Spring读源码系列番外篇---06----类型转换---下---ConversionService相关家族
Posted 大忽悠爱忽悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring读源码系列番外篇---06----类型转换---下---ConversionService相关家族相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Spring读源码系列番外篇---06----类型转换---下
系列文章:
Spring读源码系列番外篇—01–PropertyValue相关类
Spring读源码系列番外篇—02—PropertyResolver的结构体系剖析—上
Spring读源码系列番外篇—03—PropertyResolver的结构体系剖析—下
引子
Spirng 3.0全新一代的类型转换机制,它提供的三种类型转换器(Converter、ConverterFactory、GenericConverter),分别可处理1:1、1:N、N:N的类型转换。
按照Spring的设计习惯,必有一个注册中心来统一管理,负责它们的注册、删除等,它就是ConverterRegistry。
另外,内建的绝大多数转换器访问权限都是default/private,那么如何使用它们,以及屏蔽各种转换器的差异化呢?为此,Spring提供了一个统一类型转换服务,它就是ConversionService。
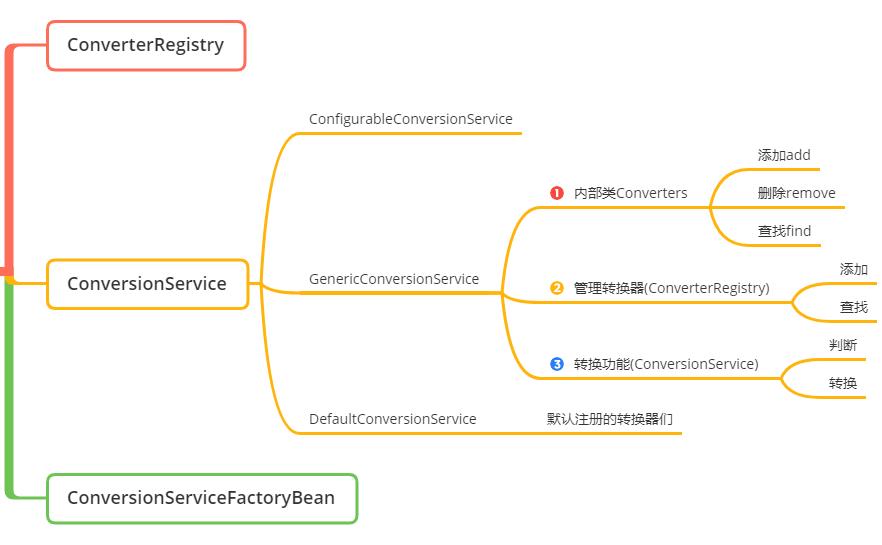
新一代类型转换组件简介
ConverterRegistry和ConversionService的关系密不可分,前者为后者提供转换器管理支撑,后者面向使用者提供服务。本文涉及到的接口/类有:
- ConverterRegistry:转换器注册中心。负责转换器的注册、删除
- ConversionService:统一的类型转换服务。属于面向开发者使用的门面接口
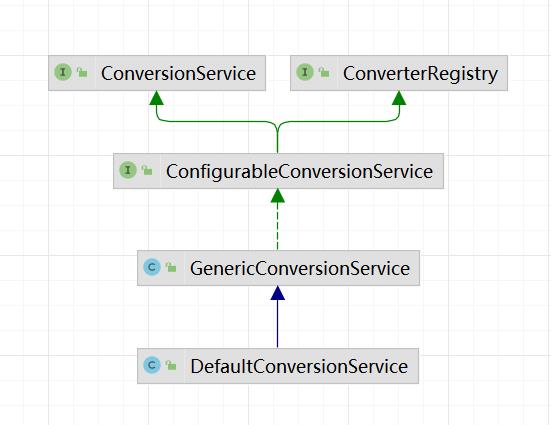
- ConfigurableConversionService:上两个接口的组合接口
- GenericConversionService:上个接口的实现,实现了注册管理、转换服务的几乎所有功能,是个实现类而非抽象类
- DefaultConversionService:继承自GenericConversionService,在其基础上注册了一批默认转换器(Spring内建),从而具备基础转换能力,能解决日常绝大部分场景
ConverterRegistry
public interface ConverterRegistry
//注册一个1:1的转换器----会尝试去参数化类型中提取sourceType和targetType
void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter);
//注册一个1:1的转换器----明确sourceType和targetType
<S, T> void addConverter(Class<S> sourceType, Class<T> targetType, Converter<? super S, ? extends T> converter);
//注册一个n:n的转换器
void addConverter(GenericConverter converter);
//注册一个1:n的转化器
void addConverterFactory(ConverterFactory<?, ?> factory);
//移除某个转换器
void removeConvertible(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);

ConverterRegistry有子接口FormatterRegistry,它属于格式化器的范畴.
ConversionService
面向使用者的统一类型转换服务。换句话说:站在使用层面,你只需要知道ConversionService接口API的使用方式即可,并不需要关心其内部实现机制,可谓对使用者非常友好。
public interface ConversionService
boolean canConvert(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);
boolean canConvert(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
<T> T convert(Object source, Class<T> targetType);
Object convert(Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);

可以看到ConversionService和ConverterRegistry的继承树殊途同归,都直接指向了ConfigurableConversionService这个分支,下面就对它进行介绍
ConfigurableConversionService
ConversionService和ConverterRegistry的组合接口,自己并未新增任何接口方法。
public interface ConfigurableConversionService extends ConversionService, ConverterRegistry
插眼: ResolvableType
为什么要先提一嘴这个类呢?
当然是因为我们下面要将的GenericConversionService源码中大量使用到了这个类
该类作用很简单,我这里简单介绍一下,就不贴出源码了,毕竟方法挺多的:
- 封装一个JAVA类型,提供对父类,接口和反向的访问已经最终解析为class的能力
- ResolvableTypes 可以从字段、方法参数、方法返回或类中获得。此类中的大多数方法本身都会返回 ResolvableTypes,从而可以轻松导航
private HashMap<Integer, List<String>> myMap;
public void example()
ResolvableType t = ResolvableType.forField(getClass().getDeclaredField("myMap"));
t.getSuperType(); // AbstractMap<Integer, List<String>>
t.asMap(); // Map<Integer, List<String>>
t.getGeneric(0).resolve(); // Integer
t.getGeneric(1).resolve(); // List
t.getGeneric(1); // List<String>
//第二个泛型,里面的泛型,即List<String>里面的String
t.resolveGeneric(1, 0); // String
通过上面这个简单案例应该可以让各位有个大概的了解,这就差不多了,那么我们进入正题吧
我觉得这个类,有空可以参考在自己项目中用用,毕竟算是一个比较方便的工具类
GenericConversionService
对ConfigurableConversionService接口提供了完整实现的实现类。换句话说:ConversionService和ConverterRegistry接口的功能均通过此类得到了实现,所以它是本文重点。
public class GenericConversionService implements ConfigurableConversionService
/**
* General NO-OP converter used when conversion is not required.
*
*/
private static final GenericConverter NO_OP_CONVERTER = new NoOpConverter("NO_OP");
/**
* Used as a cache entry when no converter is available.
* This converter is never returned.
*/
private static final GenericConverter NO_MATCH = new NoOpConverter("NO_MATCH");
//Converters是GenericConversionService的内部类,用于管理(添加、删除、查找)转换器们。
//也就说对ConverterRegistry接口的实现最终是委托给它去完成的,它是整个转换服务正常work的内核
private final Converters converters = new Converters();
//它用两个成员变量来管理转换器们,其中converterCache是缓存用于加速查找,因此更为重要的便是Converters喽。
private final Map<ConverterCacheKey, GenericConverter> converterCache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(64);
//-------------------------ConverterRegistry注册相关接口的具体实现------------------------
//增加一个1:1的转化器
@Override
public void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter)
//getRequiredTypeInfo是一个工具方法,功能是返回传入converter的具体的泛型参数数组
//泛型参数都被ResolvableType进行包裹,长度为2,一个是原对象类型,一个是目标对象类型
ResolvableType[] typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(converter.getClass(), Converter.class);
//对代理进行判断---这个地方我暂时不清楚,等后面我懂了,就回来完善一下!!!
if (typeInfo == null && converter instanceof DecoratingProxy)
//这套组合拳目的在于拿到泛型参数数组
typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(((DecoratingProxy) converter).getDecoratedClass(), Converter.class);
if (typeInfo == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to determine source type <S> and target type <T> for your " +
"Converter [" + converter.getClass().getName() + "]; does the class parameterize those types?");
//添加转换器----将所有converter都通过ConverterAdapter转换为
addConverter(new ConverterAdapter(converter, typeInfo[0], typeInfo[1]));
//和上面那个重载方法相比,少了去解析出convert泛型参数的过程
@Override
public <S, T> void addConverter(Class<S> sourceType, Class<T> targetType, Converter<? super S, ? extends T> converter)
//这一步和上面那个重载方法一样---这里也用到了适配器模式和上面一样
addConverter(new ConverterAdapter(
converter, ResolvableType.forClass(sourceType), ResolvableType.forClass(targetType)));
//上面两个重载方法最终调用的方法--这里参数需要的是GenericConverter
//因为我们之前说过有1:1,1:n,n:n三种转换器,因此我们这边把所有转换器都转换为通用的GenericConverter(n:n)进行管理
@Override
public void addConverter(GenericConverter converter)
//converters是一个内部类,它管理所有转换器,包括添加、删除、查找。
//这个一会在细聊
this.converters.add(converter);
//清除缓存集合
invalidateCache();
//添加一个1:n的转换器
@Override
public void addConverterFactory(ConverterFactory<?, ?> factory)
//同样因为转换器的泛型参数不确定,因此需要先解析出来
ResolvableType[] typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(factory.getClass(), ConverterFactory.class);
//处理代理问题
if (typeInfo == null && factory instanceof DecoratingProxy)
typeInfo = getRequiredTypeInfo(((DecoratingProxy) factory).getDecoratedClass(), ConverterFactory.class);
if (typeInfo == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to determine source type <S> and target type <T> for your " +
"ConverterFactory [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]; does the class parameterize those types?");
//ConverterFactoryAdapter是将ConverterFactory转换为通用的GenericAdapter
addConverter(new ConverterFactoryAdapter(factory,
new ConvertiblePair(typeInfo[0].toClass(), typeInfo[1].toClass())));
//移除某个转换器
@Override
public void removeConvertible(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType)
//可以看出是converters管理某个转换器的删除
this.converters.remove(sourceType, targetType);
//清空缓存
invalidateCache();
// ConversionService implementation
@Override
public boolean canConvert(@Nullable Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType)
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type to convert to cannot be null");
//将Class包装为TypeDescriptor,然后交给重载方法进行处理
return canConvert((sourceType != null ? TypeDescriptor.valueOf(sourceType) : null),
TypeDescriptor.valueOf(targetType));
@Override
public boolean canConvert(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType)
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type to convert to cannot be null");
if (sourceType == null)
return true;
//能否进行转换就是去找到有无可用的转换器
//这里如果一开始缓存中没有,那么找到后会加入缓存中,这样一会进行转换的时候,就会直接从缓存中取
//如果找不到也会放入缓存集合--相当于做个标记
GenericConverter converter = getConverter(sourceType, targetType);
return (converter != null);
/**
是否不需要进行任何类型转换
*/
public boolean canBypassConvert(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType)
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type to convert to cannot be null");
if (sourceType == null)
return true;
//如果不需要进行任何类型转换,那么getConverter会返回NO_OP_CONVERTER---表示当前类型对不需要进行转换
GenericConverter converter = getConverter(sourceType, targetType);
return (converter == NO_OP_CONVERTER);
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Nullable
//将source对象转换为targetType类型
public <T> T convert(@Nullable Object source, Class<T> targetType)
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type to convert to cannot be null");
//最终调用的是重载方法来进行处理
return (T) convert(source, TypeDescriptor.forObject(source), TypeDescriptor.valueOf(targetType));
@Override
@Nullable
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, @Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType)
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type to convert to cannot be null");
//如果原对象类型为null,那么对应的source对象肯定也为null
if (sourceType == null)
Assert.isTrue(source == null, "Source must be [null] if source type == [null]");
//convertNullSource:如果targetType是Optional类型,最终返回的是Optional.empty()
//否则返回null
//handleResult:返回第三个参数作为返回结果,如果第三个参数为null,会抛出异常
return handleResult(null, targetType, convertNullSource(null, targetType));
//sourceType必须是Source的类型--isInstance---》InstanceOf
if (source != null && !sourceType.getObjectType().isInstance(source))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Source to convert from must be an instance of [" +
sourceType + "]; instead it was a [" + source.getClass().getName() + "]");
//寻找相关的转化器
GenericConverter converter = getConverter(sourceType, targetType);
if (converter != null)
//ConversionUtils.invokeConverter最终就是调用converter的converter方法
Object result = ConversionUtils.invokeConverter(converter, source, sourceType, targetType);
//主要对第三个参数是否为空进行校验
return handleResult(sourceType, targetType, result);
//source为null,直接返回null,或者target是source的父类,返回直接返回source即可,不需要进行任何类型转换操作
return handleConverterNotFound(source, sourceType, targetType);
@Nullable
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor targetType)
return convert(source, TypeDescriptor.forObject(source), targetType);
@Override
public String toString()
return this.converters.toString();
// Protected template methods
@Nullable
protected Object convertNullSource(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType)
//null--->Optional,那么最终转换后得到的是Optional.empty()
if (targetType.getObjectType() == Optional.class)
return Optional.empty();
return null;
@Nullable
protected GenericConverter getConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType)
//构建缓存key
ConverterCacheKey key = new ConverterCacheKey(sourceType, targetType);
//先尝试从缓存中去获取
GenericConverter converter = this.converterCache.get(key);
if (converter != null)
//缓存中存在
//这里提前说一下:如果某个类型对不存在与之关联的转换器,那么在第一次查找无果后
//会在缓存中进行标记,即当前key--->NO_MATCH
//因此如果这里存在转换器,但是为NO_MATCH ,表示不存在对应的转换器可以转换该类型对,返回null即可
return (converter != NO_MATCH ? converter : null);
//converters负责通过类型对去查找到指定的转换器
converter = this.converters.find(sourceType, targetType);
//如果找不到
if (converter == null)
//如果source和target之间是父子关系,那么返回NO_OP_CONVERTER,表示不需要进行类型转换
//否则返回null
converter = getDefaultConverter(sourceType, targetType);
//如果到这里找到了对应的转换器,那么会放入缓存中
if (converter != null)
this.converterCache.put(key, converter);
return converter;
//走到这里,说明找不到,那么当前类型对会和一个NO_MATCH的转换器进行关联
this.converterCache.put(key, NO_MATCH);
return null;
//如果source和target之间是父子关系,那么返回NO_OP_CONVERTER,表示不需要进行类型转换
//否则返回null
@Nullable
protected GenericConverter getDefaultConverter(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType)
return (sourceType.isAssignableTo(targetType) ? NO_OP_CONVERTER : null);
// ---------------------Internal helpers:内部帮助的方法 --以上是关于Spring读源码系列番外篇---06----类型转换---下---ConversionService相关家族的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章