leetcode之回溯刷题总结1
Posted nuist__NJUPT
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了leetcode之回溯刷题总结1相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
leetcode之回溯刷题总结1
回溯法:一种通过探索所有可能的候选解来找出所有的解的算法。如果候选解被确认不是一个解(或者至少不是最后一个解),回溯算法会通过在上一步进行一些变化抛弃该解,即回溯并且再次尝试。
1-全排列
题目链接:题目链接戳这里!!!
思路:这个问题可以看作有 n 个排列成一行的空格,我们需要从左往右依此填入题目给定的 n 个数,每个数只能使用一次。那么很直接的可以想到一种穷举的算法,即从左往右每一个位置都依此尝试填入一个数,看能不能填完这 n 个空格,在程序中我们可以用「回溯法」来模拟这个过程。
我们定义递归函数full(k, nums) 表示从左往右填到第k个位置,如果填到最后一个位置,则代表一个排列,存入集合。
如果 k==nums.length,说明我们已经填完了 n个位置(注意下标从 0 开始),找到了一个可行的解,我们将当前排列放入答案数组中,递归结束。
如果 k<nums.length,我们要考虑这第 k 个位置我们要填哪个数。根据题目要求我们肯定不能填已经填过的数,因此很容易想到的一个处理手段是我们定义一个标记数组vis[] 来标记已经填过的数,那么在填第k 个数的时候我们遍历题目给定的 n 个数,如果这个数没有被标记过,我们就尝试填入,并将其标记,继续尝试填下一个位置,即调用函数full。回溯的时候要撤销这一个位置填的数以及标记,并继续尝试其他没被标记过的数。
AC代码如下:
class Solution
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>() ;
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>() ;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums)
full(0,nums) ;
return res ;
public void full(int k, int [] nums)
if(k==nums.length)
for(int t : nums)
temp.add(t) ;
res.add(temp) ;
temp = new ArrayList<>() ;
for(int i=k; i<nums.length; i++)
swap(nums, i,k) ;
full(k+1,nums) ;
swap(nums, i,k) ;
public void swap(int [] nums, int i, int k)
int temp = nums[i] ;
nums[i] = nums[k] ;
nums[k] = temp ;

当然这样写的话,看着更舒服,提前把数组变成集合。
不过这个效率反而低一点。
class Solution
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>() ;
List<Integer> output = new ArrayList<>() ;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums)
int n = nums.length ;
for(int num : nums)
output.add(num) ;
full(0,output,n) ;
return res ;
public void full(int k, List<Integer> output, int n)
if(k==n)
res.add(new ArrayList<>(output)) ;
for(int i=k; i<n; i++)
Collections.swap(output, i,k) ;
full(k+1,output,n) ;
Collections.swap(output, i,k) ;
2-全排列II
题目链接:题目链接戳这里!!!
思路:
我们定义递归函数f,表示当前排列为 temp,下一个待填入的位置是第k 个位置(下标从 0 开始)。那么整个递归函数分为两个情况:
如果 k==n,说明我们已经填完了 n 个位置,找到了一个可行的解,我们将temp放入答案数组中,递归结束。
如果 k<n,我们要考虑第k 个位置填哪个数。根据题目要求我们肯定不能填已经填过的数,因此很容易想到的一个处理手段是我们定义一个标记数组 vis 来标记已经填过的数,那么在填第k 个数的时候我们遍历题目给定的 n 个数,如果这个数没有被标记过,我们就尝试填入,并将其标记,继续尝试填下一个位置,即调用函数 f。搜索回溯的时候要撤销该个位置填的数以及标记,并继续尝试其他没被标记过的数。
要解决重复问题,我们只要设定一个规则,保证在填第 k
个数的时候重复数字只会被填入一次即可.
class Solution
boolean [] vis ;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums)
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>() ;
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>() ;
vis = new boolean[nums.length] ;
Arrays.sort(nums) ;
f(res,0,temp,nums) ;
return res ;
public void f(List<List<Integer>> res, int k, List<Integer> temp, int [] nums)
if(k==nums.length)
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp)) ;
return ;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++)
if(vis[i] || (i-1>=0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1] && !vis[i-1]))
continue ;
temp.add(nums[i]) ;
vis[i] = true ;
f(res, k+1, temp, nums) ;
vis[i] = false ;
temp.remove(k) ;
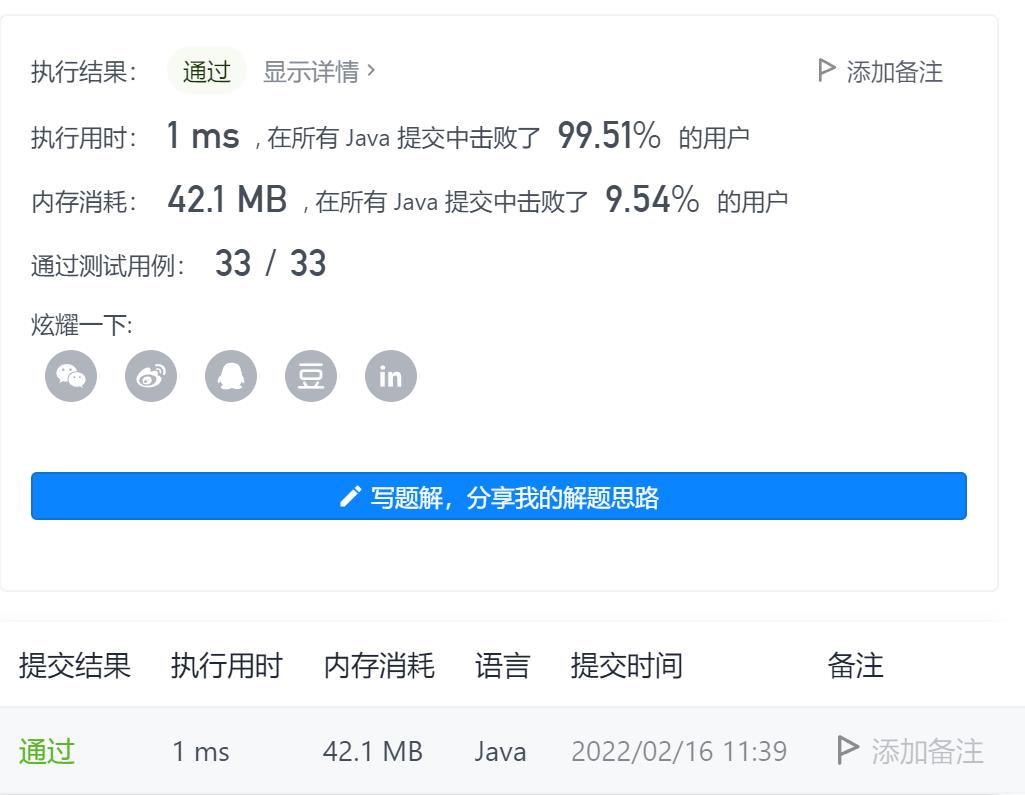
3-组合种数
题目链接:题目链接戳这里!!!
思路:搜索+剪支+回溯
1、遍历数组中的每一个数字。
2、递归枚举每一个数字可以选多少次,递归过程中维护一个target变量。如果当前数字小于等于target,我们就将其加入我们的路径数组temp中,相应的target减去当前数字的值。也就是说,每选一个分支,就减去所选分支的值。
3、当target == 0时,表示该选择方案是合法的,记录该方案,将其加入res数组中。
class Solution
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>() ;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target)
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>() ;
backTrace(candidates,target,0, temp) ;
return res ;
public void backTrace(int [] candidates, int target, int k, List<Integer> temp)
if(target<0)
return ;
if(target==0)
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp)) ;
return ;
for(int i=k; i<candidates.length; i++)
temp.add(candidates[i]) ;
backTrace(candidates,target-candidates[i],i,temp) ;
temp.remove(temp.size()-1) ;

4-总和种数II
题目链接:题目链接戳这里!!!
思路:搜索+回溯
搜索所有满足条件的数字,每个数字只用一次,如果在有序情况下出现重复使用的数字,则中止当前递归,否则后面递归得到的回有重复的集合。
class Solution
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>() ;
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>() ;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target)
Arrays.sort(candidates) ;
dfs(candidates,target,0) ;
return res ;
public void dfs(int [] candidates, int target, int k)
if(target<0)
return ;
if(target==0)
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)) ;
return ;
for(int i=k; i<candidates.length; i++)
if(i-1>=k && candidates[i]==candidates[i-1])
continue ;
path.add(candidates[i]) ;
dfs(candidates,target-candidates[i],i+1) ;
path.remove(path.size()-1) ;

5-电话号码的字母组合
题目链接:题目链接戳这里!!!
思路:对应数字映射成字符串,搜索每个键对应的值,添加到combination中,直到字符串搜索完,将当前组合combination放入集合combinations,每次搜索完成回溯到原始状态。
class Solution
List<String> combinations = new ArrayList<>() ;
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits)
if(digits.length()==0)
return combinations ;
Map<Character,String> map = new HashMap<>() ;
map.put('2',"abc") ;
map.put('3',"def") ;
map.put('4',"ghi") ;
map.put('5',"jkl") ;
map.put('6',"mno") ;
map.put('7', "pqrs") ;
map.put('8',"tuv") ;
map.put('9',"wxyz");
dfs(map,combinations,0,digits, new StringBuilder()) ;
return combinations ;
public void dfs(Map<Character,String> map, List<String> combinations, int k, String digits, StringBuilder combination)
if(k==digits.length())
combinations.add(combination.toString()) ;
else
char key = digits.charAt(k) ;
String s = map.get(key) ;
for(int i=0; i<s.length(); i++)
combination.append(s.charAt(i)) ;
dfs(map,combinations,k+1,digits, combination) ;
combination.deleteCharAt(k) ;

6-组合
题目链接:题目链接戳这里!!!
思路:搜索并记录路径,每轮搜索完,需要将组合数存入res集合,同时需要回溯到原始状态。
class Solution
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>() ;
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>() ;
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k)
dfs(n,k,1) ;
return res ;
public void dfs(int n, int k, int idx)
if(path.size()==k)
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)) ;
return ;
for(int i=idx; i<=n; i++)
path.add(i) ;
dfs(n,k,i+1) ;
path.remove(path.size()-1) ;
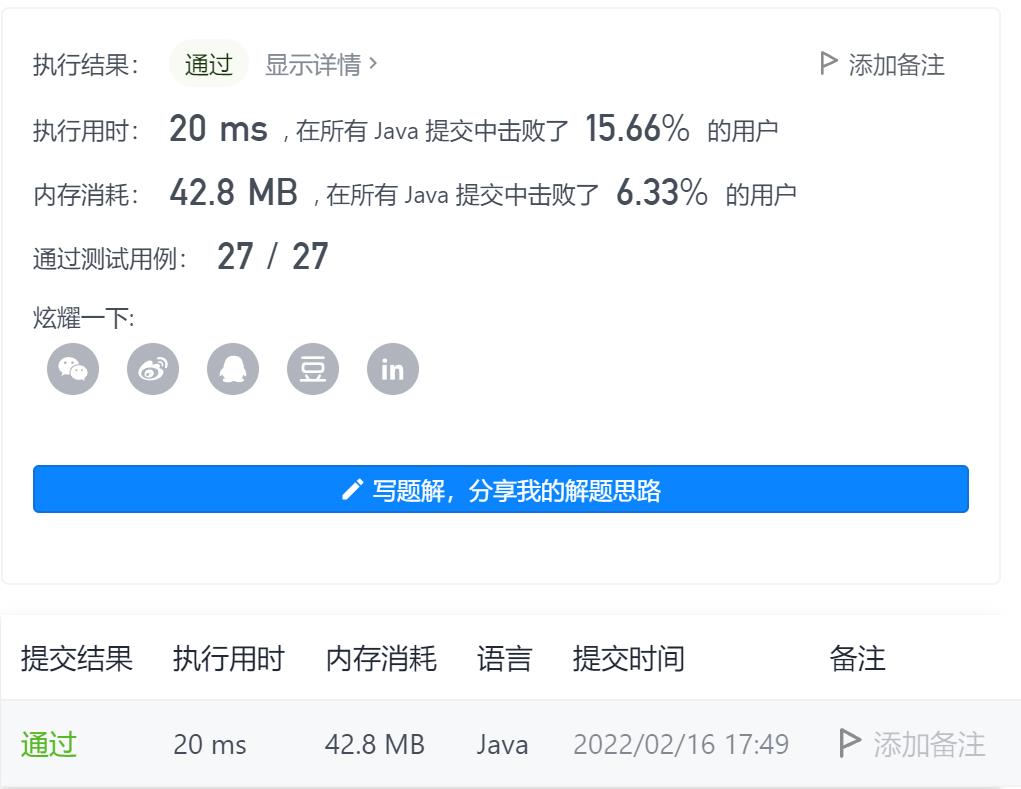
7-子集
题目链接:题目链接戳这里!!!
思路1:从钱向后遍历数组,每次将数组元素加到已有子集中去形成新的子集,新的子集继续存入res集合,直至遍历结束。
class Solution
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums)
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>() ;
res.add(new ArrayList<>()) ;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++)
int len = res.size() ;
for(int j=0; j<len; j++)
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>(res.get(j)) ;
temp.add(nums[i]) ;
res.add(temp) ;
return res ;

思路2:搜索+回溯
dfs(cur,nums) 参数表示当前位置是cur,原序列为nums。原序列的每个位置在答案序列中的状态有被选中和不被选中两种,我们用 temp 数组存放已经被选出的数字。
对于cur 位置,我们需要考虑 nums[cur] 取或者不取,如果取,我们需要把nums[cur] 放入一个临时的答案数组中(即上面代码中的 temp),再执行dfs(cur+1,nums),执行结束后
以上是关于leetcode之回溯刷题总结1的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章