如何正确写c++ boost beast websocket server
Posted qianbo_insist
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何正确写c++ boost beast websocket server相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
websocket server
这里有一个要求,就是获取客户端或者浏览器的url 请求路由
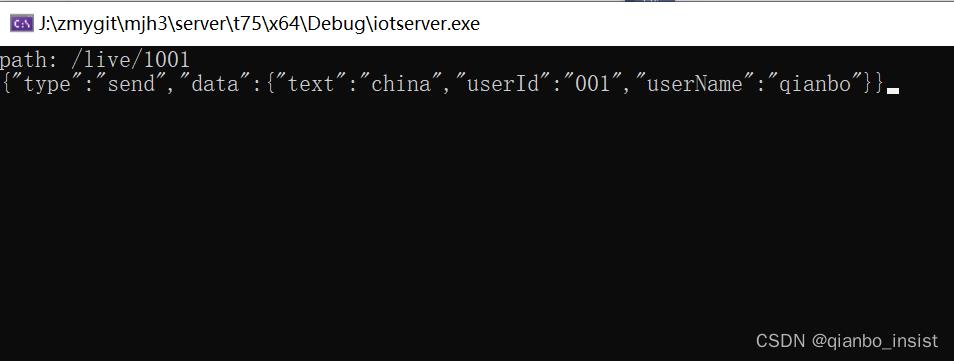
1 我们在path里面打印路径
2 我们显示beast 里的flat_buffer 的数据,根据最新的api
实际上,beast 的文档里面详细说明了如何获取路由,我给大家摘出来:路径在boost的文档lib下handshaking.html里面
libs/beast/doc/html/beast/using_websocket/handshaking.html
// This buffer is required for reading HTTP messages
flat_buffer buffer;
// Read the HTTP request ourselves
http::request<http::string_body> req;
http::read(sock, buffer, req);
// See if its a WebSocket upgrade request
if(websocket::is_upgrade(req))
// Construct the stream, transferring ownership of the socket
stream<tcp_stream> ws(std::move(sock));
// Clients SHOULD NOT begin sending WebSocket
// frames until the server has provided a response.
BOOST_ASSERT(buffer.size() == 0);
// Accept the upgrade request
ws.accept(req);
else
// Its not a WebSocket upgrade, so
// handle it like a normal HTTP request.
那么相应使用异步代码的时候,我们就要改成异步的接收
beast::flat_buffer buffer;
// Read the HTTP request ourselves
http::request<http::string_body> req;
http::read(ws_.next_layer(), buffer, req);
// See if its a WebSocket upgrade request
if (websocket::is_upgrade(req))
// Construct the stream, transferring ownership of the socket
//stream<tcp_stream> ws(std::move(sock));
// Clients SHOULD NOT begin sending WebSocket
// frames until the server has provided a response.
BOOST_ASSERT(buffer.size() == 0);
// Accept the upgrade request
ws_.async_accept(req,
beast::bind_front_handler(
&session::on_accept,
shared_from_this()));
printf("path: %s\\n", std::string(req.target().data(), req.target().length()).data());
我们知道本身websocket协议是建立在http协议之上,实际上只是头部字节需要upgrade。可以参考我自己写的websocket server,在我的文章里面,没有使用其他库,纯粹自己把websocket协议实现了。
2 、就是缓冲区,boost的缓冲区都是封装好的,我么需要解出来
asio 的streambuf 我们要这样解开:
boost::asio::streambuf sb;
...
std::size_t n = boost::asio::read_until(sock, sb, '\\n');
boost::asio::streambuf::const_buffers_type bufs = sb.data();
std::string line(
boost::asio::buffers_begin(bufs),
boost::asio::buffers_begin(bufs) + n);
beast 的缓冲区根据最新的文档,要使用 boost::beast::make_printable(buffer_.data());
而不是以前的cast了
// Echo the message
std::stringstream ss;
ss << boost::beast::make_printable(buffer_.data());
std::cout << ss.str();
ws_.text(ws_.got_text());
ws_.async_write(
buffer_.data(),
beast::bind_front_handler(
&session::on_write,
shared_from_this()));
3、timeout
超时设置
stream_base::timeout opt
std::chrono::seconds(30), // handshake timeout
stream_base::none(), // idle timeout
false
;
// Set the timeout options on the stream.
ws.set_option(opt);
web 浏览器 代码
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function WebSocketTest()
if ("WebSocket" in window)
// alert("您的浏览器支持 WebSocket!");
// 打开一个 web socket
var ws = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:80/live/1001");
console.log(ws);
ws.onopen = function (evt)
// Web Socket 已连接上,使用 send() 方法发送数据
console.log(evt)
let obj = JSON.stringify(
type: 'send',
data:
text: 'china',
userId: '001',
userName: 'qianbo'
)
ws.send(obj);
console.log("数据发送中...");
;
ws.onmessage = function (evt)
var received_msg = JSON.parse(evt.data);
console.log(received_msg)
alert(received_msg.data.userName);
;
ws.onclose = function ()
// 关闭 websocket
alert("连接已关闭...");
;
else
// 浏览器不支持 WebSocket
alert("您的浏览器不支持 WebSocket!");
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="sse">
<a href="javascript:WebSocketTest()">运行 WebSocket</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
代码里发送一些数据,控制台打印数据并且alert 一个json里面的一个成员变量
服务端代码如下:
//
// Copyright (c) 2016-2019 Vinnie Falco (vinnie dot falco at gmail dot com)
//
// Distributed under the Boost Software License, Version 1.0. (See accompanying
// file LICENSE_1_0.txt or copy at http://www.boost.org/LICENSE_1_0.txt)
//
// Official repository: https://github.com/boostorg/beast
//
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//
// Example: WebSocket server, asynchronous
//
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
#include <boost/beast.hpp>
#include <boost/beast/core.hpp>
#include <boost/beast/websocket.hpp>
#include <boost/asio/strand.hpp>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
namespace beast = boost::beast; // from <boost/beast.hpp>
namespace http = boost::beast::http; // from <boost/beast/http.hpp>
namespace websocket = beast::websocket; // from <boost/beast/websocket.hpp>
namespace net = boost::asio; // from <boost/asio.hpp>
using tcp = boost::asio::ip::tcp; // from <boost/asio/ip/tcp.hpp>
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Report a failure
void
fail(beast::error_code ec, char const* what)
std::cerr << what << ": " << ec.message() << "\\n";
// Echoes back all received WebSocket messages
class session : public std::enable_shared_from_this<session>
websocket::stream<beast::tcp_stream> ws_;
beast::flat_buffer buffer_;
public:
// Take ownership of the socket
explicit
session(tcp::socket&& socket)
: ws_(std::move(socket))
// Start the asynchronous operation
void
run()
// Set suggested timeout settings for the websocket
ws_.set_option(
websocket::stream_base::timeout::suggested(
beast::role_type::server));
// Set a decorator to change the Server of the handshake
ws_.set_option(websocket::stream_base::decorator(
[](websocket::response_type& res)
res.set(http::field::server,
std::string("web Iot server") +
" 1.0");
));
beast::flat_buffer buffer;
// Read the HTTP request ourselves
http::request<http::string_body> req;
http::read(ws_.next_layer(), buffer, req);
// See if its a WebSocket upgrade request
if (websocket::is_upgrade(req))
// Construct the stream, transferring ownership of the socket
//stream<tcp_stream> ws(std::move(sock));
// Clients SHOULD NOT begin sending WebSocket
// frames until the server has provided a response.
BOOST_ASSERT(buffer.size() == 0);
// Accept the upgrade request
ws_.async_accept(req,
beast::bind_front_handler(
&session::on_accept,
shared_from_this()));
printf("path: %s\\n", std::string(req.target().data(), req.target().length()).data());
void
on_accept(beast::error_code ec)
if (ec)
return fail(ec, "accept");
// Read a message
do_read();
void
do_read()
// Read a message into our buffer
ws_.async_read(
buffer_,
beast::bind_front_handler(
&session::on_read,
shared_from_this()));
void
on_read(
beast::error_code ec,
std::size_t bytes_transferred)
boost::ignore_unused(bytes_transferred);
// This indicates that the session was closed
if (ec == websocket::error::closed)
return;
if (ec)
fail(ec, "read");
// Echo the message
std::stringstream ss;
ss << boost::beast::make_printable(buffer_.data());
std::cout << ss.str();
ws_.text(ws_.got_text());
ws_.async_write(
buffer_.data(),
beast::bind_front_handler(
&session::on_write,
shared_from_this()));
void on_write(
beast::error_code ec,
std::size_t bytes_transferred)
boost::ignore_unused(bytes_transferred);
if (ec)
return fail(ec, "write");
// Clear the buffer
buffer_.consume(buffer_.size());
// Do another read
do_read();
;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Accepts incoming connections and launches the sessions
class listener : public std::enable_shared_from_this<listener>
net::io_context& ioc_;
tcp::acceptor acceptor_;
public:
listener(
net::io_context& ioc,
tcp::endpoint endpoint)
: ioc_(ioc)
, acceptor_(ioc)
beast::error_code ec;
// Open the acceptor
acceptor_.open(endpoint.protocol(), ec);
if (ec)
fail(ec, "open");
return;
// Allow address reuse
acceptor_.set_option(net::socket_base::reuse_address(true), ec);
if (ec)
fail(ec, "set_option");
return;
// Bind to the server address
acceptor_.bind(endpoint, ec);
if (ec)
fail(ec, "bind");
return;
// Start listening for connections
acceptor_.listen(
net::socket_base::max_listen_connections, ec);
if (ec)
fail(ec, "listen");
return;
// Start accepting incoming connections
void
run()
do_accept();
private:
void
do_accept()
// The new connection gets its own strand
acceptor_.async_accept(
net::make_strand(ioc_),
beast::bind_front_handler(
&listener::on_accept,
shared_from_this()));
void
on_accept(beast::error_code ec, tcp::socket socket)
if (ec)
fail(ec, "accept");
else
// Create the session and run it
std::make_shared<session>(std::move(socket))->run();
// Accept another connection
do_accept();
;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
auto const address = net::ip::make_address("0.0.0.0");
auto const port = 80;
auto const threads = 4;
// The io_context is required for all I/O
net::io_context ioc threads ;
// Create and launch a listening port
std::make_shared<listener>(ioc, tcp::endpoint address, 80 )->run();
// Run the I/O service on the requested number of threads
std::vector<std::thread> v;
v.reserve(threads - 1);
for (auto i = threads - 1; i > 0; --i)
v.emplace_back(
[&ioc]
ioc.run();
);
ioc.run();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
异步方式的服务器,使用多线程,读者可以自己实验
以上是关于如何正确写c++ boost beast websocket server的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章