CF 999E Reachability from the Capital
Posted chinesepikaync
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了CF 999E Reachability from the Capital相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题意:
题目描述
在 Berland 有 (n) 座城市和 (m) 条道路,每条道路连接着一对城市。
Berland 的道路都是单向的
为了能让首都能够到达所有的城市,最少需要新修建多少新道路?
新道路也是单向的
输入格式
输入的第一行包含三个整数 (n,m) 和 (s) ((1le n le 5000,0le m le 5000 , 1le s le n)) ——城市数,道路数和首都所在城市的标号。 城市的标号为 (1) ~ (n)
接下来 (m) 行每行包含一条道路连接着一对城市 (u_i,v_i) ((1le u_i,v_ile n,u_i
e v_i))
对于每对城市 (u,v),从 (u) 到 (v) 最多只能有一条道路。 允许在一对城市之间建造相反方向的道路(即从 (u) 到 (v) 和从 (v) 到 (u) )。
输出格式
输出一个整数——使从首都可以到达所有城市所需的最少新修建道路数。如果从 (s) 已经可以到达所有城市,则输出 (0)。
说明/提示
样例 1:
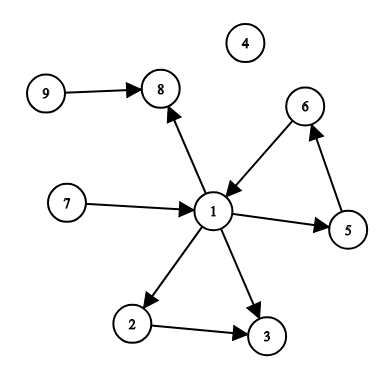
例如,您可以添加道路 ( 6, 4 ) , ( 7 , 9 ) , ( 1 , 7 ),以使从 (s = 1) 可到达所有城市。
样例 2:
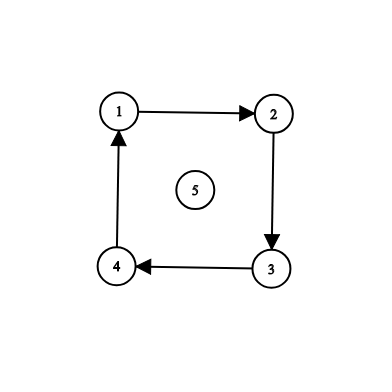
在此样例中,您可以添加道路(5 , 1),(5 , 2),(5 , 3),(5 , 4)中的任何一条,以使可从 (s = 5) 到达所有城市。
如果一个强连通分量内的一个点能被 (s) 到达,那么强连通分量里所有点都被 (s) 到达,所以先缩点
缩完点建完新图,我们看到的基本上就只有这么三种情况的连通块
A -> B -> D E -> F -> G H -> I -> J
^ |
| V
C K我们假设这三种情况都不能被 (s) 到达
第一种多个入度为0的点,必须要从 (s) 往 (A) 和 (C) 各连一条边才行
第二种一条链,(s) 往 (E) 连边就行
第三种只有一个入度为 0 的点,那么 (s) 往 (H) 连边就行
那么这里就发现了规律了,对于一个不能被 (s) 所到达的连通块,其所要新加边的数量为其中入度为 0 点的数量
那么就在新图中先从 (s) 所在新图中的点开始 dfs 一遍标记掉能到达的点
然后答案就是新图中没被标记过并且入度为 0 的点数
// This code writed by chtholly_micromaker(MicroMaker)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define reg register
using namespace std;
const int MaxN=5050;
struct Edge
{
int nxt,to;
}E[MaxN<<2],nE[MaxN<<2];
template <class t> inline void read(t &s)
{
s=0;
reg int f=1;
reg char c=getchar();
while(!isdigit(c))
{
if(c=='-')
f=-1;
c=getchar();
}
while(isdigit(c))
s=(s<<3)+(s<<1)+(c^48),c=getchar();
s*=f;
return;
}
int hd[MaxN],nhd[MaxN],en,nen,n,m;
int dfn[MaxN],low[MaxN],dep;
int col[MaxN],scc;
int sta[MaxN],top;
bool instack[MaxN];
bool vis[MaxN];
int deg[MaxN];
inline void adde(int u,int v)
{
++en;
E[en]=(Edge){hd[u],v};
hd[u]=en;
return;
}
inline void nadde(int u,int v)
{
++nen;
nE[nen]=(Edge){nhd[u],v};
nhd[u]=nen;
return;
}
inline void tarjan(int u)
{
dfn[u]=low[u]=++dep;
sta[top++]=u;
instack[u]=true;
for(int i=hd[u];~i;i=E[i].nxt)
{
reg int v=E[i].to;
if(!dfn[v])
{
tarjan(v);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
}
else if(instack[v])
low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
if(dfn[u]==low[u])
{
++scc;
do
{
--top;
instack[sta[top]]=false;
col[sta[top]]=scc;
}while(sta[top]!=u);
}
return;
}
inline void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
vis[u]=true;
for(int i=nhd[u];~i;i=nE[i].nxt)
{
reg int v=nE[i].to;
if(v==fa||vis[v])
continue;
dfs(v,u);
}
return;
}
signed main(void)
{
memset(hd,-1,sizeof hd);
memset(nhd,-1,sizeof nhd);
int s;
reg int u,v;
cin>>n>>m>>s;
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i)
{
read(u);read(v);
adde(u,v);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
if(!dfn[i])
tarjan(i);
for(int u=1;u<=n;++u)
for(int i=hd[u];~i;i=E[i].nxt)
{
reg int v=E[i].to;
if(col[u]==col[v])
continue;
nadde(col[u],col[v]);
++deg[col[v]];
}
dfs(col[s],0);
reg int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=scc;++i)
if(!vis[i]&&!deg[i])
++ans;
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}以上是关于CF 999E Reachability from the Capital的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章