高性能并行编程与优化 | 第04讲回家作业
Posted yantuguiguziPGJ
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了高性能并行编程与优化 | 第04讲回家作业相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录

一 题目4
# 高性能并行编程与优化 - 第04讲的回家作业
通过 pull request 提交作业。会批分数,但是:
没有结业证书,回家作业仅仅作为评估学习效果和巩固知识的手段,不必为分数感到紧张 :)
量力而行,只要能在本课中,学到昨天的自己不懂的知识,就是胜利,没必要和别人攀比。
注意不要偷看别人的作业哦!
- 课件:https://github.com/parallel101/course
- 录播:https://space.bilibili.com/263032155
作业提交时间不限 :) 即使完结了还想交的话我也会看的~ 不过最好在下一讲开播前完成。
- 如何开 pull request:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/51199833
- 如何设置 https 代理:https://www.jianshu.com/p/b481d2a42274
## 评分规则
- 在你的电脑上加速了多少倍,就是多少分!请在 PR 描述中写明加速前后的用时数据。
- 最好详细解释一下为什么这样可以优化。会额外以乘法的形式加分。
- 比如你优化后加速了 50 倍,讲的很详细,所以分数乘 2,变成 100 分!
- 比如你优化后加速了 1000 倍,但是你的 PR 描述是空,所以分数乘 0,变成 0 分!
## 作业要求
利用这次课上所学知识,修改 main.cpp,优化其中的多体引力求解器:
- 不允许使用多线程并行
- 不允许做算法复杂度优化
- 可以针对编译器和平台优化,这次不要求跨平台
- 可以用 xmmintrin.h,如果你觉得编译器靠不住的话
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
#include <cmath>
float frand()
return (float)rand() / RAND_MAX * 2 - 1;
struct Star
float px, py, pz;
float vx, vy, vz;
float mass;
;
std::vector<Star> stars;
void init()
for (int i = 0; i < 48; i++)
stars.push_back(
frand(), frand(), frand(),
frand(), frand(), frand(),
frand() + 1,
);
float G = 0.001;
float eps = 0.001;
float dt = 0.01;
void step()
for (auto &star: stars)
for (auto &other: stars)
float dx = other.px - star.px;
float dy = other.py - star.py;
float dz = other.pz - star.pz;
float d2 = dx * dx + dy * dy + dz * dz + eps * eps;
d2 *= sqrt(d2);
star.vx += dx * other.mass * G * dt / d2;
star.vy += dy * other.mass * G * dt / d2;
star.vz += dz * other.mass * G * dt / d2;
for (auto &star: stars)
star.px += star.vx * dt;
star.py += star.vy * dt;
star.pz += star.vz * dt;
float calc()
float energy = 0;
for (auto &star: stars)
float v2 = star.vx * star.vx + star.vy * star.vy + star.vz * star.vz;
energy += star.mass * v2 / 2;
for (auto &other: stars)
float dx = other.px - star.px;
float dy = other.py - star.py;
float dz = other.pz - star.pz;
float d2 = dx * dx + dy * dy + dz * dz + eps * eps;
energy -= other.mass * star.mass * G / sqrt(d2) / 2;
return energy;
template <class Func>
long benchmark(Func const &func)
auto t0 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
func();
auto t1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto dt = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(t1 - t0);
return dt.count();
int main()
init();
printf("Initial energy: %f\\n", calc());
auto dt = benchmark([&]
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
step();
);
printf("Final energy: %f\\n", calc());
printf("Time elapsed: %ld ms\\n", dt);
return 0;
二 原来代码运行结果
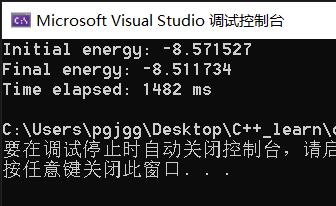
三 优秀的代码答案
//参考代码:https://github.com/parallel101/hw04/pull/3
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <immintrin.h>
#include <cassert>
float frand()
return (float)rand() / RAND_MAX * 2 - 1;
constexpr std::size_t N = 48;
constexpr float G = 0.001f;
constexpr float eps = 0.001f;
constexpr float dt = 0.01f;
constexpr float eps_sqr = eps * eps;
constexpr float G_dt = G * dt;
template<std::size_t N>
struct Star
//float px, py, pz;
//float vx, vy, vz;
//float mass;
alignas(64) float px[N], py[N], pz[N];
alignas(64) float vx[N], vy[N], vz[N];
alignas(64) float mass[N];
;
//std::vector<Star> stars;
Star<N> stars;
//void init()
// for (int i = 0; i < 48; i++)
// stars.push_back(
// frand(), frand(), frand(),
// frand(), frand(), frand(),
// frand() + 1,
// );
void init()
for (std::size_t i; i < N; ++i)
stars.px[i] = frand(), stars.py[i] = frand(), stars.pz[i] = frand();
stars.vx[i] = frand(), stars.vy[i] = frand(), stars.vz[i] = frand();
stars.mass[i] = frand() + 1;
//float G = 0.001;
//float eps = 0.001;
//float dt = 0.01;
//
//void step()
// for (auto &star: stars)
// for (auto &other: stars)
// float dx = other.px - star.px;
// float dy = other.py - star.py;
// float dz = other.pz - star.pz;
// float d2 = dx * dx + dy * dy + dz * dz + eps * eps;
// d2 *= sqrt(d2);
// star.vx += dx * other.mass * G * dt / d2;
// star.vy += dy * other.mass * G * dt / d2;
// star.vz += dz * other.mass * G * dt / d2;
//
using fsimd_t = __m256;
inline auto set1(float f) return _mm256_set1_ps(f);
inline auto load(const float* f) return _mm256_load_ps(f);
inline void store(float* f, fsimd_t a) _mm256_store_ps(f, a);
inline auto add(fsimd_t a, fsimd_t b) return _mm256_add_ps(a, b);
inline auto sub(fsimd_t a, fsimd_t b) return _mm256_sub_ps(a, b);
inline auto mul(fsimd_t a, fsimd_t b) return _mm256_mul_ps(a, b);
inline auto div(fsimd_t a, fsimd_t b) return _mm256_div_ps(a, b);
inline auto sqrt(fsimd_t a) return _mm256_sqrt_ps(a);
inline auto rsqrt(fsimd_t a) return _mm256_rsqrt_ps(a);
inline auto rcp(fsimd_t a) return _mm256_rcp_ps(a);
void step_avx()
auto eps_sqr8 = set1(eps_sqr);
for (std::size_t j; j < N; ++j)
auto mg_dt = set1(G * stars.mass[j] * dt);
auto xj = set1(stars.px[j]);
auto yj = set1(stars.py[j]);
auto zj = set1(stars.pz[j]);
auto unroll_body = [&](std::size_t i)
auto xi = load(&stars.px[i]);
auto yi = load(&stars.py[i]);
auto zi = load(&stars.pz[i]);
auto dx = sub(xj, xi);
auto dy = sub(yj, yi);
auto dz = sub(zj, zi);
auto x2 = mul(dx, dx);
auto y2 = mul(dy, dy);
auto z2 = mul(dz, dz);
auto d2 = add(add(x2, y2), add(z2, eps_sqr8));
auto inv_d2 = rcp(d2);
auto inv_d = rsqrt(d2);
auto mg_dt_invd3 = mul(mul(mg_dt, inv_d2), inv_d);
auto vx = load(&stars.vx[i]);
auto vy = load(&stars.vy[i]);
auto vz = load(&stars.vz[i]);
auto new_vx = add(mul(mg_dt_invd3, dx), vx);
auto new_vy = add(mul(mg_dt_invd3, dy), vy);
auto new_vz = add(mul(mg_dt_invd3, dz), vz);
store(&stars.vx[i], new_vx);
store(&stars.vy[i], new_vy);
store(&stars.vz[i], new_vz);
;
unroll_body(0);
unroll_body(8);
unroll_body(16);
unroll_body(24);
unroll_body(32);
unroll_body(40);
// for(std::size_t i ; i < N ; i += 8)
// unroll_body(i);
//
//for (auto &star: stars)
// star.px += star.vx * dt;
// star.py += star.vy * dt;
// star.pz += star.vz * dt;
for (std::size_t i; i < N; i += 8)
auto dt8 = set1(dt);
auto vx = load(&stars.vx[i]);
auto vy = load(&stars.vy[i]);
auto vz = load(&stars.vz[i]);
auto new_px = add(load(&stars.px[i]), mul(vx, dt8));
auto new_py = add(load(&stars.py[i]), mul(vy, dt8));
auto new_pz = add(load(&stars.pz[i]), mul(vz, dt8));
store(&stars.px[i], new_px);
store(&stars.py[i], new_py);
store(&stars.pz[i], new_pz);
float calc()
float energy = 0;
//for (auto &star: stars)
// float v2 = star.vx * star.vx + star.vy * star.vy + star.vz * star.vz;
// energy += star.mass * v2 / 2;
// for (auto &other: stars)
// float dx = other.px - star.px;
// float dy = other.py - star.py;
// float dz = other.pz - star.pz;
// float d2 = dx * dx + dy * dy + dz * dz + eps * eps;
// energy -= other.mass * star.mass * G / sqrt(d2) / 2;
for (std::size_t i; i < N; ++i)
float v2 = stars.vx[i] * stars.vx[i] + stars.vy[i] * stars.vy[i] + stars.vz[i] * stars.vz[i];
energy += stars.mass[i] * v2 / 2;
for (std::size_t j; j < N; ++j)
float dx = stars.px[j] - stars.px[i];
float dy = stars.py[j] - stars.py[i];
float dz = stars.pz[j] - stars.pz[i];
float d2 = dx * dx + dy * dy + dz * dz + eps * eps;
energy -= stars.mass[j] * stars.mass[i] * G / std::sqrt(d2) / 2;
return energy;
template <class Func>
//long benchmark(Func const &func)
auto benchmark(Func const& func)
auto t0 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
func();
auto t1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto dt = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(t1 - t0);
return dt.count();
int main()
init();
//printf("Initial energy: %f\\n", calc());
std::cout << "Initial energy: " << calc() << std::endl;
auto dt = benchmark([&]
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
//step();
step_avx();
);
//printf("Final energy: %f\\n", calc());
//printf("Time elapsed: %ld ms\\n", dt);
std::cout << "Final energy: " << calc() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Time elapsed: " << dt << " ms" << std::endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.12)
project(hellocmake LANGUAGES CXX)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
if (NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
endif()
add_executable(main main.cpp)
if(MSVC)
target_compile_options(main PUBLIC /arch:AVX2 /fp:fast /O2 /openmp:experimental)
else()
target_compile_options(main PUBLIC -ffast-math -march=native -O3)
endif()BUILD_TPYE=RelWithDebInfo
cmake . -B build \\
-DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=C:/zeno/vcpkg/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake \\
-DVCPKG_TARGET_TRIPLET=x64-windows-static \\
-DCMAKE_MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY="MultiThreaded$<$<CONFIG:Debug>:Debug>"
cmake --build build --config $BUILD_TPYE
echo "================= Baseline =================="
./baseline
echo "================= Optimized ================="
./build/$BUILD_TPYE/main.exe
echo "================== Finish ==================="
四 优秀的运行结果和解答
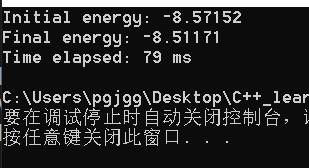
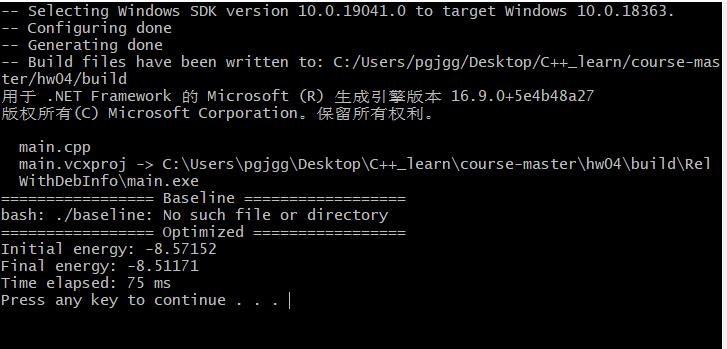
以上是关于高性能并行编程与优化 | 第04讲回家作业的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
 https://github.com/parallel101/hw04/pull/3
https://github.com/parallel101/hw04/pull/3