数据结构与算法之深入解析“合并两个有序链表”的求解思路与算法示例
Posted Serendipity·y
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构与算法之深入解析“合并两个有序链表”的求解思路与算法示例相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、题目要求
- 将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
- 示例 1:
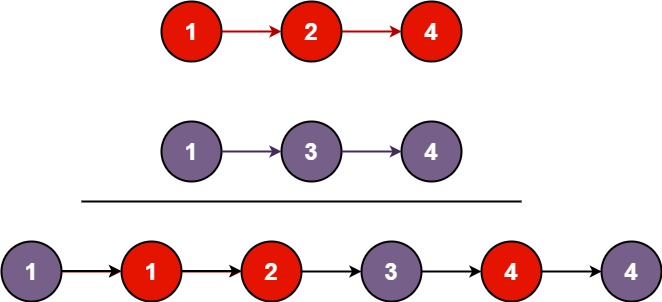
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
- 示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
- 示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
- 提示:
-
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是 [0, 50];
-
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100;
-
- l1 和 l2 均按非递减顺序排列。
二、求解算法
① 将 list2 插入 list1
- 遍历 list1,找到 list1 中需要插入 list2 片段的位置 toInsertPre;
- 转向 list2,找到 list2 中应该被插入 list1 中 toInsertPre 位置的最长片段,止分用 toInsertBeg & toInsertEnd 来标记该片段的起止;
- 将该片段 [toInsertBeg, toInsertEnd] 插入 toInsertPre 中;
- 重置 toInsertBeg & toInsertEnd,重复前三步开始下一轮查找 + 插入。
- 注意:
-
- list1 所有元素均小于 list2 中元素;
-
- list2 所有元素均小于 list1 中元素;
-
- list2 中存在比 list1 第一个元素更小的元素。
- Swift 示例:
func mergeTwoLists(_ list1: ListNode?, _ list2: ListNode?) -> ListNode?
if list1 == nil
return list2
if list2 == nil
return list1
var current1 = list1
var current2 = list2
var toInsertPre: ListNode?
var toInsertBeg: ListNode?
var toInsertEnd: ListNode?
var retHead = list1
while current1 != nil && current2 != nil
if current1!.val <= current2!.val
if toInsertBeg != nil
if toInsertPre == nil
toInsertEnd?.next = current1
retHead = toInsertBeg
else
toInsertEnd?.next = toInsertPre?.next
toInsertPre?.next = toInsertBeg
toInsertBeg = nil
toInsertEnd = nil
toInsertPre = current1
current1 = current1?.next
else
if toInsertBeg == nil
toInsertBeg = current2
toInsertEnd = current2
else
toInsertEnd = toInsertEnd?.next
current2 = current2?.next
if current1 === list1
toInsertEnd?.next = current1
return toInsertBeg
if current2 === list2
toInsertPre?.next = current2
return retHead
if current1 == nil
toInsertPre?.next = current2
else
toInsertPre?.next = toInsertBeg
toInsertEnd?.next = current1
return retHead
② 将问题分解成最简单的子问题递归求解
- 先寻找递归最底层的“子问题”,在本体中,很容易想到将一个链表和空链表合并,结果一定是它本身;
- 确定递归终止条件:两个 list 中一个为 nil,则返回另一个;
- 确定递归分解子问题方式:
-
- 对比两个 list 的 head,较小的即是合并之后的 mergedHead;
-
- 将以 mergedHead.next 作为 head 的新 list 和另一个 list 进行递归合并求解得出 mergedSubList;
-
- 则 mergedSubList 的 head 就是 mergedHead 的下一个节点。
- Swift 示例:
func mergeTwoLists(_ list1: ListNode?, _ list2: ListNode?) -> ListNode?
if list1 == nil
return list2
if list2 == nil
return list1
return merge(list1, list2)
func merge(_ list1: ListNode?, _ list2: ListNode?) -> ListNode?
if list1 == nil
return list2
if list2 == nil
return list1
if list1!.val <= list2!.val
list1?.next = merge(list1?.next, list2)
return list1
else
list2?.next = merge(list1, list2?.next)
return list2
③ 遍历两个 list,每次将较小的元素拼接在单独的结果链表中
- Swift 示例:
func mergeTwoLists(_ list1: ListNode?, _ list2: ListNode?) -> ListNode?
if list1 == nil
return list2
if list2 == nil
return list1
let retHead: ListNode? = ListNode()
var retLast = retHead
var current1 = list1
var current2 = list2
while (current1 != nil && current2 != nil)
if (current1!.val <= current2!.val)
retLast?.next = current1
current1 = current1?.next
else
retLast?.next = current2
current2 = current2?.next
retLast = retLast?.next
retLast?.next = current1 == nil ? current2 : current1
return retHead
④ 递归(LeetCode 官方解法)
- 可以如下递归地定义两个链表里的 merge 操作(忽略边界情况,比如空链表等):
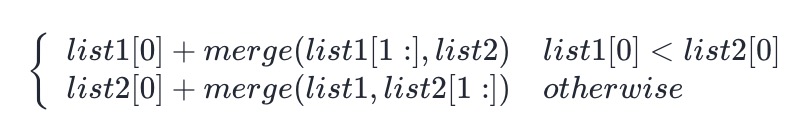
- 也就是说,两个链表头部值较小的一个节点与剩下元素的 merge 操作结果合并。
- 直接将以上递归过程建模,同时需要考虑边界情况:
-
- 如果 l1 或者 l2 一开始就是空链表 ,那么没有任何操作需要合并,所以我们只需要返回非空链表;
-
- 否则要判断 l1 和 l2 哪一个链表的头节点的值更小,然后递归地决定下一个添加到结果里的节点;
-
- 如果两个链表有一个为空,递归结束。
- Java 示例:
class Solution
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)
if (l1 == null)
return l2;
else if (l2 == null)
return l1;
else if (l1.val < l2.val)
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
else
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
- C++ 示例:
class Solution
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2)
if (l1 == nullptr)
return l2;
else if (l2 == nullptr)
return l1;
else if (l1->val < l2->val)
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
else
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
;
以上是关于数据结构与算法之深入解析“合并两个有序链表”的求解思路与算法示例的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章