2022深圳杯数学建模赛题思路 比赛通知
Posted dc_sinor
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2022深圳杯数学建模赛题思路 比赛通知相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
0 前言
2022 年深圳杯竞赛时间官方目前还未放出消息,根据往年一般在2022年7月15月 — 9月10日之间,各位同学做好准备哦!
这里先占个坑,赛题出来后第一时间在这发布赛题思路

1 赛前准备 - 建模步骤
建模资料,获奖秘籍: https://gitee.com/math-sinor/math-data/blob/master/README.md
1.1 第一步 提出问题
- 整理出问题中涉及到的常量、变量与单位。
- 团队讨论出对变量所做的全部假设,包括等式和不等式。
- 用准确的数学表达式给出问题的目标。
1.2 第二步 选择建模方法
- 选择一个解决问题的一般求解方法。
1.3 第三步 推导模型的公式
- 将第1步中得到的问题整理成第2步选择的建模方法所需要形式。
- 注意统一前后字符、公式。
1.4 第四步 求解模型
- 将第2步中所选方法应用于第3步中推导的表达式中。
- 采用适当的软件对问题进行求解计算,常见软件如下。
统计模型:EXCEL、SPSS、Eviews、Stata ,新手可直接上EXCEL。
微分方程:Maple、Mathematic、Matlab
文本排版:Word、Latex
运筹规划:Matlab,Lingo
公式整理:Mathtype
智能算法:Matlab,R
图像处理:Matlab,C++,OpenCV
综上:Matlab万能,所以新手学会Matlab就足以应付竞赛。
1.5 第五步 论文撰写
- 用非技术性的语言将所做成果整理到文本上。
- 注意检查格式以及数学符号、术语。
2 往届赛题思路 - 2021年羊狼追逐
这里学长分享一个去年拿了国一的赛题思路,2022年的赛题思路将在赛题发布会5小时内发布~
2.1 思路流程

2.2 关键代码
'''
自己设置的环境类
智能体:羊
环境:羊、犬和圆形草地,犬采用最优围堵策略围堵羊,若羊在一段时间内逃出圈则胜利,这段时间内没逃出或者被犬抓到则失败;
状态空间:整个圆组成的点集,是二维的;
动作空间:羊每一步可采取的动作的集合
回报的设计:参照pendulum-v0游戏环境源码中的回报的设计方案。
'''
import gym
from gym import spaces
import numpy as np
import math
import random
from gym.envs.classic_control import rendering
sigma=10
# 将弧度转换为角度
def trans(tmp):
return 360*(tmp/(2*np.pi))
# 更新犬的状态
def change_dog_state(thetaP,thetaE,delta_theta):
new_thetaP=thetaP
clockwise = (thetaP - delta_theta + 2 * np.pi) % (2 * np.pi) # 顺时针
counterclockwise = (thetaP + delta_theta + 2 * np.pi) % (2 * np.pi) # 逆时针
if thetaE > thetaP:
if thetaE - thetaP >= np.pi:
new_thetaP = clockwise
else:
new_thetaP = counterclockwise
elif thetaE < thetaP:
if thetaP - thetaE >= np.pi:
new_thetaP = counterclockwise
else:
new_thetaP = clockwise
return new_thetaP
# 计算夹角
def cal_angel(theta1,theta2):
ans=0
if theta1 > theta2:
ans = theta1 - theta2
if ans > np.pi:
ans = 2 * np.pi - ans # (补)角
else:
ans = theta2 - theta1
if ans > np.pi:
ans = 2 * np.pi - ans
return ans
# 判断羊是否给抓住
def catch(R,theta1,theta2,theta3):
x=R*np.cos(theta1)
y=R*np.sin(theta1)
a=R*np.cos(theta2)
b=R*np.sin(theta2)
A=R*np.cos(theta3)
B=R*np.sin(theta3)
len1=math.sqrt((x-a)*(x-a)+(y-b)*(y-b))
len2=math.sqrt((x-A)*(x-A)+(y-B)*(y-B))
if len1 <= sigma and len2 <= sigma:
return True
else:
return False
class dogSheepEnv(gym.Env):
def __init__(self):
# self.dt = 0.2 # 采样时间
self.dt=0.2
# self.thetaP=np.pi/2# 狗的极坐标
self.thetaP = random.uniform(0, 2 * np.pi)# 狗1的极坐标
self.wP=np.pi/5# 狗的角速度
self.thetaP2=random.uniform(0, 2 * np.pi)# 狗1的极坐标
self.vE=32# 羊的速度
self.thetaE=np.pi/2# 羊的极坐标
self.radiusE=0# 羊的极坐标半径
self.R=100# 圆的半径
self.state=np.array([self.thetaE,self.radiusE,self.thetaP,self.thetaP2])# 环境的初始状态
self.viewer = rendering.Viewer(400, 400)# 画板
self.lambda1=0.07# reward的参数1
self.lambda2=3.1# reward的参数2
self.lambda3=3.1
self.lambda4=6.2
# 自定义动作空间,观察空间
self.action_space = spaces.Box(
# 羊的动作空间即为转动的角度,会根据当前位置进行变化
# 由于怕出现low比high还大的情况,我们的action_space就不做周期处理,用的时候取余2pi就行
low=0, high=2*np.pi, shape=(1,), dtype=np.float32
)
self.observation_space = spaces.Box(
# 状态空间为 theta_E,R_E,theta_P
low=np.array([0,0,0,0])
,high=np.array([2*np.pi,self.R,2*np.pi,2*np.pi])
,dtype=np.float32
)
'''
羊接受一个动作进行位移: 使用PG算法的choose_action
犬沿劣弧进行位移
接着判断游戏是否结束
评价这个动作的回报
'''
def step(self, action):# u为action
# print('action: ',action)
# 根据action(即θ_E'来计算新的状态)
self.state = self._get_observation(action)
reward = self._get_reward()
done = self._get_done()
if done:# 如果逃脱失败,给予惩罚
if catch(self.R,self.state[0],self.state[2],self.state[3]):
reward=reward-1000
print('be catched')
else:
reward=0
print('no be catched')
return self.state,reward,done
# 获取reward,根据action作用之后的state来计算reward
def _get_reward(self):
# thetaP=self.state[2]
# thetaP2=self.state[3]
# thetaE=self.state[0]
thetaE,thetaP,thetaP2=self.state[0],self.state[2],self.state[3]
delta_theta1=cal_angel(thetaE,thetaP)# 羊与犬1的夹角
delta_theta2=cal_angel(thetaE,thetaP2)# 羊与犬2的夹角
delta_theta3=cal_angel(thetaP,thetaP2)# 两犬之间的夹角
# a=self.state[1]
# b=self.R
# distance=math.sqrt(a*a+b*b-2*a*b*np.cos(delta_theta))
# 羊距圆周越近越好(radiusE越大越好),羊与犬的夹角越大越好,羊离犬越远越好
# print('r1: ',self.lambda1 * abs(self.R - self.state[1]))
# print('r2: ',self.lambda2 * abs(np.pi-delta_theta1))
# print('r3: ',self.lambda3 * abs(np.pi-delta_theta2))
# print('r4: ',self.lambda4 * abs(delta_theta3))
return -(# 想要趋近于零
self.lambda1 * abs(self.R - self.state[1])# 范围 [0-2*R(200)]
+ self.lambda2 * abs(np.pi-delta_theta1) # 范围 [0-100]
+ self.lambda3 * abs(np.pi-delta_theta2) # 范围 [0-100]
+ self.lambda4 * abs(delta_theta3) # 范围 [0-100]
)
# 判断游戏是否结束
def _get_done(self):
if self.state[1]>=self.R:
return True
else:
return False
# 根据action修改环境,改变状态
def _get_observation(self,action):
# 已知现在的位置,首先计算位移后羊的极坐标
xb=self.state[1]*np.cos(self.state[0])+self.vE*self.dt*np.cos(action)
yb=self.state[1]*np.sin(self.state[0])+self.vE*self.dt*np.sin(action)
new_radiusE=math.sqrt(xb*xb+yb*yb)
# 由xb和yb进行θ转换,# 返回弧度pi
new_thetaE=math.atan2(yb,xb)
new_thetaE=(new_thetaE+2*np.pi)%(2*np.pi)
# 根据羊的action,选择狼的位移方向并位移
delta_theta=self.wP*self.dt
thetaE = self.state[0]
# 修改犬1的状态
thetaP = self.state[2]# 犬1的原状态
new_thetaP=change_dog_state(thetaP,thetaE,delta_theta)# 犬1的新状态
# 修改犬2的状态
thetaP2 = self.state[3] # 犬1的原状态
new_thetaP2 = change_dog_state(thetaP2, thetaE, delta_theta) # 犬1的新状态
# 相等的话就保持原状态
return np.array([new_thetaE,new_radiusE,new_thetaP,new_thetaP2])
# 重置羊和犬的状态
def reset(self):
thetaE=random.uniform(0, 2 * np.pi)
thetaE2=(thetaE+np.pi)%(2*np.pi)
self.state=np.array([0,0,thetaE,thetaE2],dtype=float)
return np.array(self.state)
# 画画显示犬和羊的状态
def render(self):
# 清空轨迹
# self.viewer.geoms.clear()
# 绘制大圆
ring = rendering.make_circle(radius=self.R,res=50,filled=False)
transform1 = rendering.Transform(translation=(200, 200)) # 相对偏移
ring.add_attr(transform1)# 让圆添加平移这个属性
self.viewer.add_geom(ring)
# 绘制犬1
xP,yP=self.R*np.cos(self.state[2]),self.R*np.sin(self.state[2])
ringP = rendering.make_circle(radius=2, res=50, filled=True)
ringP.set_color(0,0,1)
transform_P = rendering.Transform(translation=(200+xP, 200+yP)) # 相对偏移
ringP.add_attr(transform_P) # 让圆添加平移这个属性
self.viewer.add_geom(ringP)
# 绘制犬2
xP2, yP2 = self.R * np.cos(self.state[3]), self.R * np.sin(self.state[3])
ringP2 = rendering.make_circle(radius=2, res=50, filled=True)
ringP2.set_color(0, 0, 1)
transform_P2 = rendering.Transform(translation=(200 + xP2, 200 + yP2)) # 相对偏移
ringP2.add_attr(transform_P2) # 让圆添加平移这个属性
self.viewer.add_geom(ringP2)
# 绘制羊
xE, yE = self.state[1] * np.cos(self.state[0]), self.state[1] * np.sin(self.state[0])
ringE = rendering.make_circle(radius=2, res=50, filled=True)
ringE.set_color(1, 0, 0)
transform_E = rendering.Transform(translation=(200+xE, 200+yE)) # 相对偏移
ringE.add_attr(transform_E) # 让圆添加平移这个属性
self.viewer.add_geom(ringE)
return self.viewer.render()
# env = dogSheepEnv()
# while True:
# env.reset()
# for _ in range(2000):
# env.render()
# action=random.uniform(0,2*np.pi)
# action=np.clip(action,env.state[0]-np.pi/2,env.state[0]+np.pi/2)
# action=(action+2*np.pi)%(2*np.pi)
# state, reward, done = env.step(action) # 和环境交互
# if done:
# break
2.3 题解结果
一犬一羊情况,回报收敛的趋势图

羊的逃逸路径

犬的追捕极角

羊的逃逸极角
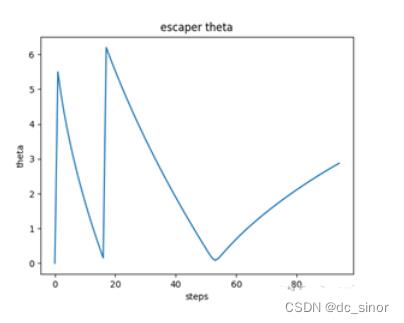
推广:两犬一只羊情况
回报收敛的趋势图

羊的逃逸路径

羊的逃逸极角
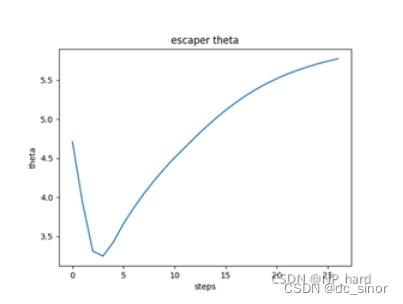
建模资料,获奖秘籍: https://gitee.com/math-sinor/math-data/blob/master/README.md
以上是关于2022深圳杯数学建模赛题思路 比赛通知的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章