2020.04.10 线上性能优化以及Linux下NIO/Epoll模型全解--实战
Posted qianbing12300
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2020.04.10 线上性能优化以及Linux下NIO/Epoll模型全解--实战相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.支付宝模拟线上优化实战
2.手写JUC工具与提升tomcat吞吐量
3.网络通信BIO设计与缺陷 -- accept() 和 read()阻塞
4.单线程解决高并发NIO精髓解读
5.OS内核下Epoll与Selete源码解读
第一部分: 性能优化
问题:如何在高并发场景下实现支付宝用户登录页面的信息获取?如用户信息,金额,积分等
浏览器 ---- Spring MVC ---- controller ----- service ---- 用户模块、余额模块、积分模块等
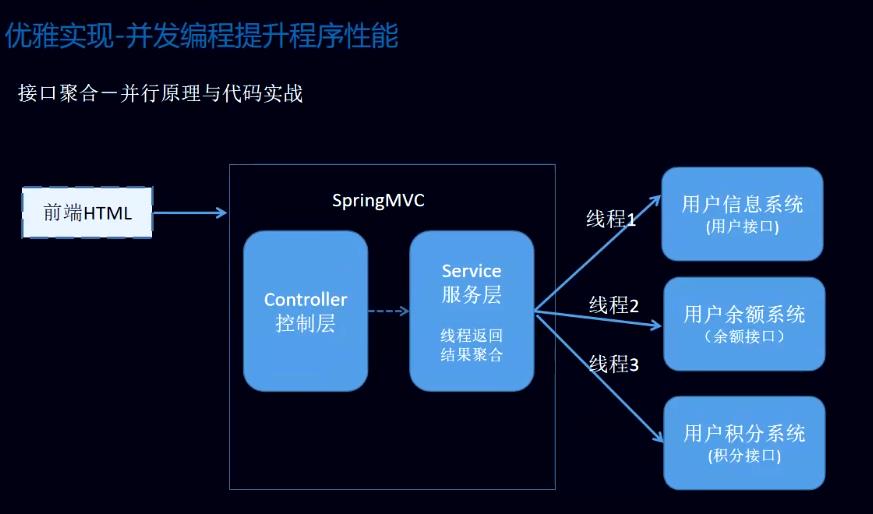
-- 调用多个系统提供的远程接口,返回数据结果(json格式)
第一种做法 传统做法:

@Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Autowired RemoteService remoteService; //做一个调多系统提供的远程接口 @Override public String getUserInfo(String userId) { String v1 = remoteService.getUserInfo(userId); JSONObject userInfo = JSONObject.parseObject(v1); // {1, 2, 3} String v2 = remoteService.getUserMoney(userId); JSONObject moneyInfo = JSONObject.parseObject(v2); // {4, 5, 6} //合并 JSONObject result = new JSONObject(); result.putAll(userInfo); result.putAll(moneyInfo); // result {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} return result.toString(); } }

4秒时间,不可以接受,时间太长
第二种:是不是考虑线程呢?
thread实现runnable接口,但是没有返回结果,也行不通。
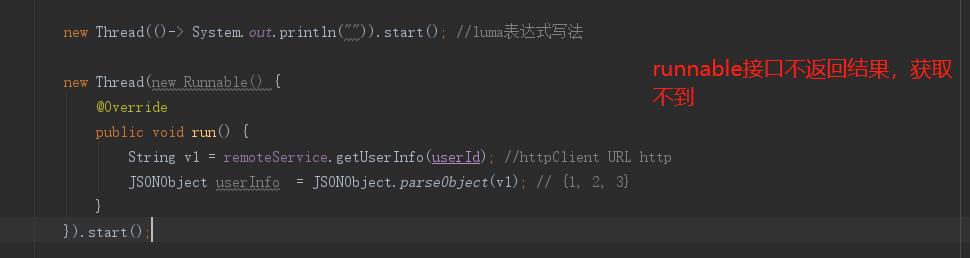
Callable接口有返回值,与 FutureTask连用
FutureTask -----extends------runnable----run(todo??)--->Callable.call()

注意:
FutureTask.get() 获取线程返回结果,阻塞的。
具体代码实现如下:

Callable<JSONObject> userCall = new Callable<JSONObject>() { @Override public JSONObject call() throws Exception { String v1 = remoteService.getUserInfo(userId); //httpClient URL http JSONObject userInfo = JSONObject.parseObject(v1); // {1, 2, 3} return userInfo; } }; Callable<JSONObject> moneyCall = new Callable<JSONObject>() { @Override public JSONObject call() throws Exception { String v1 = remoteService.getUserInfo(userId); //httpClient URL http JSONObject userInfo = JSONObject.parseObject(v1); // {1, 2, 3} return userInfo; } }; FutureTask<JSONObject> userTask = new FutureTask(userCall); FutureTask<JSONObject> moneyTask = new FutureTask(moneyCall); new Thread(userTask).start(); new Thread(moneyTask).start(); //合并 JSONObject result = new JSONObject(); try { result.putAll(userTask.get()); //阻塞 --没有拿到值,就想当与暂时,拿到值后就放行,如 F6 F8等 result.putAll(moneyTask.get()); // result {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("执行消耗时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
 时间花费从4秒瞬间将至2秒,也是不可以接受的。
时间花费从4秒瞬间将至2秒,也是不可以接受的。
第二部分:手写JUC工具与提升tomcat吞吐量
自己手写一个FutureTask实现类:QianBingFutureTask.java

package com.suning.aaa.impl.service.publicclass; import java.util.concurrent.*; public class QianBingFutureTask<V> implements Runnable, Future<V> { Callable<V> callable; V result = null; public QianBingFutureTask(Callable<V> userCall) { this.callable = callable; } @Override public void run() { try { result = callable.call(); //获取返回结果 System.out.println(result); // -----此值一定会打印 if(result != null){ synchronized (this){ this.notifyAll(); //唤醒 } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { return false; } @Override public boolean isCancelled() { return false; } @Override public boolean isDone() { return false; } @Override public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { if (result != null){ return result; } System.out.println(result); // 此值不会打印 //没有取到result值,此时会阻塞 synchronized (this){ this.wait(); //阻塞 } return null; } @Override public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { return null; } }
1. 第一步: 实现同FutureTask接口类 runnable、Future<V>
public class QianBingFutureTask<V> implements Runnable, Future<V>
第二步:构建构造函数,参数Callable
Callable<V> callable;
public QianBingFutureTask(Callable<V> userCall) {
this.callable = callable;
}
第三步:实现run()方法,得到Callable.call()返回结果值并唤醒其他线程
定义一个全局变量 V result= null;
第四步:实现get()方法,取到结果集则返回;拿不到值则阻塞

tomcat吞吐量提升
tomcat7以后 BIO NIO
一个tomcat并发量 500---800个请求。------------ 是谁在执行? tomcat线程
tomcat --- server.xml----port:8080----maxThread=150
即tomcat在启动时候, 初始化150个线程.
controller返回值定义为Callable接口

package com.suning.fiaas.controller.publicClass; import com.suning.fiaas.intf.service.publicClass.UserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; @Controller @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; /** * 获取用户信息(用户接口+余额接口) * @param userId * @return */ @RequestMapping(value = "/getUserInfo", method = RequestMethod.GET ) @ResponseBody public Callable<String> getUserInfo(String userId) { System.out.println("tomcat主线程开始-----" + Thread.currentThread() + "-----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { System.out.println("子线程开始-----" + Thread.currentThread() + "-----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); String result = userService.getUserInfo(userId); System.out.println("子线程开始-----" + Thread.currentThread() + "-----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); return result; } }; System.out.println("tomcat主线程结束-----" + Thread.currentThread() + "-----" + System.currentTimeMillis()); return callable; } }

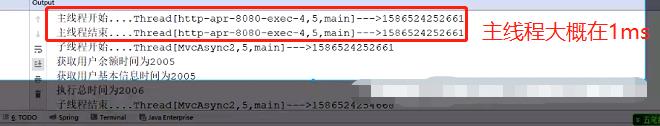
tomcat优化与第一部分优化后2s相比,吞吐量提升2000倍。150个tomcat呢,提升1500*2000倍。
第三部分:BIO和NIO
服务器端代码:
package com.suning.fiaas.controller.publicClass.socket; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; public class SocketServerTest { static byte[] bs = new byte[1024]; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket socketServer = new ServerSocket(6363); while (true){ System.out.println("==========wait connection==========="); Socket socketClinet = socketServer.accept(); //阻塞 System.out.println("==========success connection==========="); System.out.println("==========wait read==========="); socketClinet.getInputStream().read(bs); //阻塞 System.out.println("==========success read==========="); System.out.println(new String(bs)); } } }
客户端代码:
package com.suning.fiaas.controller.publicClass.socket; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.Socket; public class SocketClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 6363); socket.getOutputStream().write("abc".getBytes()); socket.close(); } }
-- 验证serverSocket.accept()是阻塞的场景
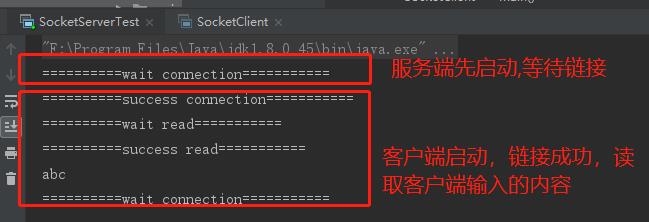
-- 验证socketClinet.getInputStream().read(bs);是阻塞的场景 --- 键盘输入
客户端: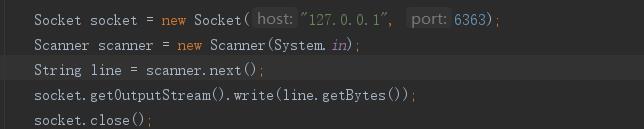

问题: 服务器端 socketServer.accept() 和 socketClinet.getInputStream().read(bs);这两方法是阻塞的 ---> BIO
10000个连接,如果只有1000个活跃,剩下的9000不活跃,也是浪费资源。
BIO: 对每一个请求都开启一个线程链接。线程越多,线程上下文切换越多,资源越浪费。

package com.suning.fiaas.controller.publicClass.socket; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.List; public class BiosocketServer { static byte[] bs = new byte[1024]; static List<Socket> socketList = null; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket socketServer = new ServerSocket(6363); while (true){ //遍历老的链接 for (Socket socket : socketList){ socket.setBlocking(false); int read = socket.getInputStream().read(bs); // 非阻塞 if (read > 0){ System.out.println("read ......" + read ); } } //添加新的链接 socketServer.setBlocking(false); Socket socketClinet = socketServer.accept(); // 非阻塞 if (socketClinet != null){ socketList.add(socketClinet); } System.out.println("socketList length当前链接数目:" + socketList.size()); } } }
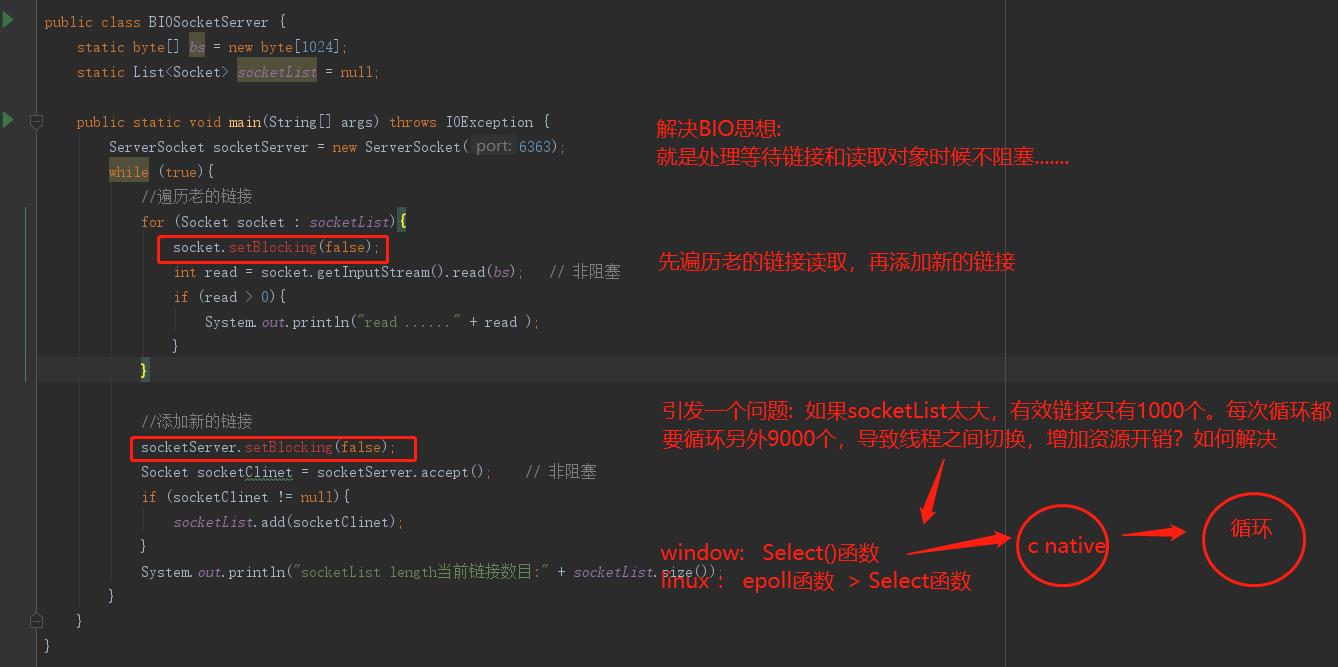
对于上面大量的for循环,java交给jvm处理-----内核。
socketList委托给内核处理,只需要1ms,性能提到大大的提升。for循环不应该出现在java中。
Selete(): java --- native c----select(socketList)----java----循环
第四部分: NIO精髓解读与OS内核下Epoll与Selete源码解读
NIO ---- 利用单线程来处理并发问题 --- epoll模型
NIOSocketServer.java
package com.suning.fiaas.controller.publicClass.socket; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.SocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class NIOSocketServer { static ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512); static List<SocketChannel> socketList = new ArrayList<>(); //NIO设计就是利用单线程来解决并发的问题 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open(); SocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6363) serverSocket.bind(socketAddress); serverSocket.configureBlocking(false); //去除阻塞 while (true){ //遍历老的链接 for (SocketChannel socketChannel : socketList){ int read = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer); if (read > 0){ System.out.println("read ......" + read ); byteBuffer.flip(); byte[] bs = new byte[read]; byteBuffer.get(bs); String content = new String(bs); System.out.println("content ......" + content ); byteBuffer.flip(); } } //添加新的链接 SocketChannel accept = serverSocket.accept(); if (accept != null){ System.out.println("conn succ"); accept.configureBlocking(false); //去除阻塞 socketList.add(accept); System.out.println("socketList length:" + socketList.size()); } } } }
操作系统
window 提供 Selete函数(socketList) ----> 非开源
linux epoll > Selete() ----> epoll效率要比Selete效率更高
-- man 2 select

-- man epoll
-- nc -l localhost 8080
比如 redis、nginx只提供了linux版本的。
linux ---> linux ---->epoll() c语言{
prinf()
}
小工具: 网络调试助手
以上是关于2020.04.10 线上性能优化以及Linux下NIO/Epoll模型全解--实战的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章

