C实现Linux中copy功能
Posted 王清河
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C实现Linux中copy功能相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
/* mycp.c */ #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<string.h> #include<dirent.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #include<getopt.h> #include<stdbool.h> #define BUFFERSIZE 1024 #define COPYMORE 0644 /*用于处理从目录文件复制到目录文件的操作,传入的参数应该是目录路径*/ int copyD2D(char *src, char *dest); /*用于处理从文件复制到文件的操作,输入的参数是文件名*/ int copyF2F(char *src, char *dest); /*判断filename是否是目录名*/ bool isdir(char *filename); /*字符串反转*/ char *strrev(char *str); /*main函数用于接收命令行传进来的参数,并判断是否符合规范。 然后根据不同的情况调用不同的子函数。*/ int main(int argc, char **argv) { /* 标记-r/-R选项,该选项代表递归复制文件夹 标记-l选项,-l选项代表创建硬链接 标记-s选项,-s选项代表创建符号链接 */ bool opt_r = false; bool opt_l = false; bool opt_s = false; /* 用于记录源文件 用于记录目标文件 记录选项的字符 */ char *src = NULL; char *dest = NULL; char c; /*循环检测命令行参数中的选项*/ while((c = getopt(argc, argv, "rRls")) != -1) { switch(c) { case \'R\': case \'r\': opt_r = true; break; case \'l\': opt_l = true; break; case \'s\': opt_s = true; break; } } /*命令行参数中应该有两个文件名。若没有,则输出提示,并终止程序*/ if (optind >= argc - 1) { printf("lack operator \\n"); exit(1); } /*从命令行参数中读取源文件和目标文件名*/ src = argv[optind]; dest = argv[optind + 1]; /*根据opt_l选项的真假,做相应操作。 若为真,则创建硬链接,使用link函数。*/ if (opt_l) { if (isdir(src)) { printf("dirent canot build hard linker\\n"); exit(1); } /*link 函数的返回值:若成功,则返回0;若出错,返回-1*/ if ((link(src, dest)) == 0) { return 0; } else { printf("create hard linker error\\n"); exit(1); } } /*根据opt_s选项的真假,做相应操作。 若为真,则创建符号链接,使用symlink函数。*/ if (opt_s) { if(isdir(src)) { printf("dirent cannot create soft linker\\n"); exit(1); } if (symlink(src, dest) == 0) { return 0; } else { printf("create soft linker error\\n"); exit(1); } } if (!isdir(src)) { /*若源文件src不是目录,直接调用copyF2F函数。*/ if ((copyF2F(src, dest)) == 0) { return 0; } else { printf("copy file error\\n"); exit(1); } } else if(isdir(src)) { if (!isdir(dest)) { printf("Canot copy the dirent to a file\\n"); exit(1); } /*若源文件src和目标文件dest都是目录,直接调用copyD2D函数。*/ else if(isdir(dest) && opt_r) { if (copyD2D(src, dest) != 0) { printf("copy catalog error\\n"); exit(1); } else { return 0; } } else { printf("copy catalog need option -r\\n"); exit(1); } } else { printf("the operation is illegal\\n"); exit(1); } return 0; } /*该函数用于处理复制目录的情况*/ int copyD2D(char *src_dir, char *dest_dir) { DIR *dp = NULL; struct dirent *dirp; char tempDest[256]; char tempSrc[256]; strcpy(tempDest, dest_dir); strcpy(tempSrc, src_dir); /*使用opendir函数打开src_dir目录,获得指向该目录名字的指针*/ if ((dp = opendir(src_dir)) == NULL) { return 1; } else { while((dirp = readdir(dp))) { struct stat file_stat; if (!isdir(dirp->d_name)) { /*将dirent结构中的d_name成员变量链接到上级目录字符串*/ strcat(tempDest, dirp->d_name); strcat(tempSrc, dirp->d_name); /*此处转换为文件复制函数的方式处理目录复制*/ copyF2F(tempSrc, tempDest); /*通过字符串拷贝函数,将tempDest和tempSrc还原为上级的目录名*/ strcpy(tempDest, dest_dir); strcpy(tempSrc, src_dir); } } closedir(dp); } return 0; } /*该函数通过read,write等基本的系统函数,完成文件的拷贝工作*/ int copyF2F(char *src_file, char *dest_file) { int in_fd, out_fd, n_chars; char buf[BUFFERSIZE]; /*如果目标文件是一个目录,那么默认是在该目录下建立一个与源文件同名的文件*/ if (isdir(dest_file)) { char c; char temp[10] = {0}; char *r_temp; int n = strlen(src_file); int m = 0; /*读取源文件的最后一级文件名作为目标文件名*/ while((c = src_file[n-1]) != \'/\') { temp[m] = c; m++; n--; } r_temp = strrev(temp); strcat(dest_file, r_temp); } /* 以可读模式打开源文件 */ if ((in_fd = open(src_file, O_RDONLY)) == -1) { printf("%s file read error!\\n", src_file); return 1; } /* O_WRONLY代表以读写的方式打开目标文件,O_CREAT选项代表若文件不存在则创建, COPYMORE = 0644,文件所有者可读可写,其他可读 */ if ((out_fd = open(dest_file, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, COPYMORE)) == -1) { return 1; } /* 通过read和write系统调用实现文件的复制 */ while ((n_chars = read(in_fd, buf, BUFFERSIZE)) > 0) { if (write(out_fd, buf, n_chars) != n_chars) { printf("%s file write error!\\n", src_file); return 1; } if (n_chars == -1) { printf("%s file read error!\\n", src_file); return 1; } } if (close(in_fd) == -1 || close(out_fd) == -1) { printf("close file error\\n"); return 1; } return 0; } /*判断filename是否为目录文件*/ bool isdir(char *filename) { struct stat fileInfo; if (stat(filename, &fileInfo) >= 0) { if (S_ISDIR(fileInfo.st_mode)) { return true; } else { return false; } } } char *strrev(char *str) { int i = strlen(str) - 1, j = 0; char ch; while(i > j) { ch = str[i]; str[i] = str[j]; str[j] = ch; i--; j++; } return str; }
运行结果:
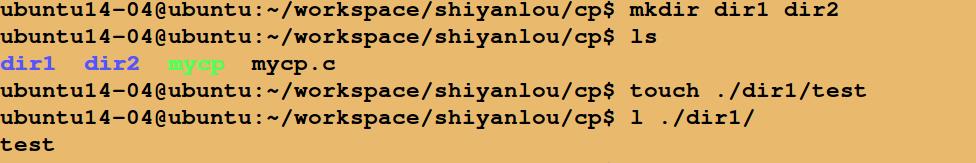
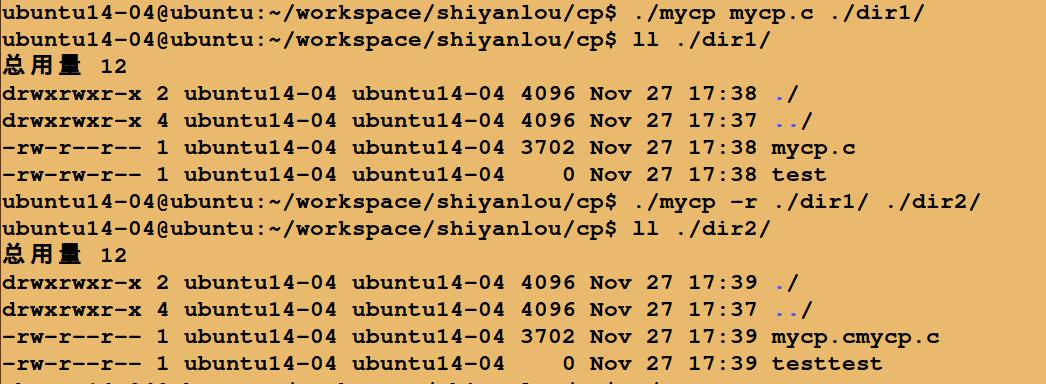
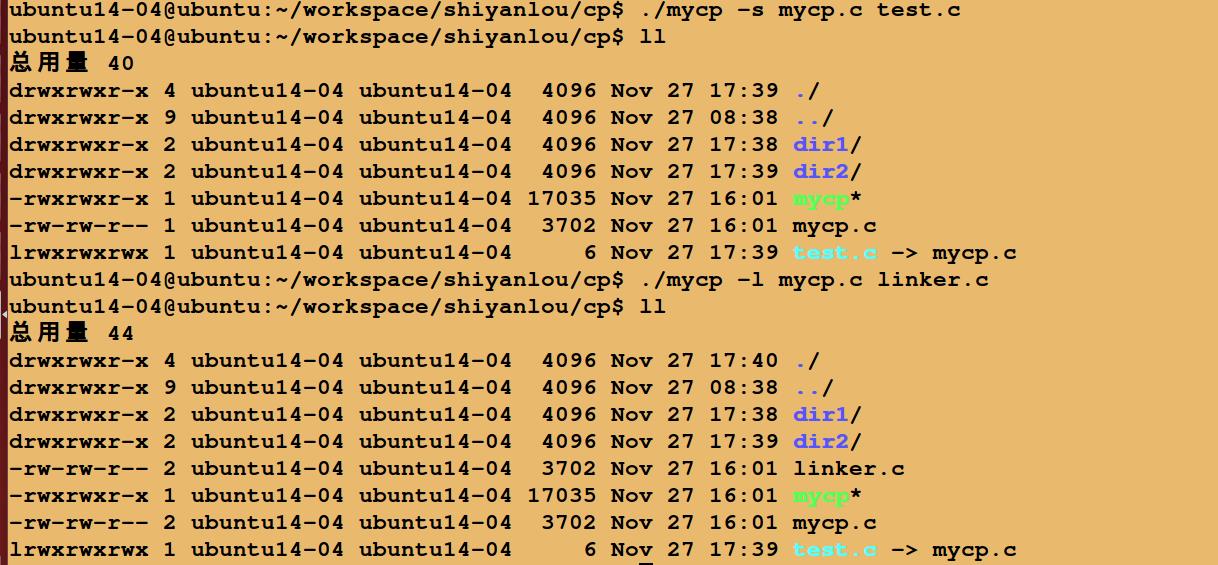
以上是关于C实现Linux中copy功能的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章