SQL基础教程(第2版)第7章 集合运算:7-2 联结(以列为单位对表进行联结)
Posted 绍耕
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SQL基础教程(第2版)第7章 集合运算:7-2 联结(以列为单位对表进行联结)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
第7章 集合运算:7-2 联结(以列为单位对表进行联结)
● 联结( JOIN)就是将其他表中的列添加过来,进行“添加列”的集合运算。UNION是以行(纵向)为单位进行操作,而联结则是以列(横向)为单位进行的。
● 联结大体上分为内联结和外联结两种。首先请大家牢牢掌握这两种联结的使用方法。
● 请大家一定要使用标准SQL的语法格式来写联结运算,对于那些过时的或者特定SQL中的写法,了解一下即可,不建议使用。
■ 什么是联结
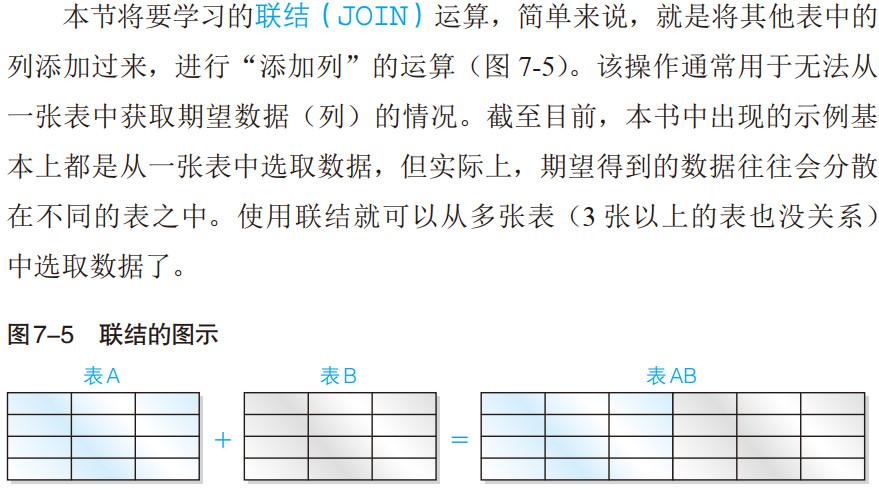
■ 内联结——INNER JOIN
首先我们来学习内联结( INNER JOIN),它是应用最广泛的联结运算。
本例中我们会继续使用Product 表和第 6 章创建的ShopProduct表。下面我们再来回顾一下这两张表的内容。 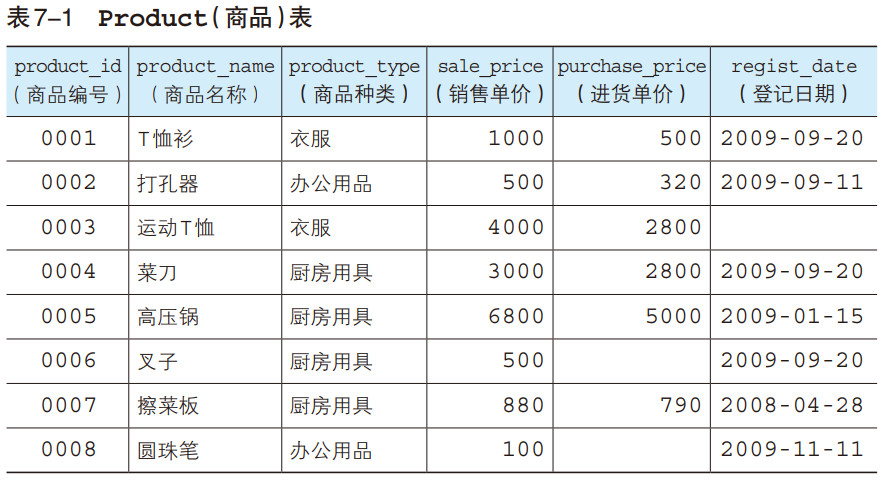
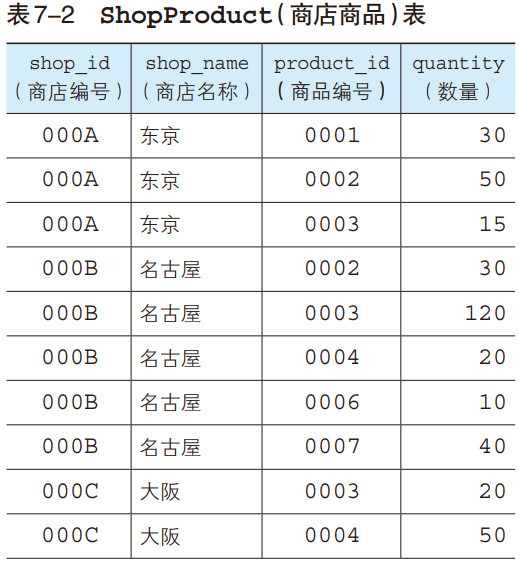
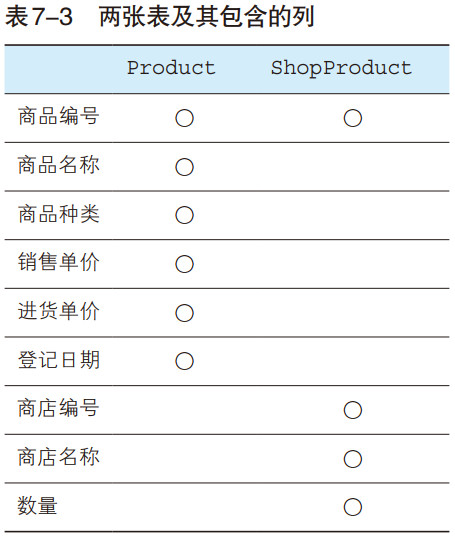
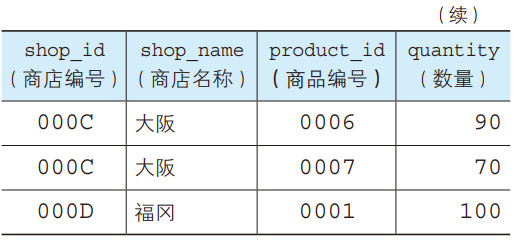

试着从 Product 表中取出商品名称(product_name)和销售单价(sale_price),并与ShopProduct 表中的内容进行结合,所得到的结果如下所示。
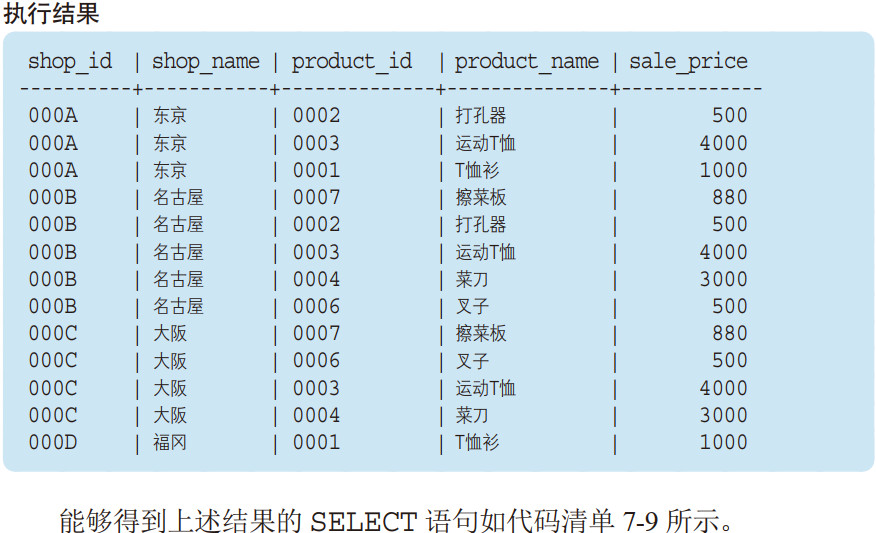

由于表名太长会影响 SQL 语句的可读性,因此还是希望大家能够习惯使用别名。

像这样使用联结运算将满足相同规则的表联结起来时, WHERE、GROUP BY、 HAVING、 ORDER BY 等工具都可以正常使用。我们可以将联结之后的结果想象为新创建出来的一张表(表 7-4)
当然,这张“表”只在 SELECT 语句执行期间存在, SELECT 语句执行之后就会消失。如果希望继续使用这张“表”,还是将它创建成视图吧。
■ 外联结——OUTER JOIN
相反,对于外联结来说,只要数据存在于某一张表当中,就能够读取出来。
在实际的业务中,例如想要生成固定行数的单据时,就需要使用外联结。
如果使用内联结的话,根据 SELECT 语句执行时商店库存状况的不同,
结果的行数也会发生改变,生成的单据的版式也会受到影响,而使用
外联结能够得到固定行数的结果。
●外联结要点①——选取出单张表中全部的信息
●外联结要点②——每张表都是主表吗?
外联结还有一点非常重要,那就是要把哪张表作为主表。最终的结果中会包含主表内所有的数据。指定主表的关键字是 LEFT 和 RIGHT。
顾名思义, 使用 LEFT 时 FROM 子句中写在左侧的表是主表,使用 RIGHT时右侧的表是主表。

大家可能会犹豫外联结到底应该使用 LEFT 还是 RIGHT,其实它们的功能没有任何区别,使用哪一个都可以。通常使用 LEFT 的情况会多一些。
■ 3张以上的表的联结
通常联结只涉及 2 张表,但有时也会出现必须同时联结 3 张以上的表的情况。
首先我们创建一张用来管理库存商品的表(表 7-5)。假设商品都保存在 P001 和 P002 这 2 个仓库之中。

代码清单7-13 创建InventoryProduct表并向其中插入数据

--mysql -- DDL:创建表 CREATE TABLE InventoryProduct ( inventory_id CHAR(4) NOT NULL, product_id CHAR(4) NOT NULL, inventory_quantity. INTEGER NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (inventory_id, product_id)); -- DML:插入数据 START TRANSACTION; INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S001\', \'0001\', 0); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity)VALUES (\'S001\', \'0002\', 120); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S001\', \'0003\', 200); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S001\', \'0004\', 3); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S001\', \'0005\', 0); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S001\', \'0006\', 99); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S001\', \'0007\', 999); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S001\', \'0008\', 200); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity)VALUES (\'S002\', \'0001\', 10); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S002\', \'0002\', 25); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S002\', \'0003\', 34); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S002\', \'0004\', 19); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S002\', \'0005\', 99); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S002\', \'0006\', 0); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S002\', \'0007\', 0); INSERT INTO InventoryProduct (inventory_id, product_id, inventory_quantity) VALUES (\'S002\', \'0008\', 18); COMMIT;

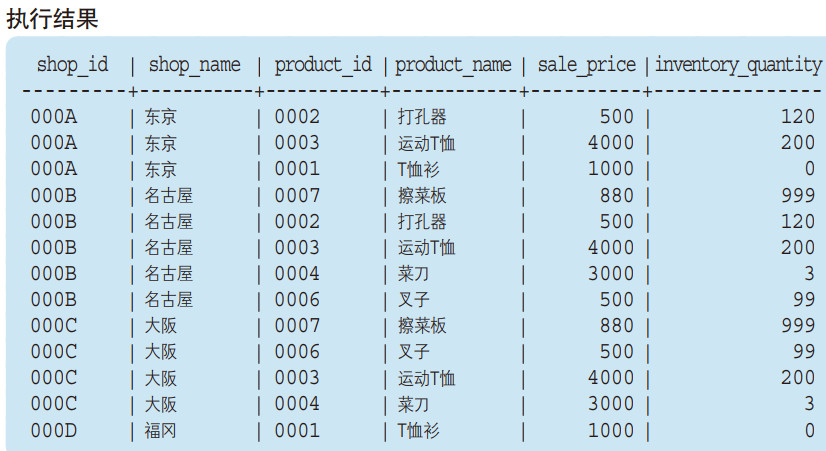
通过 ON 子句指定联结条件的方式也没有发生改变,使用等号将作为联结条件的 Product 表和 ShopProduct 表中的商品编号(product_id)联结起来。
由于 Product 表和 ShopProduct 表已经进行了联结,因此这里无需再对 Product 表和 InventoryProduct 表进行联结了(虽然也可以进行联结,但结果并不会发生改变)。
以上是关于SQL基础教程(第2版)第7章 集合运算:7-2 联结(以列为单位对表进行联结)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
