基于ubuntu环境,搭建Arduino+ESP32+MPU6050验证系统,并利用Processing仿真
Posted pocean2012
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于ubuntu环境,搭建Arduino+ESP32+MPU6050验证系统,并利用Processing仿真相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
具体姿态解算和原理性验证,姿态反馈控制另文描述,本文只针对基本验证环境搭建。
1. 建立基于Arduino的ESP32开发环境
原来用micro和promini都做了环境,但是隔了一段时间居然串口烧录把板子搞挂了,pro mini串口烧录也老出问题,先放一放,手上刚好有EPS32的开发板,毕竟ESP32带了wifi和蓝牙,也有多个串口,资源够用,也方便数据传输,用来读取MPU6050开发板的数据做原理性验证绰绰有余了。
Arduino直接下ESP32的包
GitHub - pocean2001/arduino-esp32: Arduino core for the ESP32
在Arduino下建立hardware/espressif目录,下载后解压,可以把目录名改为esp32
记得要运行工具
(base) hy@hy-Mi-Gaming-Laptop-15-6:~/arduino-1.8.13/hardware/espressif/arduino-esp32/tools$ python get.py
System: Linux, Bits: 64, Info: Linux-5.4.0-65-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.10
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
Downloading xtensa-esp32-elf-linux64-1.22.0-80-g6c4433a-5.2.0.tar.gz ...
Done
Extracting xtensa-esp32-elf-linux64-1.22.0-80-g6c4433a-5.2.0.tar.gz ...
Downloading esptool-2.6.1-linux.tar.gz ...
Done
Extracting esptool-2.6.1-linux.tar.gz ...
Downloading mkspiffs-0.2.3-arduino-esp32-linux64.tar.gz ...
Done
Extracting mkspiffs-0.2.3-arduino-esp32-linux64.tar.gz ...
Renaming mkspiffs-0.2.3-arduino-esp32-linux64 to mkspiffs ...
Platform Tools Installed
打开Arduino,选择板子和端口,此时需要把串口的权限开一下
sudo chmod 777 /dev/ttyUSB0
2. 下载MPU6050的开发库
能下的都搞下来玩一遍
3. 修改接口,测试传感器数据输出
用的esp32的引脚图
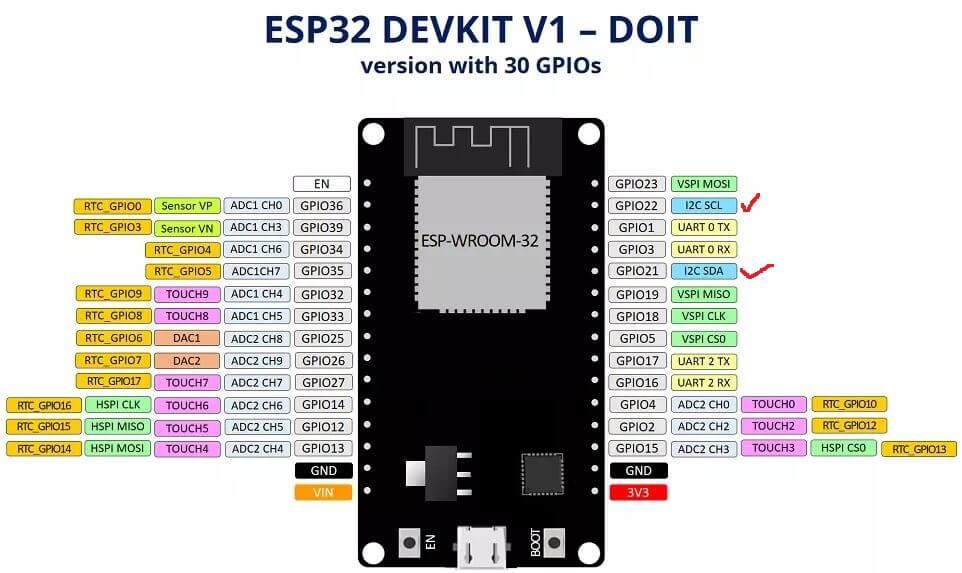
例子MPU6050_DMP6有多种数据输出形式,就用它,要改几个地方。
用wire.h库做驱动
#include "Wire.h"
定义中断引脚
#define INTERRUPT_PIN 5
定义I2C接口引脚scl/sda
Wire.begin(4,15);
这一段宏定义定义数据输出方式:
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_QUATERNION" if you want to see the actual
// quaternion components in a [w, x, y, z] format (not best for parsing
// on a remote host such as Processing or something though)
#define OUTPUT_READABLE_QUATERNION
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_EULER" if you want to see Euler angles
// (in degrees) calculated from the quaternions coming from the FIFO.
// Note that Euler angles suffer from gimbal lock (for more info, see
// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gimbal_lock)
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_EULER
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL" if you want to see the yaw/
// pitch/roll angles (in degrees) calculated from the quaternions coming
// from the FIFO. Note this also requires gravity vector calculations.
// Also note that yaw/pitch/roll angles suffer from gimbal lock (for
// more info, see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gimbal_lock)
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_REALACCEL" if you want to see acceleration
// components with gravity removed. This acceleration reference frame is
// not compensated for orientation, so +X is always +X according to the
// sensor, just without the effects of gravity. If you want acceleration
// compensated for orientation, us OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL instead.
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_REALACCEL
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL" if you want to see acceleration
// components with gravity removed and adjusted for the world frame of
// reference (yaw is relative to initial orientation, since no magnetometer
// is present in this case). Could be quite handy in some cases.
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL
// uncomment "OUTPUT_TEAPOT" if you want output that matches the
// format used for the InvenSense teapot demo
//#define OUTPUT_TEAPOT
对应下面的数据处理输出:
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_QUATERNION
// display quaternion values in easy matrix form: w x y z
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
Serial.print("quat\\t");
Serial.print(q.w);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(q.x);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(q.y);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(q.z);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_EULER
// display Euler angles in degrees
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetEuler(euler, &q);
Serial.print("euler\\t");
Serial.print(euler[0] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(euler[1] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(euler[2] * 180/M_PI);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
// display Euler angles in degrees
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity);
Serial.print("ypr\\t");
Serial.print(ypr[0] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(ypr[1] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(ypr[2] * 180/M_PI);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_REALACCEL
// display real acceleration, adjusted to remove gravity
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetAccel(&aa, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetLinearAccel(&aaReal, &aa, &gravity);
Serial.print("areal\\t");
Serial.print(aaReal.x);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(aaReal.y);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(aaReal.z);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL
// display initial world-frame acceleration, adjusted to remove gravity
// and rotated based on known orientation from quaternion
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetAccel(&aa, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetLinearAccel(&aaReal, &aa, &gravity);
mpu.dmpGetLinearAccelInWorld(&aaWorld, &aaReal, &q);
Serial.print("aworld\\t");
Serial.print(aaWorld.x);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(aaWorld.y);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(aaWorld.z);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_TEAPOT
// display quaternion values in InvenSense Teapot demo format:
teapotPacket[2] = fifoBuffer[0];
teapotPacket[3] = fifoBuffer[1];
teapotPacket[4] = fifoBuffer[4];
teapotPacket[5] = fifoBuffer[5];
teapotPacket[6] = fifoBuffer[8];
teapotPacket[7] = fifoBuffer[9];
teapotPacket[8] = fifoBuffer[12];
teapotPacket[9] = fifoBuffer[13];
Serial.write(teapotPacket, 14);
teapotPacket[11]++; // packetCount, loops at 0xFF on purpose
#endif
TEAPOT格式下的输出输出格式:
// packet structure for InvenSense teapot demo
uint8_t teapotPacket[14] = '$', 0x02, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0x00, 0x00, '\\r', '\\n' ;
在processing仿真读取的数据就是teapot格式
4. processing环境下读取数据并建立仿真模型
processing的安装直接上官网,速度还可以,基于java或者基于python,也可以下载例程由浅入深学习,此处不展开。
其实不用下载额外的库,直接用刚才arduino的mpu6050库配套的例程就可以,路径
/home/hy/Arduino/libraries/MPU6050/examples/MPU6050_DMP6/Processing/MPUTeapot/MPUTeapot.pde
运行结果
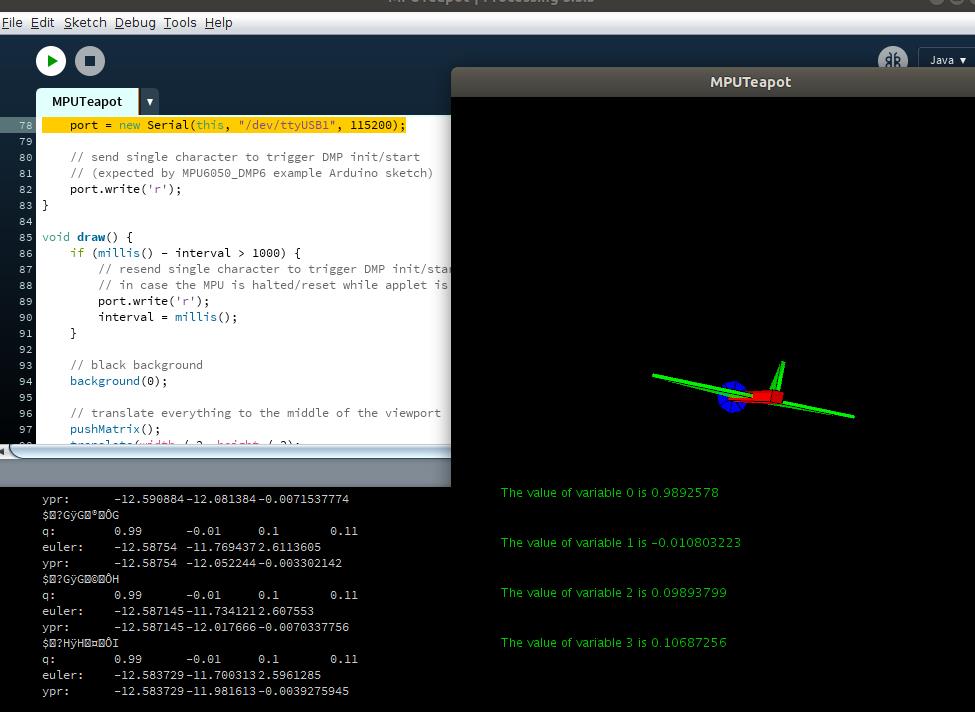
数据还是会有漂移 ,是精度问题?还是需要引入卡尔曼滤波? 下一步考虑
下面是arduino和processing完整代码
#include "I2Cdev.h"
#include "MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h"
//#include "MPU6050.h" // not necessary if using MotionApps include file
// Arduino Wire library is required if I2Cdev I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE implementation
// is used in I2Cdev.h
//#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
#include "Wire.h"
//#endif
// class default I2C address is 0x68
// specific I2C addresses may be passed as a parameter here
// AD0 low = 0x68 (default for SparkFun breakout and InvenSense evaluation board)
// AD0 high = 0x69
MPU6050 mpu;
//MPU6050 mpu(0x69); // <-- use for AD0 high
/* =========================================================================
NOTE: In addition to connection 3.3v, GND, SDA, and SCL, this sketch
depends on the MPU-6050's INT pin being connected to the Arduino's
external interrupt #0 pin. On the Arduino Uno and Mega 2560, this is
digital I/O pin 2.
* ========================================================================= */
/* =========================================================================
NOTE: Arduino v1.0.1 with the Leonardo board generates a compile error
when using Serial.write(buf, len). The Teapot output uses this method.
The solution requires a modification to the Arduino USBAPI.h file, which
is fortunately simple, but annoying. This will be fixed in the next IDE
release. For more info, see these links:
http://arduino.cc/forum/index.php/topic,109987.0.html
http://code.google.com/p/arduino/issues/detail?id=958
* ========================================================================= */
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_QUATERNION" if you want to see the actual
// quaternion components in a [w, x, y, z] format (not best for parsing
// on a remote host such as Processing or something though)
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_QUATERNION
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_EULER" if you want to see Euler angles
// (in degrees) calculated from the quaternions coming from the FIFO.
// Note that Euler angles suffer from gimbal lock (for more info, see
// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gimbal_lock)
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_EULER
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL" if you want to see the yaw/
// pitch/roll angles (in degrees) calculated from the quaternions coming
// from the FIFO. Note this also requires gravity vector calculations.
// Also note that yaw/pitch/roll angles suffer from gimbal lock (for
// more info, see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gimbal_lock)
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_REALACCEL" if you want to see acceleration
// components with gravity removed. This acceleration reference frame is
// not compensated for orientation, so +X is always +X according to the
// sensor, just without the effects of gravity. If you want acceleration
// compensated for orientation, us OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL instead.
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_REALACCEL
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL" if you want to see acceleration
// components with gravity removed and adjusted for the world frame of
// reference (yaw is relative to initial orientation, since no magnetometer
// is present in this case). Could be quite handy in some cases.
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL
// uncomment "OUTPUT_TEAPOT" if you want output that matches the
// format used for the InvenSense teapot demo
#define OUTPUT_TEAPOT
#define INTERRUPT_PIN 5 // use pin 2 on Arduino Uno & most boards
#define LED_PIN 2 // (Arduino is 13, Teensy is 11, Teensy++ is 6)
bool blinkState = false;
// MPU control/status vars
bool dmpReady = false; // set true if DMP init was successful
uint8_t mpuIntStatus; // holds actual interrupt status byte from MPU
uint8_t devStatus; // return status after each device operation (0 = success, !0 = error)
uint16_t packetSize; // expected DMP packet size (default is 42 bytes)
uint16_t fifoCount; // count of all bytes currently in FIFO
uint8_t fifoBuffer[64]; // FIFO storage buffer
// orientation/motion vars
Quaternion q; // [w, x, y, z] quaternion container
VectorInt16 aa; // [x, y, z] accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaReal; // [x, y, z] gravity-free accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaWorld; // [x, y, z] world-frame accel sensor measurements
VectorFloat gravity; // [x, y, z] gravity vector
float euler[3]; // [psi, theta, phi] Euler angle container
float ypr[3]; // [yaw, pitch, roll] yaw/pitch/roll container and gravity vector
// packet structure for InvenSense teapot demo
uint8_t teapotPacket[14] = '$', 0x02, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0x00, 0x00, '\\r', '\\n' ;
// ================================================================
// === INTERRUPT DETECTION ROUTINE ===
// ================================================================
volatile bool mpuInterrupt = false; // indicates whether MPU interrupt pin has gone high
void dmpDataReady()
mpuInterrupt = true;
// ================================================================
// === INITIAL SETUP ===
// ================================================================
void setup()
// join I2C bus (I2Cdev library doesn't do this automatically)
//#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
Wire.begin(4,15);
Wire.setClock(400000); // 400kHz I2C clock. Comment this line if having compilation difficulties
// #elif I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_BUILTIN_FASTWIRE
// Fastwire::setup(400, true);
// #endif
// initialize serial communication
// (115200 chosen because it is required for Teapot Demo output, but it's
// really up to you depending on your project)
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial); // wait for Leonardo enumeration, others continue immediately
// NOTE: 8MHz or slower host processors, like the Teensy @ 3.3V or Arduino
// Pro Mini running at 3.3V, cannot handle this baud rate reliably due to
// the baud timing being too misaligned with processor ticks. You must use
// 38400 or slower in these cases, or use some kind of external separate
// crystal solution for the UART timer.
// initialize device
Serial.println(F("Initializing I2C devices..."));
mpu.initialize();
pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT);
// verify connection
Serial.println(F("Testing device connections..."));
Serial.println(mpu.testConnection() ? F("MPU6050 connection successful") : F("MPU6050 connection failed"));
// wait for ready
Serial.println(F("\\nSend any character to begin DMP programming and demo: "));
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer
while (!Serial.available()); // wait for data
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer again
// load and configure the DMP
Serial.println(F("Initializing DMP..."));
devStatus = mpu.dmpInitialize();
// supply your own gyro offsets here, scaled for min sensitivity
mpu.setXGyroOffset(220);
mpu.setYGyroOffset(76);
mpu.setZGyroOffset(-85);
mpu.setZAccelOffset(1788); // 1688 factory default for my test chip
// make sure it worked (returns 0 if so)
if (devStatus == 0)
// Calibration Time: generate offsets and calibrate our MPU6050
mpu.CalibrateAccel(6);
mpu.CalibrateGyro(6);
mpu.PrintActiveOffsets();
// turn on the DMP, now that it's ready
Serial.println(F("Enabling DMP..."));
mpu.setDMPEnabled(true);
// enable Arduino interrupt detection
Serial.print(F("Enabling interrupt detection (Arduino external interrupt "));
Serial.print(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN));
Serial.println(F(")..."));
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN), dmpDataReady, RISING);
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
// set our DMP Ready flag so the main loop() function knows it's okay to use it
Serial.println(F("DMP ready! Waiting for first interrupt..."));
dmpReady = true;
// get expected DMP packet size for later comparison
packetSize = mpu.dmpGetFIFOPacketSize();
else
// ERROR!
// 1 = initial memory load failed
// 2 = DMP configuration updates failed
// (if it's going to break, usually the code will be 1)
Serial.print(F("DMP Initialization failed (code "));
Serial.print(devStatus);
Serial.println(F(")"));
// configure LED for output
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
// ================================================================
// === MAIN PROGRAM LOOP ===
// ================================================================
void loop()
// if programming failed, don't try to do anything
if (!dmpReady) return;
// wait for MPU interrupt or extra packet(s) available
while (!mpuInterrupt && fifoCount < packetSize)
if (mpuInterrupt && fifoCount < packetSize)
// try to get out of the infinite loop
fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
// other program behavior stuff here
// .
// .
// .
// if you are really paranoid you can frequently test in between other
// stuff to see if mpuInterrupt is true, and if so, "break;" from the
// while() loop to immediately process the MPU data
// .
// .
// .
// reset interrupt flag and get INT_STATUS byte
mpuInterrupt = false;
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
// get current FIFO count
fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
if(fifoCount < packetSize)
//Lets go back and wait for another interrupt. We shouldn't be here, we got an interrupt from another event
// This is blocking so don't do it while (fifoCount < packetSize) fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
// check for overflow (this should never happen unless our code is too inefficient)
else if ((mpuIntStatus & (0x01 << MPU6050_INTERRUPT_FIFO_OFLOW_BIT)) || fifoCount >= 1024)
// reset so we can continue cleanly
mpu.resetFIFO();
// fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount(); // will be zero after reset no need to ask
Serial.println(F("FIFO overflow!"));
// otherwise, check for DMP data ready interrupt (this should happen frequently)
else if (mpuIntStatus & (0x01 << MPU6050_INTERRUPT_DMP_INT_BIT))
// read a packet from FIFO
while(fifoCount >= packetSize) // Lets catch up to NOW, someone is using the dreaded delay()!
mpu.getFIFOBytes(fifoBuffer, packetSize);
// track FIFO count here in case there is > 1 packet available
// (this lets us immediately read more without waiting for an interrupt)
fifoCount -= packetSize;
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_QUATERNION
// display quaternion values in easy matrix form: w x y z
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
Serial.print("quat\\t");
Serial.print(q.w);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(q.x);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(q.y);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(q.z);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_EULER
// display Euler angles in degrees
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetEuler(euler, &q);
Serial.print("euler\\t");
Serial.print(euler[0] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(euler[1] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(euler[2] * 180/M_PI);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
// display Euler angles in degrees
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity);
Serial.print("ypr\\t");
Serial.print(ypr[0] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(ypr[1] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(ypr[2] * 180/M_PI);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_REALACCEL
// display real acceleration, adjusted to remove gravity
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetAccel(&aa, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetLinearAccel(&aaReal, &aa, &gravity);
Serial.print("areal\\t");
Serial.print(aaReal.x);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(aaReal.y);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(aaReal.z);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL
// display initial world-frame acceleration, adjusted to remove gravity
// and rotated based on known orientation from quaternion
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetAccel(&aa, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetLinearAccel(&aaReal, &aa, &gravity);
mpu.dmpGetLinearAccelInWorld(&aaWorld, &aaReal, &q);
Serial.print("aworld\\t");
Serial.print(aaWorld.x);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.print(aaWorld.y);
Serial.print("\\t");
Serial.println(aaWorld.z);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_TEAPOT
// display quaternion values in InvenSense Teapot demo format:
teapotPacket[2] = fifoBuffer[0];
teapotPacket[3] = fifoBuffer[1];
teapotPacket[4] = fifoBuffer[4];
teapotPacket[5] = fifoBuffer[5];
teapotPacket[6] = fifoBuffer[8];
teapotPacket[7] = fifoBuffer[9];
teapotPacket[8] = fifoBuffer[12];
teapotPacket[9] = fifoBuffer[13];
Serial.write(teapotPacket, 14);
teapotPacket[11]++; // packetCount, loops at 0xFF on purpose
#endif
// blink LED to indicate activity
blinkState = !blinkState;
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, blinkState);
processing
import processing.serial.*;
import processing.opengl.*;
import toxi.geom.*;
import toxi.processing.*;
// NOTE: requires ToxicLibs to be installed in order to run properly.
// 1. Download from http://toxiclibs.org/downloads
// 2. Extract into [userdir]/Processing/libraries
// (location may be different on Mac/Linux)
// 3. Run and bask in awesomeness
ToxiclibsSupport gfx;
Serial port; // The serial port
char[] teapotPacket = new char[14]; // InvenSense Teapot packet
int serialCount = 0; // current packet byte position
int synced = 0;
int interval = 0;
float[] q = new float[4];
Quaternion quat = new Quaternion(1, 0, 0, 0);
float[] gravity = new float[3];
float[] euler = new float[3];
float[] ypr = new float[3];
void setup()
// 300px square viewport using OpenGL rendering
size(600, 600, OPENGL);
// textFont(createFont("SourceCodePro-Regular.ttf",24));
gfx = new ToxiclibsSupport(this);
// setup lights and antialiasing
lights();
smooth();
// display serial port list for debugging/clarity
println(Serial.list());
// get the first available port (use EITHER this OR the specific port code below)
String portName = Serial.list()[0];
// get a specific serial port (use EITHER this OR the first-available code above)
//String portName = "COM4";
// open the serial port
port = new Serial(this, "/dev/ttyUSB1", 115200);
// send single character to trigger DMP init/start
// (expected by MPU6050_DMP6 example Arduino sketch)
port.write('r');
void draw()
if (millis() - interval > 1000)
// resend single character to trigger DMP init/start
// in case the MPU is halted/reset while applet is running
port.write('r');
interval = millis();
// black background
background(0);
// translate everything to the middle of the viewport
pushMatrix();
translate(width / 2, height / 2);
// 3-step rotation from yaw/pitch/roll angles (gimbal lock!)
// ...and other weirdness I haven't figured out yet
//rotateY(-ypr[0]);
//rotateZ(-ypr[1]);
//rotateX(-ypr[2]);
// toxiclibs direct angle/axis rotation from quaternion (NO gimbal lock!)
// (axis order [1, 3, 2] and inversion [-1, +1, +1] is a consequence of
// different coordinate system orientation assumptions between Processing
// and InvenSense DMP)
float[] axis = quat.toAxisAngle();
rotate(axis[0], -axis[1], axis[3], axis[2]);
// draw main body in red
fill(255, 0, 0, 200);
box(10, 10, 200);
// draw front-facing tip in blue
fill(0, 0, 255, 200);
pushMatrix();
translate(0, 0, -120);
rotateX(PI/2);
drawCylinder(0, 20, 20, 8);
popMatrix();
// draw wings and tail fin in green
fill(0, 255, 0, 200);
beginShape(TRIANGLES);
vertex(-100, 2, 30); vertex(0, 2, -80); vertex(100, 2, 30); // wing top layer
vertex(-100, -2, 30); vertex(0, -2, -80); vertex(100, -2, 30); // wing bottom layer
vertex(-2, 0, 98); vertex(-2, -30, 98); vertex(-2, 0, 70); // tail left layer
vertex( 2, 0, 98); vertex( 2, -30, 98); vertex( 2, 0, 70); // tail right layer
endShape();
beginShape(QUADS);
vertex(-100, 2, 30); vertex(-100, -2, 30); vertex( 0, -2, -80); vertex( 0, 2, -80);
vertex( 100, 2, 30); vertex( 100, -2, 30); vertex( 0, -2, -80); vertex( 0, 2, -80);
vertex(-100, 2, 30); vertex(-100, -2, 30); vertex(100, -2, 30); vertex(100, 2, 30);
vertex(-2, 0, 98); vertex(2, 0, 98); vertex(2, -30, 98); vertex(-2, -30, 98);
vertex(-2, 0, 98); vertex(2, 0, 98); vertex(2, 0, 70); vertex(-2, 0, 70);
vertex(-2, -30, 98); vertex(2, -30, 98); vertex(2, 0, 70); vertex(-2, 0, 70);
endShape();
popMatrix();
text("The value of variable 0 is " + q[0], 50, 400);
text("The value of variable 1 is " + q[1], 50, 450);
text("The value of variable 2 is " + q[2], 50, 500);
text("The value of variable 3 is " + q[3], 50, 550);
void serialEvent(Serial port)
interval = millis();
while (port.available() > 0)
int ch = port.read();
if (synced == 0 && ch != '$') return; // initial synchronization - also used to resync/realign if needed
synced = 1;
print ((char)ch);
if ((serialCount == 1 && ch != 2)
|| (serialCount == 12 && ch != '\\r')
|| (serialCount == 13 && ch != '\\n'))
serialCount = 0;
synced = 0;
return;
if (serialCount > 0 || ch == '$')
teapotPacket[serialCount++] = (char)ch;
if (serialCount == 14)
serialCount = 0; // restart packet byte position
// get quaternion from data packet
q[0] = ((teapotPacket[2] << 8) | teapotPacket[3]) / 16384.0f;
q[1] = ((teapotPacket[4] << 8) | teapotPacket[5]) / 16384.0f;
q[2] = ((teapotPacket[6] << 8) | teapotPacket[7]) / 16384.0f;
q[3] = ((teapotPacket[8] << 8) | teapotPacket[9]) / 16384.0f;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) if (q[i] >= 2) q[i] = -4 + q[i];
// set our toxilibs quaternion to new data
quat.set(q[0], q[1], q[2], q[3]);
// below calculations unnecessary for orientation only using toxilibs
// calculate gravity vector
gravity[0] = 2 * (q[1]*q[3] - q[0]*q[2]);
gravity[1] = 2 * (q[0]*q[1] + q[2]*q[3]);
gravity[2] = q[0]*q[0] - q[1]*q[1] - q[2]*q[2] + q[3]*q[3];
// calculate Euler angles
euler[0] = atan2(2*q[1]*q[2] - 2*q[0]*q[3], 2*q[0]*q[0] + 2*q[1]*q[1] - 1);
euler[1] = -asin(2*q[1]*q[3] + 2*q[0]*q[2]);
euler[2] = atan2(2*q[2]*q[3] - 2*q[0]*q[1], 2*q[0]*q[0] + 2*q[3]*q[3] - 1);
// calculate yaw/pitch/roll angles
ypr[0] = atan2(2*q[1]*q[2] - 2*q[0]*q[3], 2*q[0]*q[0] + 2*q[1]*q[1] - 1);
ypr[1] = atan(gravity[0] / sqrt(gravity[1]*gravity[1] + gravity[2]*gravity[2]));
ypr[2] = atan(gravity[1] / sqrt(gravity[0]*gravity[0] + gravity[2]*gravity[2]));
// output various components for debugging
println("q:\\t" + round(q[0]*100.0f)/100.0f + "\\t" + round(q[1]*100.0f)/100.0f + "\\t" + round(q[2]*100.0f)/100.0f + "\\t" + round(q[3]*100.0f)/100.0f);
println("euler:\\t" + euler[0]*180.0f/PI + "\\t" + euler[1]*180.0f/PI + "\\t" + euler[2]*180.0f/PI);
println("ypr:\\t" + ypr[0]*180.0f/PI + "\\t" + ypr[1]*180.0f/PI + "\\t" + ypr[2]*180.0f/PI);
void drawCylinder(float topRadius, float bottomRadius, float tall, int sides)
float angle = 0;
float angleIncrement = TWO_PI / sides;
beginShape(QUAD_STRIP);
for (int i = 0; i < sides + 1; ++i)
vertex(topRadius*cos(angle), 0, topRadius*sin(angle));
vertex(bottomRadius*cos(angle), tall, bottomRadius*sin(angle));
angle += angleIncrement;
endShape();
// If it is not a cone, draw the circular top cap
if (topRadius != 0)
angle = 0;
beginShape(TRIANGLE_FAN);
// Center point
vertex(0, 0, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < sides + 1; i++)
vertex(topRadius * cos(angle), 0, topRadius * sin(angle));
angle += angleIncrement;
endShape();
// If it is not a cone, draw the circular bottom cap
if (bottomRadius != 0)
angle = 0;
beginShape(TRIANGLE_FAN);
// Center point
vertex(0, tall, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < sides + 1; i++)
vertex(bottomRadius * cos(angle), tall, bottomRadius * sin(angle));
angle += angleIncrement;
endShape();
以上是关于基于ubuntu环境,搭建Arduino+ESP32+MPU6050验证系统,并利用Processing仿真的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章