPropertyInternal<T>(Expression<Func<T>> propertyExpression)
{
if (_observedPropertiesExpressions.Contains(propertyExpression.ToString()))
{
throw new ArgumentException($"{propertyExpression.ToString()} is already being observed.",
nameof(propertyExpression));
}
else
{
_observedPropertiesExpressions.Add(propertyExpression.ToString());
PropertyObserver.Observes(propertyExpression, RaiseCanExecuteChanged);
}
}
这个方法最重要的一点就是调用PropertyObserver.Observes的时候将当前的DelegateCommand中的RaiseCanExecuteChanged作为委托传递到后面PropertyObserver中去了,这样在属性变化的时候就能够调用当前RaiseCanExecuteChanged委托,从而最终触发CanExecuteChanged事件从而达到目的,到了这里是不是整个过程就豁然开朗了。
2 PropertyObserver类的实现
这个部分其实是一个非常独立的过程就是监控通过拉姆达表达式传入的属性的变化,然后触发这个传入的RaiseCanExecuteChanged委托,当然这个监控属性变化肯定要考虑到各种属性的类型有简单和复杂的,我们来一步步分析。
/// <summary>
/// Provide a way to observe property changes of INotifyPropertyChanged objects and invokes a
/// custom action when the PropertyChanged event is fired.
/// </summary>
internal class PropertyObserver
{
private readonly Action _action;
private PropertyObserver(Expression propertyExpression, Action action)
{
_action = action;
SubscribeListeners(propertyExpression);
}
private void SubscribeListeners(Expression propertyExpression)
{
var propNameStack = new Stack<PropertyInfo>();
while (propertyExpression is MemberExpression temp) // Gets the root of the property chain.
{
propertyExpression = temp.Expression;
propNameStack.Push(temp.Member as PropertyInfo); // Records the member info as property info
}
if (!(propertyExpression is ConstantExpression constantExpression))
throw new NotSupportedException("Operation not supported for the given expression type. " +
"Only MemberExpression and ConstantExpression are currently supported.");
var propObserverNodeRoot = new PropertyObserverNode(propNameStack.Pop(), _action);
PropertyObserverNode previousNode = propObserverNodeRoot;
foreach (var propName in propNameStack) // Create a node chain that corresponds to the property chain.
{
var currentNode = new PropertyObserverNode(propName, _action);
previousNode.Next = currentNode;
previousNode = currentNode;
}
object propOwnerObject = constantExpression.Value;
if (!(propOwnerObject is INotifyPropertyChanged inpcObject))
throw new InvalidOperationException("Trying to subscribe PropertyChanged listener in object that " +
$"owns \'{propObserverNodeRoot.PropertyInfo.Name}\' property, but the object does not implements INotifyPropertyChanged.");
propObserverNodeRoot.SubscribeListenerFor(inpcObject);
}
/// <summary>
/// Observes a property that implements INotifyPropertyChanged, and automatically calls a custom action on
/// property changed notifications. The given expression must be in this form: "() => Prop.NestedProp.PropToObserve".
/// </summary>
/// <param name="propertyExpression">Expression representing property to be observed. Ex.: "() => Prop.NestedProp.PropToObserve".</param>
/// <param name="action">Action to be invoked when PropertyChanged event occurs.</param>
internal static PropertyObserver Observes<T>(Expression<Func<T>> propertyExpression, Action action)
{
return new PropertyObserver(propertyExpression.Body, action);
}
}
这个方法内部重要的就是SubscribeListeners这个方法了,这个会根据当前的传入表达式类型来决定创建PropertyObserverNode,下面以一个复杂的属性为例,这个其实在前面的一篇文章中也提到过,我们还是来仔细看看下面的单元测试。
[Fact]
public void NonGenericDelegateCommandShouldObserveOneComplexProperty()
{
ComplexProperty = new ComplexType()
{
InnerComplexProperty = new ComplexType()
};
bool canExecuteChangedRaised = false;
var command = new DelegateCommand(() => { })
.ObservesProperty(() => ComplexProperty.InnerComplexProperty.IntProperty);
command.CanExecuteChanged += delegate { canExecuteChangedRaised = true; };
ComplexProperty.InnerComplexProperty.IntProperty = 10;
Assert.True(canExecuteChangedRaised);
}
我们来看看这个ComplexType的定义。
public class ComplexType : TestPurposeBindableBase
{
private int _intProperty;
public int IntProperty
{
get { return _intProperty; }
set { SetProperty(ref _intProperty, value); }
}
private ComplexType _innerComplexProperty;
public ComplexType InnerComplexProperty
{
get { return _innerComplexProperty; }
set { SetProperty(ref _innerComplexProperty, value); }
}
}
所以这个属性实际上有三层,我们需要监控的是最里面一层的IntProperty,我们来看看通过SubscribeListeners方法解析表达式后创建的Root PropertyObserverNode是什么样的,然后通过这个结果来分析代码。
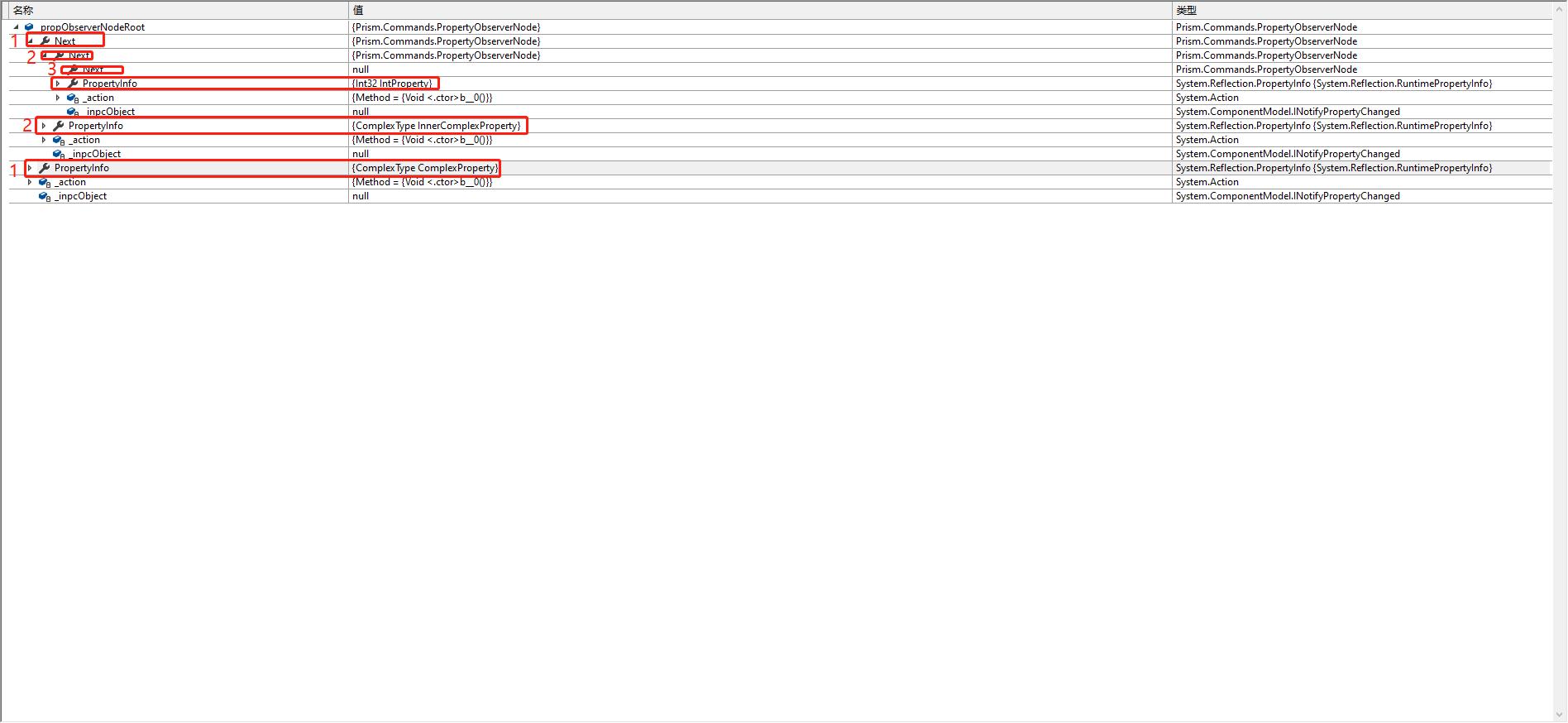
图一 解析PropertyObserverNode过程
通过上面的图你可以看到总共通过传入的表达式解析三层属性,创建三个PropertyObserverNode,并通过其内部的Next属性相互关联在一起。最后一个重要的过程就是创建完这些PropertyObserverNode内部的SubscribeListenerFor方法完成最终的一步。
/// <summary>
/// Represents each node of nested properties expression and takes care of
/// subscribing/unsubscribing INotifyPropertyChanged.PropertyChanged listeners on it.
/// </summary>
internal class PropertyObserverNode
{
private readonly Action _action;
private INotifyPropertyChanged _inpcObject;
public PropertyInfo PropertyInfo { get; }
public PropertyObserverNode Next { get; set; }
public PropertyObserverNode(PropertyInfo propertyInfo, Action action)
{
PropertyInfo = propertyInfo ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(propertyInfo));
_action = () =>
{
action?.Invoke();
if (Next == null) return;
Next.UnsubscribeListener();
GenerateNextNode();
};
}
public void SubscribeListenerFor(INotifyPropertyChanged inpcObject)
{
_inpcObject = inpcObject;
_inpcObject.PropertyChanged += OnPropertyChanged;
if (Next != null) GenerateNextNode();
}
private void GenerateNextNode()
{
var nextProperty = PropertyInfo.GetValue(_inpcObject);
if (nextProperty == null) return;
if (!(nextProperty is INotifyPropertyChanged nextInpcObject))
throw new InvalidOperationException("Trying to subscribe PropertyChanged listener in object that " +
$"owns \'{Next.PropertyInfo.Name}\' property, but the object does not implements INotifyPropertyChanged.");
Next.SubscribeListenerFor(nextInpcObject);
}
private void UnsubscribeListener()
{
if (_inpcObject != null)
_inpcObject.PropertyChanged -= OnPropertyChanged;
Next?.UnsubscribeListener();
}
private void OnPropertyChanged(object sender, PropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (e?.PropertyName == PropertyInfo.Name || string.IsNullOrEmpty(e?.PropertyName))
{
_action?.Invoke();
}
}
}
在这个方法中会监控当前PropertyObserverNode所属的类(继承自INotifyPropertyChanged接口)的PropertyChanged方法,如果其所属的类中刚好变化的属性和当前PropertyObserverNode定义的属性一直时候触发委托完成整个过程,至此整个过程分析完毕,到此整个过程全部完成,非常完美的设计过程。
以上是关于Prism框架中的DelagateCommand(下)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章