Linux&C编程之Linux系统命令“ls -l”的简单实现
Posted Apollon_krj
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux&C编程之Linux系统命令“ls -l”的简单实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、基础知识:
1、获取文件详细信息的函数:
(1)、获取文件信息的函数:
#include<sys/stat.h>
int stat(const char * path,struct stat * buf);/*将path参数(文件或目录)的文件信息写到buf中,buf为传出参数*/(2)、文件信息结构体:
/*用不到的成员被注释掉,只需了解需要的成员即可*/
struct stat{
//dev_t st_dev;/*设备id号*/
//ino_t st_ino;/*i节点号*/
mode_t st_mode;/*权限与文件类型*/
nlink_t st_nlink;/*硬链接数*/
uid_t st_uid;/*用户id*/
ggid_t st_gid;/*所在组id*/
//dev_t st_rdev;/*设备id,对于特殊文件才有*/
off_t st_size;/*大小,较为常用*/
//blksize_t st_blocks;/*blocksize for file system I/O*/
//blkcnt_t st_blksize;/*number of 512B blocks allocated*/
//time_t st_atime;/*最后的访问时间*/
time_t st_mtime;/*最后的修改时间,较为常用*/
//time_t st_ctime;/*最后的状态改变时间*/
}2、在C里表示时间的方式:
①秒差形式,1970年1月1日0时0分0秒的秒数差,得到的类型为time_t;
②结构(man time.h)形式:
struct tm{
int tm_sec; /*Second [0,60].包含闰秒*/
int tm_min; /*Minutes [0,59].*/
int tm_hour; /*Hour [0,23].*/
int tm_mday; /*Day of month [1,31].*/
int tm_mon; /*Month of year [0,11].(January = 0)*/
int tm_year; /*Year Since 1900.*/
int tm_wday; /*Day of week [0,6] (Sunday = 0).*/
int tm_yday; /*Day of year [0,365].包含闰年*/
int tm_isdat; /*Daylight Savings flag*//*夏时制,夏时令(Daylight Saving Time:DST)*/
}计算机大多数情况使用time_t,因为效率高。但是显示时为tm结构形式。localtime()函数可以实现: time_t 到 tm 的转换。time_t的指针做参数,返回值tm的指针。
也可以使用:ctime打印出美式时间显示方式(我们不采用)。
char * time_buf = ctime(&st.st_mtime);
printf("%s",time_buf);3、mode权限与类型判断:
由于mode_t mode;参数中包含的信息不止一个需要根据不同的方式进行提取:
(1)、判断文件类型的宏函数:
The following POSIX macros are defined to check the file type using the st_mode field:
S_ISREG(m) is it a regular file?/*判断是否是普通文件*/
S_ISDIR(m) directory?/*判断是否是目录*/
S_ISCHR(m) character device?/*判断是否是字符设备*/
S_ISBLK(m) block device?/*判断是否是块设备*/
S_ISFIFO(m) FIFO (named pipe)?/*判断是否是管道文件*/
S_ISLNK(m) symbolic link? (Not in POSIX.1-1996.)/*判断使是否是符号链接(软连接)*/
S_ISSOCK(m) socket? (Not in POSIX.1-1996.)/*判断是否是SOCKET文件*/当然也可以采用宏变量的方式,但是我更习惯用宏函数。
(2)、表示文件权限与类型的宏变量:
The following flags are defined for the st_mode field:
/*我们不会用到文件类型的宏变量(与宏函数功能类似)*/
S_IFMT 0170000 bit mask for the file type bit fields
S_IFSOCK 0140000 socket
S_IFLNK 0120000 symbolic link
S_IFREG 0100000 regular file
S_IFBLK 0060000 block device
S_IFDIR 0040000 directory
S_IFCHR 0020000 character device
S_IFIFO 0010000 FIFO
S_ISUID 0004000 set UID bit
S_ISGID 0002000 set-group-ID bit (see below)
S_ISVTX 0001000 sticky bit (see below)
/*我们会用到的文件权限宏变量*/
S_IRWXU 00700 mask for file owner permissions
S_IRUSR 00400 owner has read permission
S_IWUSR 00200 owner has write permission
S_IXUSR 00100 owner has execute permission
S_IRWXG 00070 mask for group permissions
S_IRGRP 00040 group has read permission
S_IWGRP 00020 group has write permission
S_IXGRP 00010 group has execute permission
S_IRWXO 00007 mask for permissions for others (not in group)
S_IROTH 00004 others have read permission
S_IWOTH 00002 others have write permission
S_IXOTH 00001 others have execute permission
4、重要的目录操作函数:
DIR * opendir(const char * name);/*打开一个目录*/
struct dirent * readdir(DIR *);/*读目录,依次返回目录的子项(一次返回一个,读一个目录指针后移一次),到目录尾或出错时返回NULL,出错会设置errno*/目录信息结构体struct dirent:
struct dirent{
ino_t d_ino;//子项的i节点
off_t d_off;//节点的偏移量
unsigned short d_reclen;//长度
unsigned char d_type;//子项类型(常用)
char d_name[256];//子文件名(常用)
};其它函数与结构体这里就不再介绍,有不懂得可以去查man手册。
二、功能测试结果:
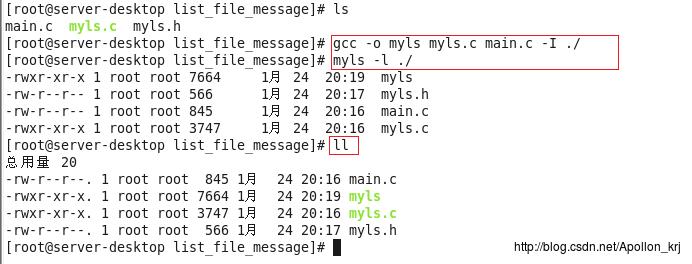
结果除了格式以外(没有排序),基本相同。对于最上面一层占空间大小没有写,有兴趣的可以自己加上该功能。并且代码是笔者一次性写完,并没有过多的进行测试,对于潜在BUG没有排除,可简化的代码也没有过多处理。
三、“myls -l ”功能实现代码:
1、myls.h:
/*filename:myls.h*/
#ifndef _MYLS_H_
#define _MYLS_H_
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<pwd.h>
#include<grp.h>
#include<time.h>
void error_print(const char *);
void mylist_dir(const char *);
void list_message(const char *,const struct stat *);
void file_type(const struct stat *);
void file_power(const struct stat *);
void file_power_char(mode_t,mode_t,const char);
void id_to_string(const struct stat *);
void timet_to_tm(const struct stat *);
#endif2、myls.c:
/*filename:myls.c*/
#include<myls.h>
void error_print(const char * ptr)/*errno错误处理*/
{
perror(ptr);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
void mylist_dir(const char * pathname) /*读取目录中的文件*/
{
DIR * ret_opendir = opendir(pathname);/*打开传递的目录pathname*/
if(ret_opendir == NULL) /*判断错误并处理*/
error_print("opendir");
int ret_chdir = chdir(pathname);/*先change dir到需要list的目录中*/
if(ret_chdir == -1) /*判断错误并处理*/
error_print("chdir");
struct dirent * ret_readdir = NULL;/*定义接收readdir函数返回的结构体变量*/
while(ret_readdir = readdir(ret_opendir)){/*判断读取是否到目录尾*/
char * filename = ret_readdir->d_name;
struct stat get_message = {};
int ret_stat = stat(filename,&get_message);/*用stat函数读取filenmae文件的信息,并将结果写到get_message结构体中*/
if(ret_stat == -1)/*stat函数不出错则进行信息输出*/
error("stat %s",filename);
else if(strcmp(filename,".") && strcmp(filename,".."))/*ls -l 不会输出当期那目录与上一级目录*/
list_message(filename,&get_message);
}
}
void list_message(const char * filename,const struct stat * get_message)/*处理读取到的文件*/
{
file_type(get_message);/*判断并打印文件类型*/
file_power(get_message);/*判断并打印文件权限*/
printf("%d ",get_message->st_nlink);/*打印硬链接数*/
id_to_string(get_message);/*用户id与组id转换成用户名与组名并打印*/
printf("%d\\t",get_message->st_size);/*打印所占空间文件大小*/
timet_to_tm(get_message);/*将GMT时间的秒数转换成标准时间格式输出*/
printf("%s\\n",filename);/*输出文件名*/
}
void file_type(const struct stat * get_message)
{
mode_t mode = (*get_message).st_mode;
if(S_ISREG(mode))
printf("-");/*普通文件*/
else if(S_ISDIR(mode))
printf("d");/*目录文件*/
#if 0
else if(S_ISCHR(mode))
printf("c");/*字符设备文件*/
else if(S_ISBLK(mode))
printf("b");/*块设备文件*/
else if(S_ISFIFO(mode))
printf("p");/*管道文件*/
else if(S_ISLNK(mode))
printf("l");/*链接文件*/
else if(S_ISSOCK(mode))
printf("s");/*socket文件*/
#endif
}
void file_power(const struct stat * get_message)
{
mode_t mode = (*get_message).st_mode & 07777;/*取后四位*/
file_power_char(mode,S_IRUSR,'r');/*判断user有无读权限*/
file_power_char(mode,S_IWUSR,'w');/*判断user有无写权限*/
file_power_char(mode,S_IXUSR,'x');/*判断user有无可执行权限*/
file_power_char(mode,S_IRGRP,'r');/*判断group有无读权限*/
file_power_char(mode,S_IWGRP,'w');/*判断group有无写权限*/
file_power_char(mode,S_IXGRP,'x');/*判断group有无可执行权限*/
file_power_char(mode,S_IROTH,'r');/*判断other有无读权限*/
file_power_char(mode,S_IWOTH,'w');/*判断other有无写权限*/
file_power_char(mode,S_IXOTH,'x');/*判断other有无可执行权限*/
printf(" ");
}
void file_power_char(mode_t mode,mode_t type,const char ch)
{
if((mode & type) == type)
printf("%c",ch);
else
printf("-");
}
void id_to_string(const struct stat * get_message)
{
struct passwd * pwd;/*根据用户id获取用户名*/
pwd = getpwuid(get_message->st_uid);
printf("%s ",pwd->pw_name);
struct group * grp;/*根据组id获取组名*/
grp = getgrgid(get_message->st_gid);
printf("%s ",grp->gr_name);
}
void timet_to_tm(const struct stat * get_message)
{
struct tm * chtm = localtime(&(get_message->st_mtime));
if(chtm == NULL){
printf("localtime is error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else
printf("%d月 %d ",chtm->tm_mon+1,chtm->tm_mday);/*tm_mon属于[0,11]*/
if(chtm->tm_hour < 10)/*0~9的数要写成0X格式*/
printf("0");/*先打印0*/
printf("%d:",chtm->tm_hour);/*再打印X*/
if(chtm->tm_min < 10)
printf("0");
printf("%d ",chtm->tm_min);
}3、main.c:
/**
*filename:main.c
* 函数功能:ls -l pathname
* 时间:2017/1/24--19时05分57秒
* 局限性:不能模糊匹配,不能使用正则,且只能判断普通文件(-)与目录(d)
* */
#include<myls.h>
int main(char argc,char ** argv)
{
if(argc != 3){
printf("Too few parameter!");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if((argc == 3) && !(strcmp(argv[1],"-l"))){/*判断是myls -l argv[2]格式*/
struct stat get_message = {};
int ret_stat = stat(argv[2],&get_message);
if(ret_stat == -1)
error_print("stat %s",argv[2]);
if(S_ISDIR(get_message.st_mode))/*判断是否是目录,是目录则进一步处理目录中个文件*/
mylist_dir(argv[2]);
else/*不是目录则直接处理普通文件*/
list_message(argv[2],&get_message); /*文件stat信息输出函数*/
}
else{/*不符合格式则结束进程*/
printf("error in main!\\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return 0;
}以上是关于Linux&C编程之Linux系统命令“ls -l”的简单实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章