题目内容
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
Example:
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
return [0, 1].
分析过程
- 题目归类:
数组,遍历。 - 边界分析:
- 空值分析
当nums 为null时应该返回null。 - 循环边界分析
循环变量不能超过nums.length-1;
- 空值分析
- 方法分析:
- 数据结构分析
数据的遍历,tmp = target - 当前值,向后查找是否有和tmp相同的数据。返回下标。
提前定义一个int[] indice数组用来保存下标。 - 状态机
无 - 状态转移方程
无 - 最优解
无
- 数据结构分析
- 测试用例构建
[].
[1,2,3,4].
代码实现
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] indice = new int[2];
if(nums.length==0)
return indice;
for(int i = 0; i<nums.length;i++){
int tmp = target - nums[i];
for(int j = i+1; j<nums.length;j++){
if(tmp == nums[j]){
indice[0]=i;
indice[1]=j;
}
}
}
return indice;
}
}
效率提高
采用HashMap每次添加值,key为具体值,value 为 indice。
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer,Integer> hashTable = new HashMap<>();
int [] indice = new int[2];
if(nums == null)
return indice;
for(int i = 0; i<nums.length;i++){
int tmp = target - nums[i];
if(hashTable.containsKey(tmp)){
indice[0] = i;
indice[1] = hashTable.get(tmp);
break;
}else{
hashTable.put(nums[i],i);
}
}
return indice;
}
}
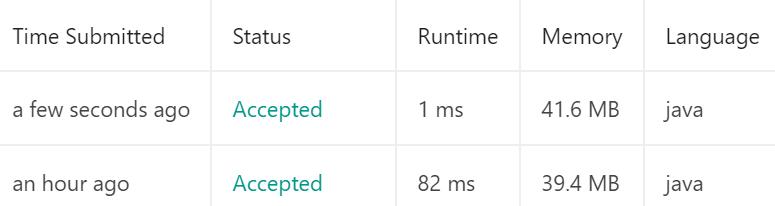
可以看到时间复杂度提高了40倍。
拓展问题
- 出现多种情况满足相加和等于target,且可以用自己自身两次,求所有的indice 保存到List
中。 - 3Sum
- 4Sum
- Two Sum II - Input array is sorted
- Two Sum III - Data structure design
- Subarray Sum Equals K
- Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
- Two Sum Less Than K