leetcode刷题
Posted 知是行之始,行是知之成
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了leetcode刷题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、数组
三数之和
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
例如, 给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
满足要求的三元组集合为:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum
class Solution(object):
def threeSum(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
def double_pointer_search(left, right, first_num, nums, result):
while left < right:
if 0 < left < right and nums[left] == nums[left - 1] or first_num + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0:
left += 1
if left < right < len(nums)-1 and nums[right] == nums[right + 1] or first_num + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0:
right -= 1
else:
result.append([first_num, nums[left], nums[right]])
left += 1
right -= 1
result = []
if len(nums) < 3:
return result
nums.sort()
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n - 2):
if nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + nums[i + 2] > 0:
break
if nums[i] + nums[-1] + nums[-2] < 0:
continue
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]:
continue
double_pointer_search(i + 1, n - 1, nums[i], nums, result)
return result
2、排序
最大数
给定一组非负整数,重新排列它们的顺序使之组成一个最大的整数。
示例 1:
输入: [10,2]
输出: 210
示例 2:
输入: [3,30,34,5,9]
输出: 9534330
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/largest-number
from functools import cmp_to_key
class Solution(object):
def largestNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: str
"""
def new_sort(num1, num2):
if num1 + num2 > num2 + num1:
return -1
elif num1 + num2 < num2 + num1:
return 1
return 0
result = "".join(sorted(list(map(lambda num: str(num), nums)), key=cmp_to_key(lambda x, y: new_sort(x, y))))
while result.startswith("0") and len(result) > 1:
result = result[1:]
return result
3、多维数组
区间列表的交集
给定两个由一些闭区间组成的列表,每个区间列表都是成对不相交的,并且已经排序。
返回这两个区间列表的交集。
(形式上,闭区间 [a, b](其中 a <= b)表示实数 x 的集合,而 a <= x <= b。两个闭区间的交集是一组实数,要么为空集,要么为闭区间。例如,[1, 3] 和 [2, 4] 的交集为 [2, 3]。)
示例:
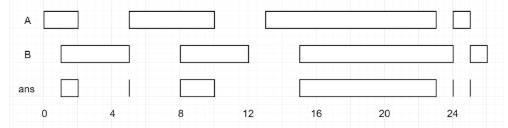
输入:A = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], B = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
输出:[[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
注意:输入和所需的输出都是区间对象组成的列表,而不是数组或列表。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/interval-list-intersections
class Solution(object):
def intervalIntersection(self, A, B):
"""
:type A: List[List[int]]
:type B: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
result = []
i, j = 0, 0
while i < len(A) and j < len(B):
left, right = max(A[i][0], B[j][0]), min(A[i][1], B[j][1])
if left <= right:
result.append([left, right])
if A[i][1] < B[j][1]:
i += 1
else:
j += 1
return result
4、特殊矩阵
01 矩阵
给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的矩阵,找出每个元素到最近的 0 的距离。
两个相邻元素间的距离为 1 。
示例 1:
输入:
0 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 0
输出:
0 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 0
示例 2:
输入:
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 1 1
输出:
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 2 1
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/01-matrix
class Solution(object):
def updateMatrix(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
def bfs(i, j):
que, distance, visited = [(i, j)], 0, set()
while que:
distance += 1
new_que = []
for new_point in que:
for i, j in [(0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (1, 0)]:
new_i, new_j = new_point[0] + i, new_point[1] + j
if 0 <= new_i < len(matrix) and 0 <= new_j < len(matrix[0]) and (new_i,new_j) not in visited:
if matrix[new_i][new_j] != 0:
new_que.append((new_i, new_j))
visited.add((new_i, new_j))
else:
return distance
que = new_que
return distance
new_matrix = [[0 for i in range(len(matrix[0]))] for j in range(len(matrix))]
for row_index, row in enumerate(matrix):
for col_index, point in enumerate(row):
if matrix[row_index][col_index] != 0:
new_matrix[row_index][col_index] = bfs(row_index, col_index)
return new_matrix
5、查找
在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
class Solution(object):
def searchRange(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not nums:
return [-1, -1]
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while left + 1 < right:
mid = left + (right - left) / 2
if nums[mid] == target:
i = mid - 1
while i >= 0 and nums[i] == target:
i -= 1
j = mid + 1
while j < len(nums) and nums[j] == target:
j += 1
return [i + 1, j - 1]
if nums[mid] > target:
right = mid
elif nums[mid] < target:
left = mid
if nums[left] == target and nums[right] == target:
return [left, right]
if nums[right] == target:
return [right, right]
if nums[left] == target:
return [left, left]
return [-1, -1]
6、字符串
单词拆分 II
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词列表的字典 wordDict,在字符串中增加空格来构建一个句子,使得句子中所有的单词都在词典中。返回所有这些可能的句子。
说明:
分隔时可以重复使用字典中的单词。
你可以假设字典中没有重复的单词。
示例 1:
输入:
s = "catsanddog"
wordDict = ["cat", "cats", "and", "sand", "dog"]
输出:
[
"cats and dog",
"cat sand dog"
]
示例 2:
输入:
s = "pineapplepenapple"
wordDict = ["apple", "pen", "applepen", "pine", "pineapple"]
输出:
[
"pine apple pen apple",
"pineapple pen apple",
"pine applepen apple"
]
解释: 注意你可以重复使用字典中的单词。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-break-ii
class Solution(object):
def wordBreak(self, s, wordDict):
"""
:type s: str
:type wordDict: List[str]
:rtype: List[str]
"""
def dfs(s, word_dict, sets):
if s in sets:
return sets[s]
if len(s) == 0:
return []
partitions = []
if s in word_dict:
partitions.append(s)
for i in range(1, len(s)):
word = s[:i]
if word not in word_dict:
continue
sub_partitions = dfs(s[i:], word_dict, sets)
partitions.extend(map(lambda sub_partition: word + " " + sub_partition, sub_partitions))
# for sub_partition in sub_partitions:
# partitions.append(word + " " + sub_partition)
sets[s] = partitions
return partitions
return dfs(s, set(wordDict), {})
7、最长子串
最长回文子串
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词列表的字典 wordDict,在字符串中增加空格来构建一个句子,使得句子中所有的单词都在词典中。返回所有这些可能的句子。
说明:
分隔时可以重复使用字典中的单词。
你可以假设字典中没有重复的单词。
示例 1:
输入:
s = "catsanddog"
wordDict = ["cat", "cats", "and", "sand", "dog"]
输出:
[
"cats and dog",
"cat sand dog"
]
示例 2:
输入:
s = "pineapplepenapple"
wordDict = ["apple", "pen", "applepen", "pine", "pineapple"]
输出:
[
"pine apple pen apple",
"pineapple pen apple",
"pine applepen apple"
]
解释: 注意你可以重复使用字典中的单词。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-break-ii
class Solution(object):
def longestPalindrome(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
if not s:
return ""
n, start, longest = len(s), 0, 1
f = [[False]*n for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n-1, -1, -1):
f[i][i] = True
for j in range(i + 1, n):
f[i][j] = s[i] == s[j] and (j - i < 2 or f[i+1][j-1])
if f[i][j] and longest < j - i + 1:
longest = j - i + 1
start = i
return s[start:start + longest]
8、链表
旋转链表
给定一个链表,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
输出: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
输出: 2->0->1->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 2->0->1->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 1->2->0->NULL
向右旋转 3 步: 0->1->2->NULL
向右旋转 4 步: 2->0->1->NULL
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-list
class Solution(object):
def rotateRight(self, head, k):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type k: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head:
return head
cur_node = head
size = self.calculate_size(cur_node)
k = k % size
if k == 0:
return head
cur_node = head
new_head = self.get_new_head(cur_node, k, size)
cur_node = new_head
self.attach_two_linked_list(cur_node, head)
return new_head
def attach_two_linked_list(self, cur_node, head):
while cur_node.next:
cur_node = cur_node.next
cur_node.next = head
def get_new_head(self, cur_node, k, size):
len = 1
while len < size - k:
len += 1
cur_node = cur_node.next
new_head = cur_node.next
cur_node.next = None
return new_head
def calculate_size(self, node):
size = 0
while node != None:
size += 1
node = node.next
return size
以上是关于leetcode刷题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章