Tomcat8源码学习之九连接器
Posted cac2020
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Tomcat8源码学习之九连接器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Tomcat源码版本:apache-tomcat-8.5.54-src
JDK源码版本:jdk1.8.0_171
Tomcat的Service包含一个容器组件和多个连接器组件,连接器负责接收请求,容器负责处理请求。
一、连接器代码包
org.apache.coyote是Tomcat连接器框架包。Coyote封装了底层的网络通信,为Catalina容器提供统一的接口,使得Catalina容器和具体的请求协议及I/O方式解耦。Coyote将Socket输入转换为自定义的Request对象,交由Catalina容器处理,处理完请求后,Catalina容器通过Coyote提供的自定义Response对象将结果写入输出流。Coyote是相对独立的模块,和Servlet的规范实现没有直接关系,它只负责网络协议和I/O的处理,由它自定义的Request和Response对象也没有实现Servlet规范对应的接口,而是在Catalina容器中进一步被封装成ServletRequest和ServletResponse。

1、Coyote支持的协议
在server.xml中可以看到这样的配置:
<Service name="Catalina">
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443"/>
<Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443"/>
...
<Service/>
这个配置是说一个Service可以配置多个Connector,支持不同的网络协议。由配置可知,Tomcat主要支持两种协议:
(1)HTTP/1.1协议:这是大部分Web应用采用的访问协议,多用于Tomcat单独运行的情况。
(2)AJP协议:用于和Web服务器集成(如Apache HTTP Server),以实现针对静态资源的优化及集群部署。
2、Coyote I/O方案
Tomcat自8.5及9.0版本起,已经移除了对BIO的支持,目前支持的I/O方案有:
NIO:采用Java NIO类库实现。
NIO2:采用JDK 7最新的NIO2类库实现。
APR:采用APR(Apache可移植运行库)实现,是使用C/C++编写的本地库,选择该方案,需要单独安装APR库。
二、coyote重要组件
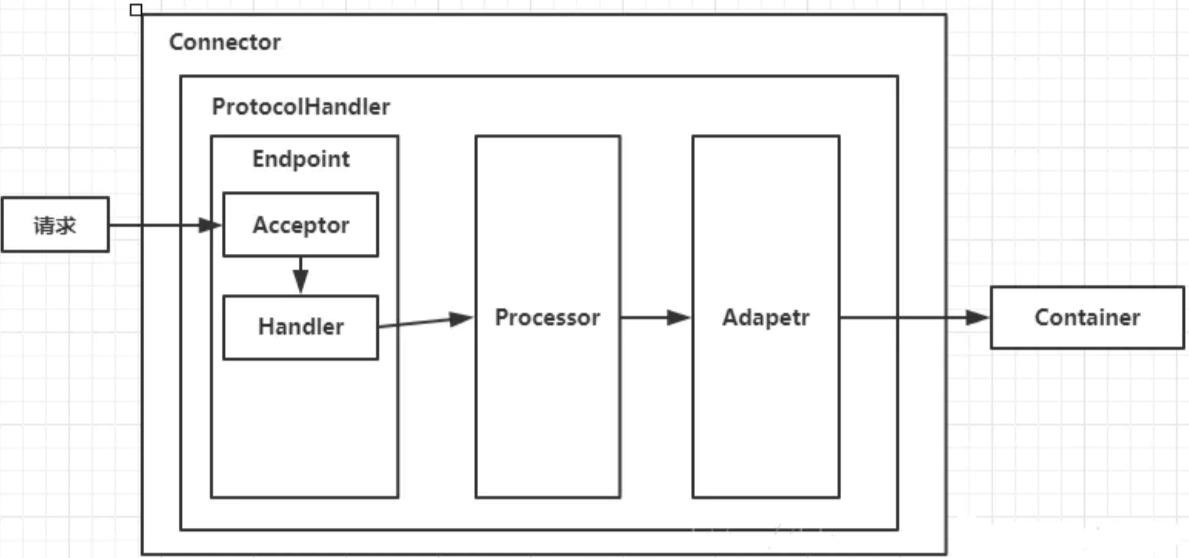
1、Connector 连接器
public class Connector extends LifecycleMBeanBase { ... //协议处理类 protected final ProtocolHandler protocolHandler; //适配器 protected Adapter adapter = null; //默认Http1.1 protected String protocolHandlerClassName = "org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"; //在Digester环节创建 public Connector() { this(null); } public Connector(String protocol) { setProtocol(protocol); ProtocolHandler p = null; try { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(protocolHandlerClassName); p = (ProtocolHandler) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error(sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"), e); } finally { this.protocolHandler = p; } .... } @Override protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); // 初始化adapter adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this); protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter); // Make sure parseBodyMethodsSet has a default if (null == parseBodyMethodsSet) { setParseBodyMethods(getParseBodyMethods()); } .....try { protocolHandler.init();//初始化 } catch (Exception e) { throw new LifecycleException( sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e); } } }
2、ProtocolHandler 协议接口
ProtocolHandler是Tomcat协议接口,连接器使用ProtocolHandler来处理不同协议的请求。比如HTTP/1.1、AJP,实现针对具体协议的处理功能。
在server.xml中设置连接器时,需要指定具体的ProtocolHandler,也可以制定协议的名称,比如HTTP/1.1。
按照协议和I/O有如下继承关系:

3、AbstractEndpoint 抽象类
Endpoint是通信端点,即通信监听的接口,是具体的Socket接收处理类,是对传输层的抽象。由于是处理底层的Socket网络连接,因此Endpoint是用来实现TCP/IP协议的。
Tomcat并没有Endpoint接口,而是一个抽象类AbstractEndpoint,根据I/O方式的不同,提供了如下的实现:
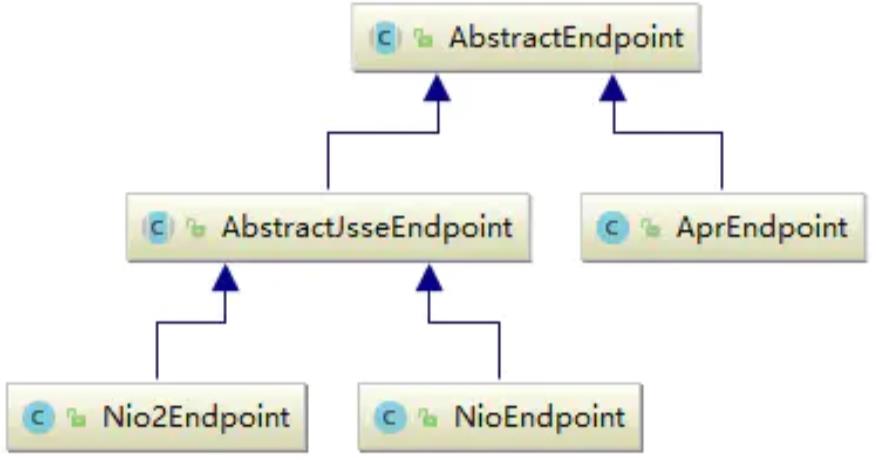
AbstractEndpoint内部有个Handler接口,用于处理接收到的Socket,在内部调用Processor进行处理。Acceptor是Endpoint的一个部件,用于监听请求。
public abstract class AbstractEndpoint<S> { private int acceptCount = 100;//默认处理100个连接 public void setAcceptCount(int acceptCount) { if (acceptCount > 0) this.acceptCount = acceptCount; } public int getAcceptCount() { return acceptCount; } public static interface Handler<S> { public enum SocketState { OPEN, CLOSED, LONG, ASYNC_END, SENDFILE, UPGRADING, UPGRADED, SUSPENDED } //处理接收到的Socket public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> socket,SocketEvent status); public Object getGlobal(); public Set<S> getOpenSockets(); public void release(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper); public void pause(); public void recycle(); } //监听请求 public abstract static class Acceptor implements Runnable { public enum AcceptorState { NEW, RUNNING, PAUSED, ENDED } protected volatile AcceptorState state = AcceptorState.NEW; public final AcceptorState getState() { return state; } private String threadName; protected final void setThreadName(final String threadName) { this.threadName = threadName; } protected final String getThreadName() { return threadName; } } ...... } public class NioEndpoint extends AbstractJsseEndpoint<NioChannel> { //初始化绑定端口方法 默认处理100个链接 @Override public void bind() throws Exception { if (!getUseInheritedChannel()) { serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open(); socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket()); InetSocketAddress addr = (getAddress()!=null?new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(),getPort()):new InetSocketAddress(getPort())); serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount());//默认100 } else { // Retrieve the channel provided by the OS Channel ic = System.inheritedChannel(); if (ic instanceof ServerSocketChannel) { serverSock = (ServerSocketChannel) ic; } if (serverSock == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("endpoint.init.bind.inherited")); } } ...... selectorPool.open(); } ...... } protected static class ConnectionHandler<S> implements AbstractEndpoint.Handler<S> { @Override public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> wrapper, SocketEvent status) { ...... Processor processor = connections.get(socket); ...... do { state = processor.process(wrapper, status); if (state == SocketState.UPGRADING) { // Get the HTTP upgrade handler UpgradeToken upgradeToken = processor.getUpgradeToken(); // Retrieve leftover input ByteBuffer leftOverInput = processor.getLeftoverInput(); if (upgradeToken == null) { // Assume direct HTTP/2 connection UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = getProtocol().getUpgradeProtocol("h2c"); if (upgradeProtocol != null) { processor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter()); wrapper.unRead(leftOverInput); // Associate with the processor with the connection connections.put(socket, processor); } else { if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug(sm.getString( "abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail", "h2c")); } return SocketState.CLOSED; } } else { HttpUpgradeHandler httpUpgradeHandler = upgradeToken.getHttpUpgradeHandler(); // Release the Http11 processor to be re-used release(processor); // Create the upgrade processor processor = getProtocol().createUpgradeProcessor(wrapper, upgradeToken); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.upgradeCreate", processor, wrapper)); } wrapper.unRead(leftOverInput); wrapper.setUpgraded(true); connections.put(socket, processor); if (upgradeToken.getInstanceManager() == null) { httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor); } else { ClassLoader oldCL = upgradeToken.getContextBind().bind(false, null); try { httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor); } finally { upgradeToken.getContextBind().unbind(false, oldCL); } } } } } while ( state == SocketState.UPGRADING); ...... } } protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor { @Override public void run() { int errorDelay = 0; while (running) { while (paused && running) { state = AcceptorState.PAUSED; try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } if (!running) { break; } state = AcceptorState.RUNNING; try { countUpOrAwaitConnection(); SocketChannel socket = null; try { //接收socket请求 socket = serverSock.accept(); } catch (IOException ioe) { countDownConnection(); if (running) { errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay); throw ioe; } else { break; } } errorDelay = 0; if (running && !paused) { if (!setSocketOptions(socket)) { closeSocket(socket); } } else { closeSocket(socket); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t); } } state = AcceptorState.ENDED; } private void closeSocket(SocketChannel socket) { countDownConnection(); try { socket.socket().close(); } catch (IOException ioe) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.close"), ioe); } } try { socket.close(); } catch (IOException ioe) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.close"), ioe); } } } }
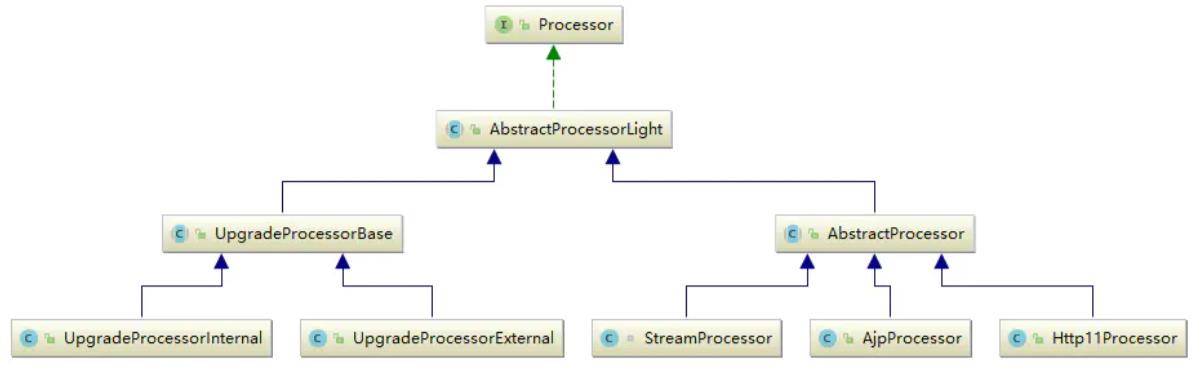
4、Processor
Processor是协议处理接口,负责构造Request和Response对象,并通过Adapter将其提交到Catalina容器处理,是对应用层协议的抽象。
在Coyote中,根据协议的不同有三个不同的实现类,另外还有两个具体的升级协议处理的实现
public abstract class AbstractProcessorLight implements Processor { private Set<DispatchType> dispatches = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>(); @Override public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper, SocketEvent status) throws IOException { SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED; Iterator<DispatchType> dispatches = null; do { if (dispatches != null) { DispatchType nextDispatch = dispatches.next(); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug("Processing dispatch type: [" + nextDispatch + "]"); } state = dispatch(nextDispatch.getSocketStatus()); if (!dispatches.hasNext()) { state = checkForPipelinedData(state, socketWrapper); } } else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT) { } else if (isAsync() || isUpgrade() || state == SocketState.ASYNC_END) { state = dispatch(status); state = checkForPipelinedData(state, socketWrapper); } else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) { state = SocketState.LONG; } else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ) { state = service(socketWrapper); } else if (status == SocketEvent.CONNECT_FAIL) { logAccess(socketWrapper); } else { state = SocketState.CLOSED; } if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug("Socket: [" + socketWrapper + "], Status in: [" + status + "], State out: [" + state + "]"); } if (isAsync()) { state = asyncPostProcess(); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug("Socket: [" + socketWrapper + "], State after async post processing: [" + state + "]"); } } if (dispatches == null || !dispatches.hasNext()) { // Only returns non-null iterator if there are // dispatches to process. dispatches = getIteratorAndClearDispatches(); } } while (state == SocketState.ASYNC_END || dispatches != null && state != SocketState.CLOSED); return state; } ...... } public abstract class AbstractProcessor extends AbstractProcessorLight implements ActionHook { @Override public final SocketState dispatch(SocketEvent status) throws IOException { if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE && response.getWriteListener() != null) { asyncStateMachine.asyncOperation(); try { if (flushBufferedWrite()) { return SocketState.LONG; } } catch (IOException ioe) { if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug("Unable to write async data.", ioe); } status = SocketEvent.ERROR; request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, ioe); } } else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ && request.getReadListener() != null) { dispatchNonBlockingRead(); } else if (status == SocketEvent.ERROR) { if (request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION) == null) { request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, socketWrapper.getError()); } if (request.getReadListener() != null || response.getWriteListener() != null) { asyncStateMachine.asyncOperation(); } } RequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor(); try { rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE); if (!getAdapter().asyncDispatch(request, response, status)) { setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, null); } } catch (InterruptedIOException e) { setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, t); getLog().error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), t); } rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED); SocketState state; if (getErrorState().isError()) { request.updateCounters(); state = SocketState.CLOSED; } else if (isAsync()) { state = SocketState.LONG; } else { request.updateCounters(); state = dispatchEndRequest(); } if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug("Socket: [" + socketWrapper + "], Status in: [" + status + "], State out: [" + state + "]"); } return state; } ...... }
5、Adapter
Adapter充当适配器,将Processor构造的Request对象转换为ServletRequest交给Container进行具体的处理。只有一个实现类:CoyoteAdapter
public class CoyoteAdapter implements Adapter { @Override public boolean asyncDispatch(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res, SocketEvent status) throws Exception { Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); if (request == null) { throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.nullRequest")); } boolean success = true; AsyncContextImpl asyncConImpl = request.getAsyncContextInternal(); req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(THREAD_NAME.get()); try { if (!request.isAsync()) { response.setSuspended(false); } if (status==SocketEvent.TIMEOUT) { if (!asyncConImpl.timeout()) { asyncConImpl.setErrorState(null, false); } } else if (status==SocketEvent.ERROR) { success = false; Throwable t = (Throwable)req.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION); req.getAttributes().remove(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION); ClassLoader oldCL = null; try { oldCL = request.getContext().bind(false, null); if (req.getReadListener() != null) { req.getReadListener().onError(t); } if (res.getWriteListener() != null) { res.getWriteListener().onError(t); } } finally { request.getContext().unbind(false, oldCL); } if (t != null) { asyncConImpl.setErrorState(t, true); } } if (!request.isAsyncDispatching() && request.isAsync()) { WriteListener writeListener = res.getWriteListener(); ReadListener readListener = req.getReadListener(); if (writeListener != null && status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) { ClassLoader oldCL = null; try { oldCL = request.getContext().bind(false, null); res.onWritePossible(); if (request.isFinished() && req.sendAllDataReadEvent() && readListener != null) { readListener.onAllDataRead(); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); writeListener.onError(t); success = false; } finally { request.getContext().unbind(false, oldCL); } } else if (readListener != null && status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ) { ClassLoader oldCL = null; try { oldCL = request.getContext().bind(false, null); if (!request.isFinished()) { readListener.onDataAvailable(); } if (request.isFinished() && req.sendAllDataReadEvent()) { readListener.onAllDataRead(); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); readListener.onError(t); success = false; } finally { request.getContext().unbind(false, oldCL); } } } if (!request.isAsyncDispatching() && request.isAsync() && response.isErrorReportRequired()) { connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response); } if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) { connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response); Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION); if (t != null) { asyncConImpl.setErrorState(t, true); } } if (!request.isAsync()) { request.finishRequest(); response.finishResponse(); } AtomicBoolean error = new AtomicBoolean(false); res.action(ActionCode.IS_ERROR, error); if (error.get()) { if (request.isAsyncCompleting()) { res.action(ActionCode.ASYNC_POST_PROCESS, null); } success = false; } } catch (IOException e) { success = false; // Ignore } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); success = false; log.error(sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.asyncDispatch"), t); } finally { if (!success) { res.setStatus(500); } // Access logging if (!success || !request.isAsync()) { long time = 0; if (req.getStartTime() != -1) { time = System.currentTimeMillis() - req.getStartTime(); } Context context = request.getContext(); if (context != null) { context.logAccess(request, response, time, false); } else { log(req, res, time); } } req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null); if (!success || !request.isAsync()) { updateWrapperErrorCount(request, response); request.recycle(); response.recycle(); } } return success; } //真正处理请求的方法 @Override public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res) throws Exception { Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); if (request == null) { request = connector.createRequest();//创建请求 request.setCoyoteRequest(req); response = connector.createResponse();//创建响应 response.setCoyoteResponse(res); request.setResponse(response); response.setRequest(request); req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request); res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response); req.getParameters().setQueryStringCharset(connector.getURICharset()); } if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) { response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY); } boolean async = false; boolean postParseSuccess = false; req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(THREAD_NAME.get()); try { //解析POST请求内容 postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response); if (postParseSuccess) { request.setAsyncSupported(connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response); } if (request.isAsync()) { async = true; ReadListener readListener = req.getReadListener(); if (readListener != null && request.isFinished()) { ClassLoader oldCL = null; try { oldCL = request.getContext().bind(false, null); if (req.sendAllDataReadEvent()) { req.getReadListener().onAllDataRead(); } } finally { request.getContext().unbind(false, oldCL); } } Throwable throwable = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION); if (!request.isAsyncCompleting() && throwable != null) { request.getAsyncContextInternal().setErrorState(throwable, true); } } else { request.finishRequest(); response.finishResponse(); } } catch (IOException e) { // Ignore } finally { AtomicBoolean error = new AtomicBoolean(false); res.action(ActionCode.IS_ERROR, error); if (request.isAsyncCompleting() && error.get()) { res.action(ActionCode.ASYNC_POST_PROCESS, null); async = false; } // Access log if (!async && postParseSuccess) { Context context = request.getContext(); Host host = request.getHost(); long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - req.getStartTime(); if (context != null) { context.logAccess(request, response, time, false); } else if (response.isError()) { if (host != null) { host.logAccess(request, response, time, false); } else { connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess(request, response, time, false); } } } req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null); // Recycle the wrapper request and response if (!async) { updateWrapperErrorCount(request, response); request.recycle(); response.recycle(); } } } }
以上是关于Tomcat8源码学习之九连接器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章