Java Review - 创建线程和线程池时建议指定与业务相关的名称
Posted 小小工匠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java Review - 创建线程和线程池时建议指定与业务相关的名称相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录

概述
在日常开发中,当在一个应用中需要创建多个线程或者线程池时最好给每个线程或者线程池根据业务类型设置具体的名称,以便在出现问题时方便进行定位。
下面就通过实例来说明不设置为何难以定位问题,以及如何进行设置。
线程
不指定线程名称为何难定位问题
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2021/11/20 12:09
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
public class ThreadWithName
public static void main(String[] args)
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> System.out.println("模块A开始处理业务"));
Thread t2 = new Thread(() ->
// 模拟业务
System.out.println("模块B开始处理业务");
try
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
// 模拟异常
throw new NullPointerException();
);
t1.start();
t2.start();
如上代码分别创建了t1和t2,运行上面的代码, 【输出结果】
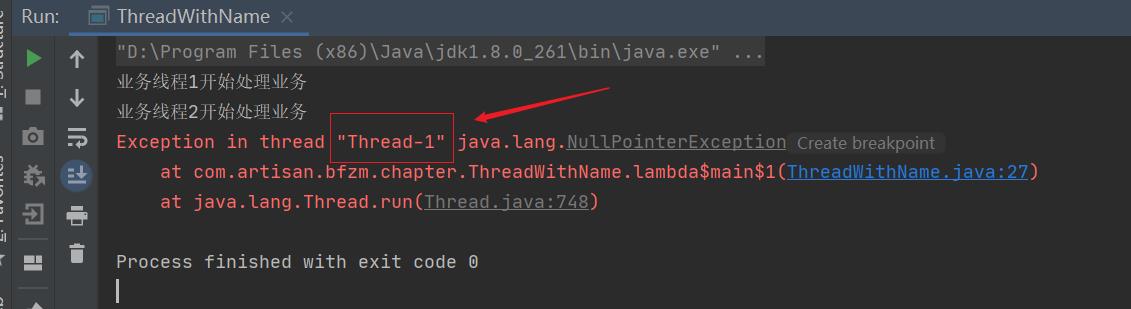
Thread默认的线程名称
从运行结果可知,Thread-1抛出了NPE异常,那么单看这个日志根本无法判断是哪个模块的的线程抛出的异常。首先我们分析下这个Thread-1是怎么来的,我们看一下创建线程时的代码。
/**
* Allocates a new @code Thread object. This constructor has the same
* effect as @linkplain #Thread(ThreadGroup,Runnable,String) Thread
* @code (null, target, gname), where @code gname is a newly generated
* name. Automatically generated names are of the form
* @code "Thread-"+<i>n</i>, where <i>n</i> is an integer.
*
* @param target
* the object whose @code run method is invoked when this thread
* is started. If @code null, this classes @code run method does
* nothing.
*/
public Thread(Runnable target)
init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
嘿 看到了吗 "Thread-" + nextThreadNum()

/* For autonumbering anonymous threads. */
private static int threadInitNumber;
private static synchronized int nextThreadNum()
return threadInitNumber++;
由此可知,threadInitNumber是static变量,nextThreadNum是static方法,所以线程的编号是全应用唯一的并且是递增的。
因为涉及多线程递增threadInitNumber,也就是执行读取—递增—写入操作,而这是线程不安全的,所以要使用方法级别的synchronized进行同步。
当一个系统中有多个业务模块而每个模块又都使用自己的线程时,除非抛出与业务相关的异常,否则你根本没法判断是哪一个模块出现了问题。现在修改代码如下。

指定线程名称
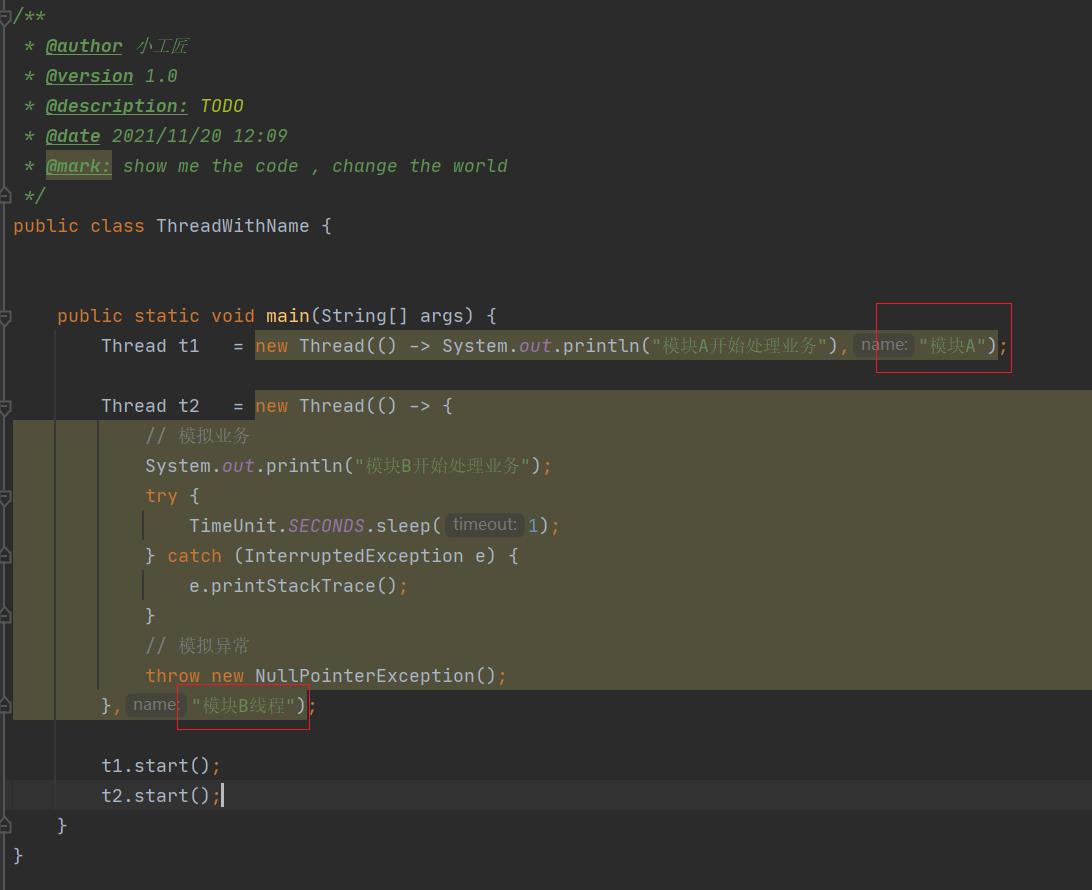
如上代码在创建线程时给线程指定了一个与具体业务模块相关的名称,运行代码,输出结果为
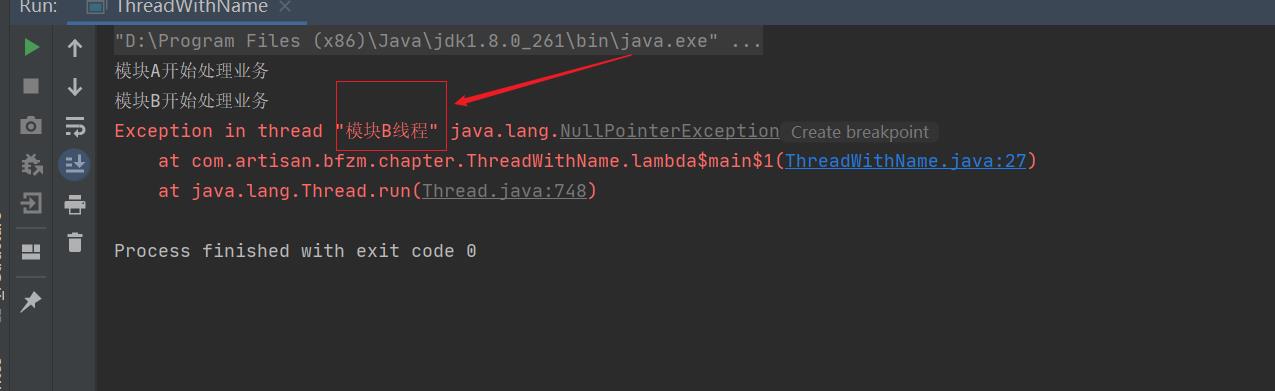
从运行结果就可以定位到是模块B抛出了NPE异常,一下子就可以找到问题所在。
线程池
不指定线程池名称为何难定位问题
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2021/11/20 12:09
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
public class ThreadPoolWithName
public static void main(String[] args)
ThreadPoolExecutor tpe1 = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,5,10,TimeUnit.MINUTES,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
ThreadPoolExecutor tpe2 = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,5,10,TimeUnit.MINUTES,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
tpe1.execute(()->System.out.println("模块A 执行业务"));
tpe2.execute(()->
System.out.println("模块B 执行业务");
// 模拟业务异常
throw new NullPointerException();
);
tpe1.shutdown();
tpe2.shutdown();
运行代码,输出结果如下
加粗样式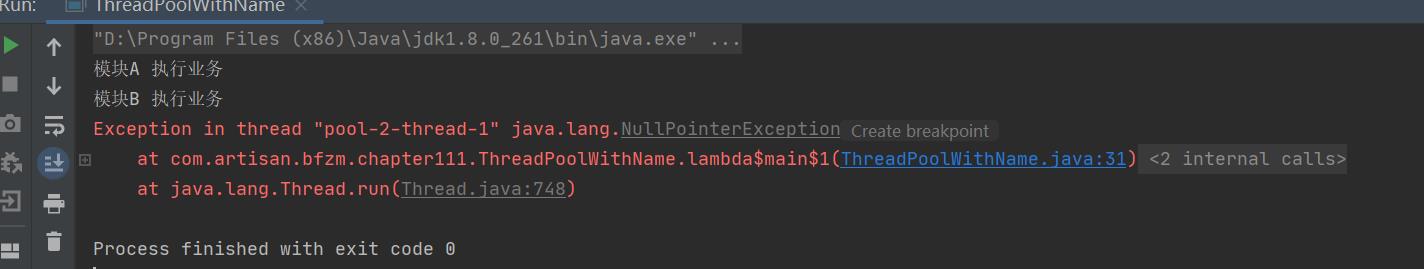
同样,我们并不知道是哪个模块的线程池抛出了这个异常,那么我们看下这个pool-2-thread-1是如何来的。
指定线程名称
其实这里使用了线程池默认的ThreadFactory,查看线程池创建的源码如下
/**
* Creates a new @code ThreadPoolExecutor with the given initial
* parameters and default thread factory and rejected execution handler.
* It may be more convenient to use one of the @link Executors factory
* methods instead of this general purpose constructor.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless @code allowCoreThreadTimeOut is set
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the @code keepAliveTime argument
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the @code Runnable
* tasks submitted by the @code execute method.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:<br>
* @code corePoolSize < 0<br>
* @code keepAliveTime < 0<br>
* @code maximumPoolSize <= 0<br>
* @code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize
* @throws NullPointerException if @code workQueue is null
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue)
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
Here we go -------------> Executors.defaultThreadFactory()
public static ThreadFactory defaultThreadFactory()
return new DefaultThreadFactory();
/**
* The default thread factory
*/
static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultThreadFactory()
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
public Thread newThread(Runnable r)
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
-
poolNumber是static的原子变量,用来记录当前线程池的编号,它是应用级别的,所有线程池共用一个,比如创建第一个线程池时线程池编号为1,创建第二个线程池时线程池的编号为2,所以pool-2-thread-1里面的pool-1中的1就是这个值
-
threadNumber是线程池级别的,每个线程池使用该变量来记录该线程池中线程的编号,所以pool-2-thread-1里面的thread-1中的1就是这个值。
-
namePrefix是线程池中线程名称的前缀,默认固定为pool。
-
具体创建线程,线程的名称是使用namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement()拼接的

自定义线程名称
由此我们知道,只需对DefaultThreadFactory的代码中的namePrefix的初始化做下手脚,即当需要创建线程池时传入与业务相关的namePrefix名称就可以了
我们看下hutool中是如何封装的
import java.lang.Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
/**
* 线程创建工厂类,此工厂可选配置:
*
* <pre>
* 1. 自定义线程命名前缀
* 2. 自定义是否守护线程
* </pre>
*
* @author looly
* @since 4.0.0
*/
public class NamedThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory
/** 命名前缀 */
private final String prefix;
/** 线程组 */
private final ThreadGroup group;
/** 线程组 */
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
/** 是否守护线程 */
private final boolean isDaemon;
/** 无法捕获的异常统一处理 */
private final UncaughtExceptionHandler handler;
/**
* 构造
*
* @param prefix 线程名前缀
* @param isDaemon 是否守护线程
*/
public NamedThreadFactory(String prefix, boolean isDaemon)
this(prefix, null, isDaemon);
/**
* 构造
*
* @param prefix 线程名前缀
* @param threadGroup 线程组,可以为null
* @param isDaemon 是否守护线程
*/
public NamedThreadFactory(String prefix, ThreadGroup threadGroup, boolean isDaemon)
this(prefix, threadGroup, isDaemon, null);
/**
* 构造
*
* @param prefix 线程名前缀
* @param threadGroup 线程组,可以为null
* @param isDaemon 是否守护线程
* @param handler 未捕获异常处理
*/
public NamedThreadFactory(String prefix, ThreadGroup threadGroup, boolean isDaemon, UncaughtExceptionHandler handler)
this.prefix = StrUtil.isBlank(prefix) ? "Hutool" : prefix;
if (null == threadGroup)
threadGroup = ThreadUtil.currentThreadGroup();
this.group = threadGroup;
this.isDaemon = isDaemon;
this.handler = handler;
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r)
final Thread t = new Thread(this.group, r, StrUtil.format("", prefix, threadNumber.getAndIncrement()));
//守护线程
if (false == t.isDaemon())
if (isDaemon)
// 原线程为非守护则设置为守护
t.setDaemon(true);
else if (false == isDaemon)
// 原线程为守护则还原为非守护
t.setDaemon(false);
//异常处理
if(null != this.handler)
t.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(handler);
//优先级
if (Thread.NORM_PRIORITY != t.getPriority())
// 标准优先级
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
测试一下

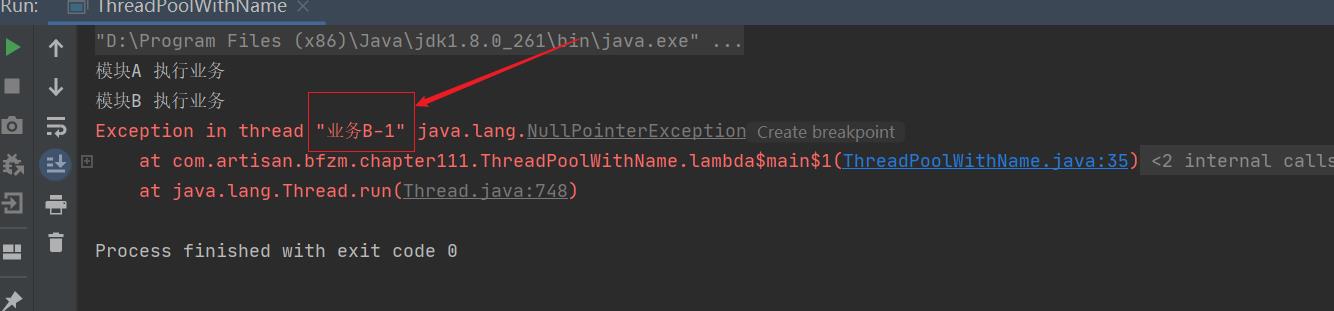
从业务B-1就可以知道,这是接受用户链接线程池抛出的异常。
小结
-
我们这里介绍了为何不为线程或者线程池起名字会给问题排查带来麻烦,然后通过源码分析介绍了线程和线程池名称及默认名称是如何来的,以及如何定义线程池名称以便追溯问题。
-
另外,在run方法内使用try-catch块,避免将异常抛到run 方法之外,同时打印日志也是一个最佳实践。

以上是关于Java Review - 创建线程和线程池时建议指定与业务相关的名称的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章