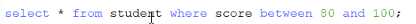mysql
Posted mljqqh
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mysql相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
条件关键字
where可以被having代替
having用于分组之后可以接聚合函数,弥补了where不能接聚合函数的缺陷,可以代替where
on用于链接
update user set host = ‘%‘ where user = ‘root‘;
增:
create table 数据库名称 ; 创建数据库
create 表名{
字段名称 字段类型(长度) 约束,
};
create table students(
id int not null primary key auto_increment,
name char(10),
age int,
);
char char(3)(长度固定 ,不可以变,没有存的空间空格补齐 )
String varchar(3)(长度可以变)
3代表的是可以存三个字符
date YYYY-MM-DD
time hh:mm:ss
datetime YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss 默认是null
timestamp YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss 默认是当前时间
text 存文本
blob 存放二进制
约束:
主键: primary key
唯一约束: unique
非空约束: not null
增加字段;
alter table 表名 add 字段名 数据类型 约束;
alter table students add score int not null;
修改字段大小和字段类型:
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 varchar(20);
alter table students modify name varchar(20);
修改字段名称:
alter table students change name student_name varchar(20);
删除字段:
alter table students drop score;
修改表名:
rename table students to studentssss;
修改表的字符集:
alter table students character set utf8;
删除表;
drop students;
创建表
创建数据库的指定字符集 create database name character set utf8 collate utf8_bin
collate 校对字符集
修改:
修改数据库字符集 alter databae 数据库名称 character set 字符集
删除:
drop database 数据库名字; 删除数据库
查:
使用数据库:
use 数据库名称;
查看正在使用的数据库:
select database();
查看表:
show tabLe;
查看库的定义过程:
show create database test;
查看表的创建过程;
show create table students;
查看表结构:
desc students;
-------------------------------------------------------------------
对表操作:
增:
insert into students(id,name,age) values(11,‘mlj‘,111);
简单写法:
insert into students values(11,‘mlj‘,111);
批量插入:
insert into students values
(12,‘mlj‘,111),
(13,‘mlj‘,111),
(14,‘mlj‘,111),
(15,‘mlj‘,111),
(17,‘mlj‘,111),
(18,‘mlj‘,111),
(19,‘mlj‘,111);
删:
delete from students where id=10;
delete from students; 删除整个表的数据
truncate students; 删除表后重新建表
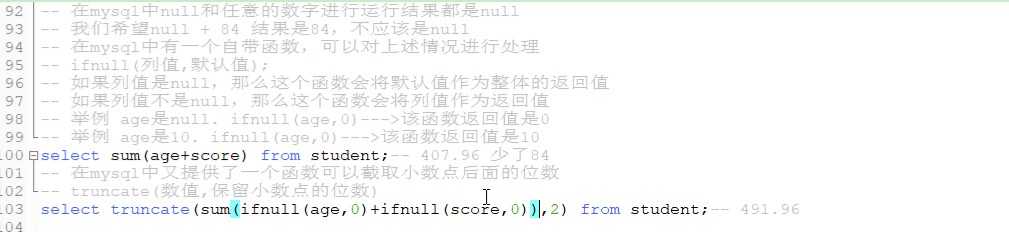
truncate ()也是个函数 保留 小数位
delete和truncate drop
区别:delete是一条一条的删除记录
truncate是删除所有记录后重启启动创建表
drop删除后表就啥都不存在了
改:
若果参数是字符串或者是日期要加单引号
update students set id=1080 ,name=‘ssss‘ where id=19;
查:select [distinct][*][字段,字段2] from 表名 [where 条件]
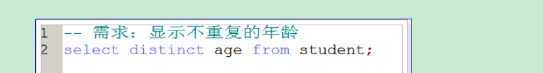
distinct表示去除重复
在表中,可能会包含重复值。这并不成问题,不过,有时您也许希望仅仅列出不同(distinct)的值。关键词 distinct用于返回唯一不同的值。
表A:
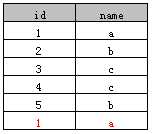
表B:
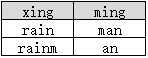
1.作用于单列
select distinct name from A
执行后结果如下:
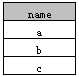
2.作用于多列
示例2.1
select distinct name, id from A
执行后结果如下:
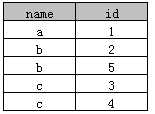
实际上是根据name和id两个字段来去重的,这种方式Access和SQL Server同时支持。
示例2.2
select distinct xing, ming from B
返回如下结果:
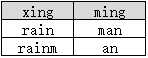
返回的结果为两行,这说明distinct并非是对xing和ming两列“字符串拼接”后再去重的,而是分别作用于了xing和ming列。
3.COUNT统计
select count(distinct name) from A; --表中name去重后的数目, SQL Server支持,而Access不支持
count是不能统计多个字段的,下面的SQL在SQL Server和Access中都无法运行。
select count(distinct name, id) from A;
若想使用,请使用嵌套查询,如下:
select count(*) from (select distinct xing, name from B) AS M;
4.distinct必须放在开头
select id, distinct name from A; --会提示错误,因为distinct必须放在开头
5.其他
distinct语句中select显示的字段只能是distinct指定的字段,其他字段是不可能出现的。例如,假如表A有“备注”列,如果想获取distinc name,以及对应的“备注”字段,想直接通过distinct是不可能实现的。但可以通过其他方法实现关于SQL Server将一列的多行内容拼接成一行的问题讨论
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/rainman/archive/2013/05/03/3058451.html
别名查询
as可以省略
select p.name ,p.price from product as p;表别名
--去掉重复的值
select distinct pprice from product;
---select运算查询
select * ,pprice*2 折后价 from product ;
-----条件查询
查询价格大于60的产品
select* from product where pprice>60;
as作为临时表
用到的知识点 内连接
SELECT student.*,temp.score FROM
student ,
(SELECT student_id ,score FROM studentcourse WHERE score<60) as temp
WHERE student.id = temp.student_id;
关系运算符
> >= < <= = != <>不等于
逻辑运算 and or not
between..and....
模糊查询
-:代表的是任意一个字符
%:代表的是0个或多个字符
过滤查询(distinct)
去掉重复的值
select * from product where pname like ‘%米%‘;
select * from product where pname like ‘_米%‘;
查询排序
使用order by 子句排序查询结果。
语法:select * from 表名 order by 列名1 asc|desc,列名2(asc|desc),列名3(asc|desc) 。。。。。;
按照列名1,列名2,列名3 进行排序输出。
asc是升序排列,desc是降序排列。默认是asc升序。
按照第一列进行排序,如果第一列相同,按照第二列在进行排序。
--in 在某个范围中获得值
select * from product where pnum in (1,3,5);
--排序查询:order by 关键字
asc:ascend 升序 (默认的排序方式)
desc:descend 降序
select * from product order by pprice desc;价格降序
select * from product where pname like ‘%米%‘ order by pprice asc;//包含米字并且升序排序
--聚合查询:
sum()
avg()
count()
max()
min()
select sum(pprice) from product;查看所有商品价格的总和
select count(*) from product;查看商品的个数
select * from product where pprice > (select avg(pprice) from product);查询产品大于平均值的信息
----分组
group by
顺序
先分组之后聚合函数再计算
select pnum ,count(pnum)from product group by pnum; 按pnum分组,求出分组个数
显示的列名跟聚合函数一致 ,pnum ,count(pnum) 不要出现其他列名
having 可以接聚合函数 出现在分组之后
select pnum ,avg(pprice)from product group by pnum having avg(pprice)> 60; 根据pnum分组 并且要求分组avg大于60
where 他不可以接聚合函数 出现在分组之前
group by在我之前的工作中不一定用到,可惜group by在一般的笔试测试的时候经常用到。所以今天刚开一个博客记录下group by用法,为避免以后再犯这个错误。 聚合函数
求和函数——SUM()
计数函数——COUNT()
最大/最小值函数—MAX()/MIN()
均值函数——AVG()
—————————————————————————————————————————
GROUP BY 是分组查询, 一般 GROUP BY 是和 聚合函数配合使用,你可以想想
你用了GROUP BY 按 ITEM.ITEMNUM 这个字段分组,那其他字段内容不同,变成一对多又改如何显示呢,比如下面所示
A B
1 abc
1 bcd
1 asdfg
select A,B from table group by A
你说这样查出来是什么结果,
A B
abc
1 bcd
asdfg
右边3条如何变成一条,所以需要用到聚合函数,比如
select A,count(B) 数量 from table group by A
这样的结果就是
A 数量
1 3
——————————————————————————————————————
Store_Information 表格
store_name Sales Date
Los Angeles $1500 Jan-05-1999
San Diego $250 Jan-07-1999
Los Angeles $300 Jan-08-1999
Boston $700 Jan-08-1999
我们就打入
SELECT store_name, SUM(Sales) FROM Store_Information GROUP BY store_name
结果:
store_name SUM(Sales)
Los Angeles $1800
San Diego $250
Boston $700
————————————————————————————————————————
group by 有一个原则,就是 select 后面的所有列中,没有使用聚合函数的列,必须出现在 group by 后面
group by报错
any_value()
sql_mode=STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION;
|
多个列名分组
where和分组没有关系
select ... from ... where 条件1 ... group by ... having 条件2
执行顺序:
条件1 会先执行过滤
进行分组
条件2进行过滤
开发中什么情况下使用分组?小技巧。
当在需求中遇到每种,每个等字眼的时候就使用分组。
create table product(
pid int primary key auto_increment,
pname varchar(20),
pprice int,
ptime timestamp,
pnum int
);
insert into product values
(null,‘小米6‘,5000,null,3),
(null,‘辣条‘,1,null,32),
(null,‘啤酒‘,4,null,3),
(null,‘啤酒‘,5000,null,3);
--------------------多表操作-----------------------------------
---外键操作------------
给product中的这个cno
添加一个外键约束
alter table product add foreign key(cno) references category(cid);
pid int primary key auto_increment,//主键设置为外键
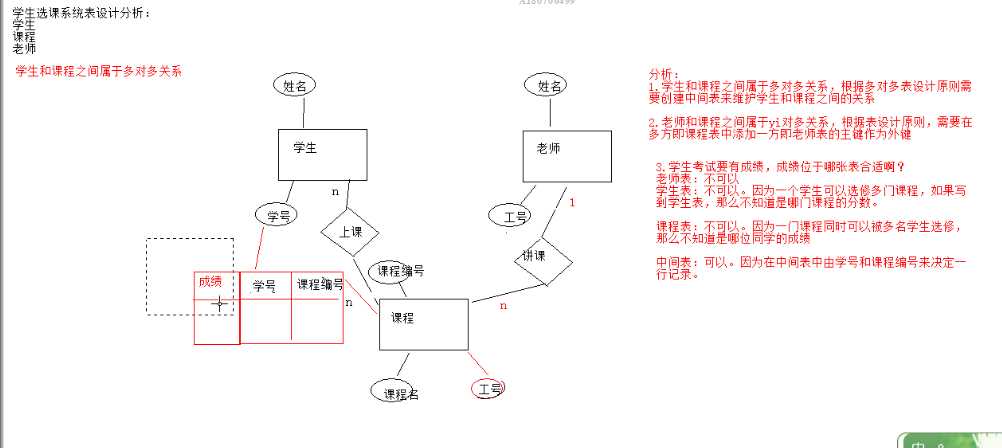
一对多
多对多(多建一张中间表, 将多对多的关系拆成一对多关系,中间至少要有两个外键,这两个外键分别指向原来的那张表)
一对一
--------------------多表操作-----------------------------------
关于sql中constraint 前缀的用意(PK、UK、DF、CK、FK)
constraint 约束
--主键
constraint PK_字段 primary key(字段),
--唯一约束
constraint UK_字段 unique key(字段),
--默认约束
constrint DF_字段 default(‘默认值‘) for 字段,
--检查约束
constraint CK_字段 check(约束。如:len(字段)>1),
--主外键关系
constraint FK_主表_从表 foreign(外键字段) references 主表(主表主键字段)
------------------------------------------------------------------------
mysqld --initialize-insecure --user=mysql
mysqld -install
mysqld -remove
mysqladmin -u root -p password 新密码
1.登录常用参数
-u 用户名
-p 密码
mysql -uroot -p
mysql -uroot -proot
-h 服务器名称
mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p
mysql -h127.0.0.1 -uroot -p
-P 端口号
mysql -uroot -p -P3306
-D 打开指定数据库
-V 输出版本信息并退出
mysql -V
mysql -uroot -p -Vte
2.退出
quit
exit
多表设计原则:
扩展:
sum
limit
语法:select * from 表名 limit offset, row_count;
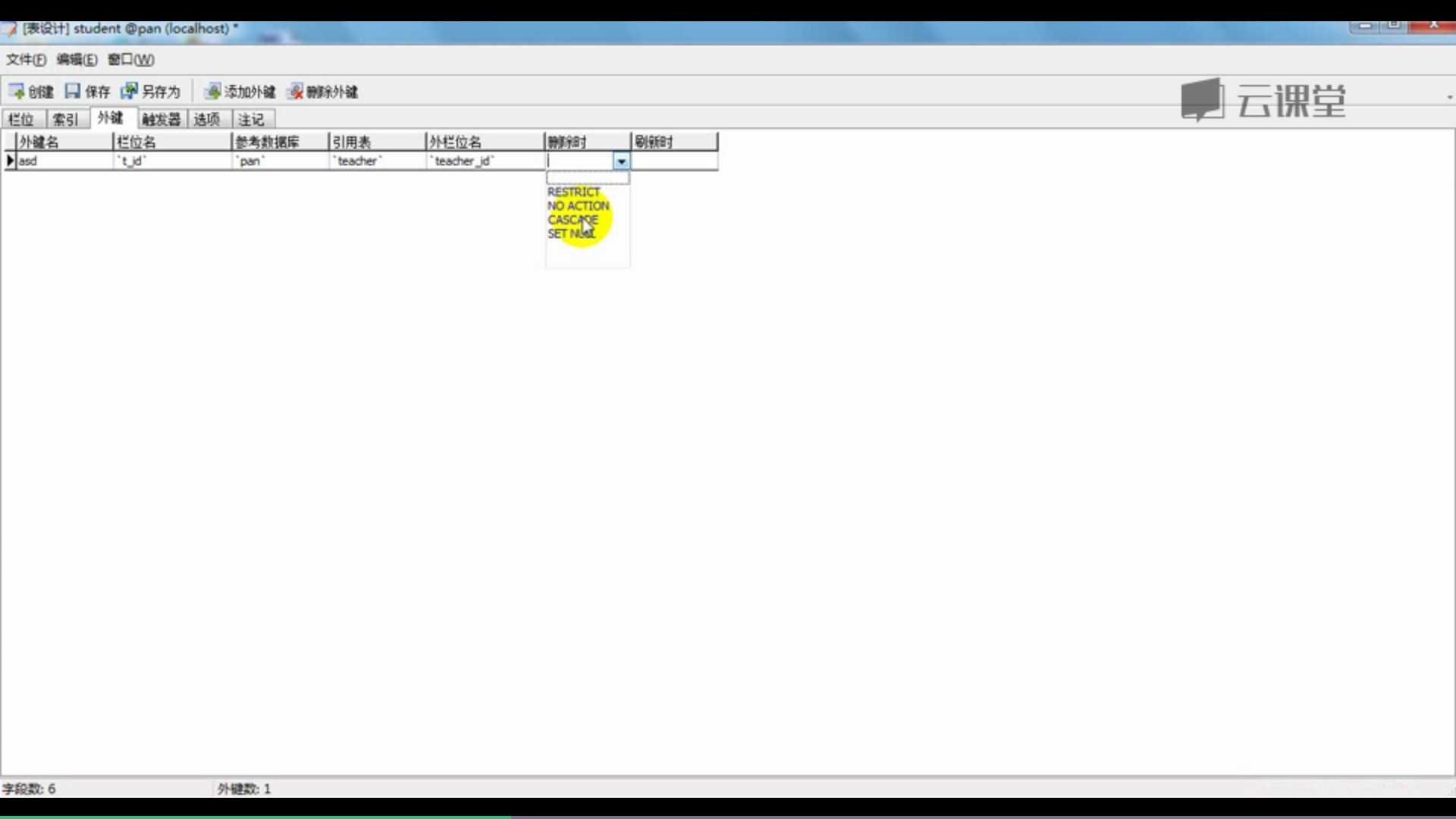
外键:
restrict 限制 主从表有联系
cascade 删除一个表的记录时,已知关联的表的记录也会被删除.
set null 删除一个表的记录时,已知关联的表的记录的值被设置为null
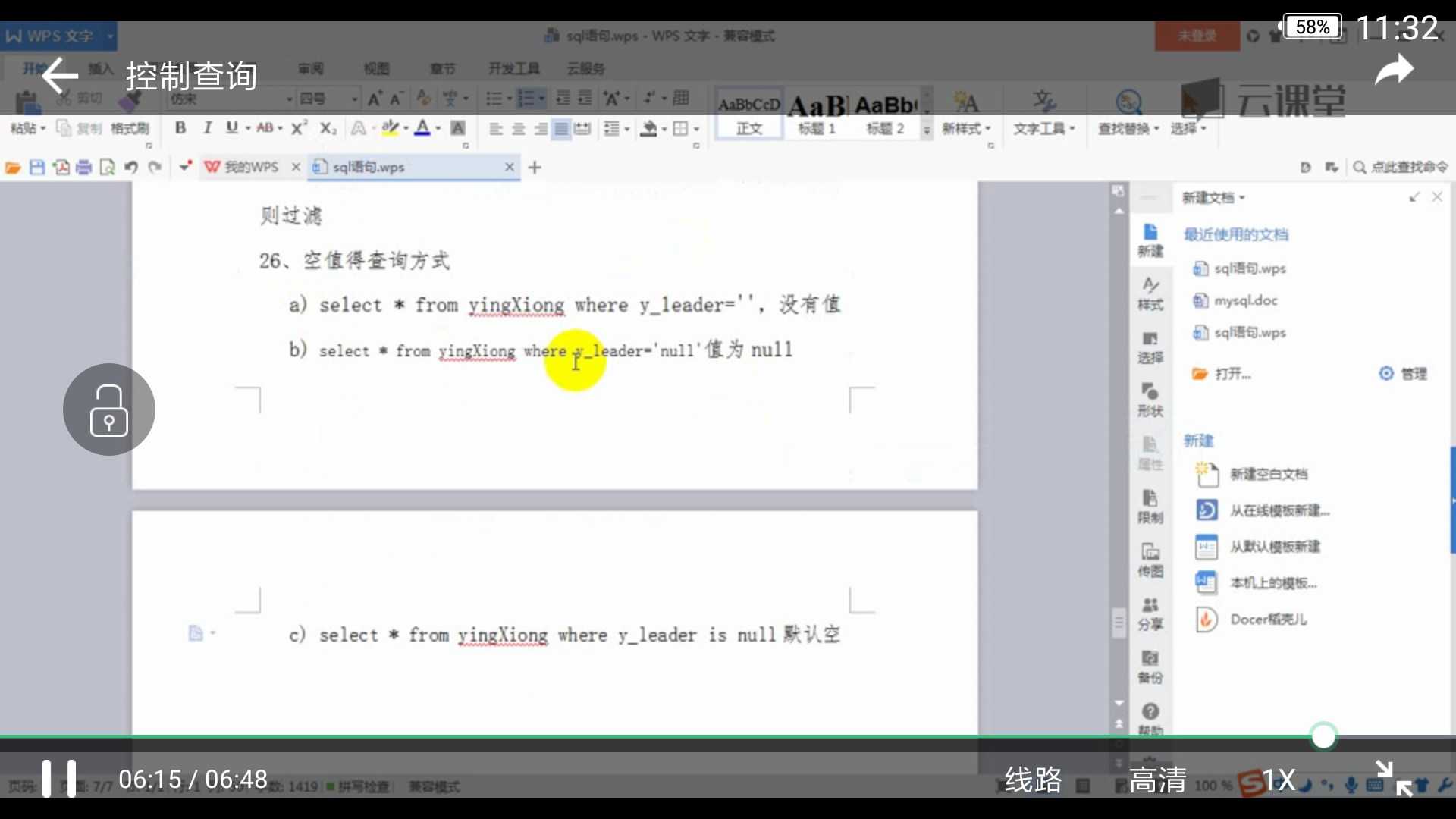
null查询
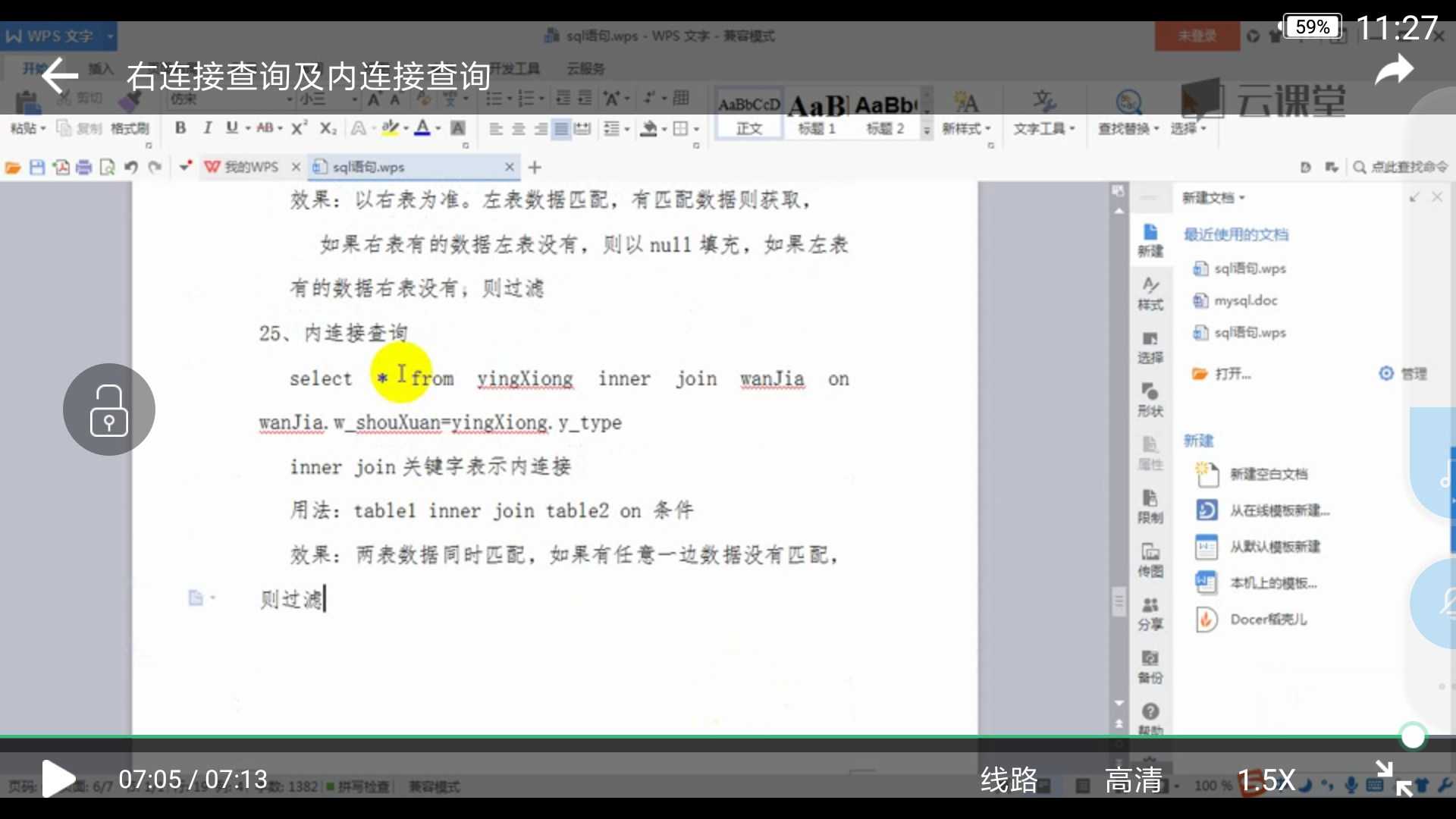
内连接
两边都有才会查出来的
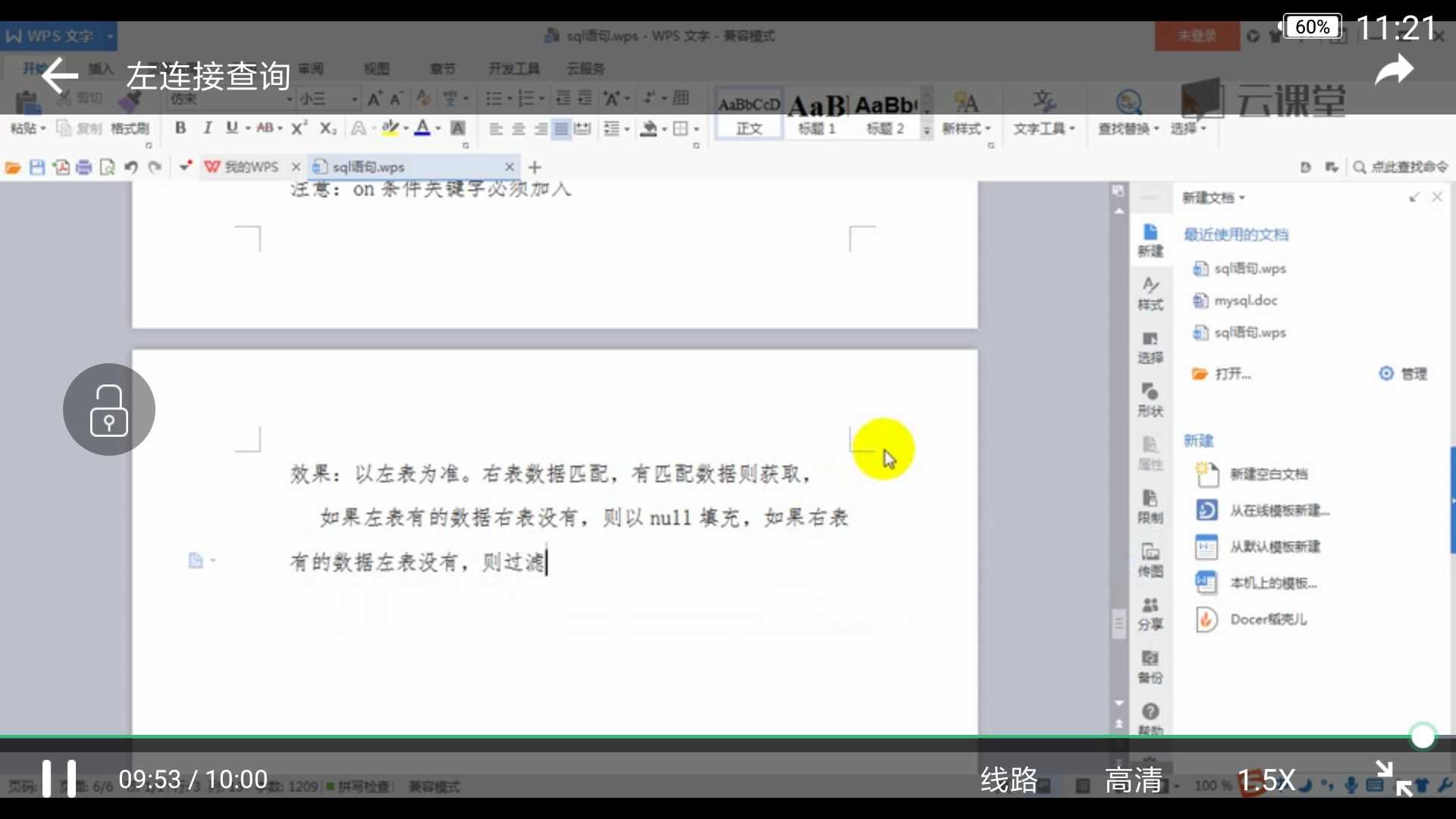
左链接
on条件必须加入
两表联合查询及条件过滤
解决了迪卡尔集问题
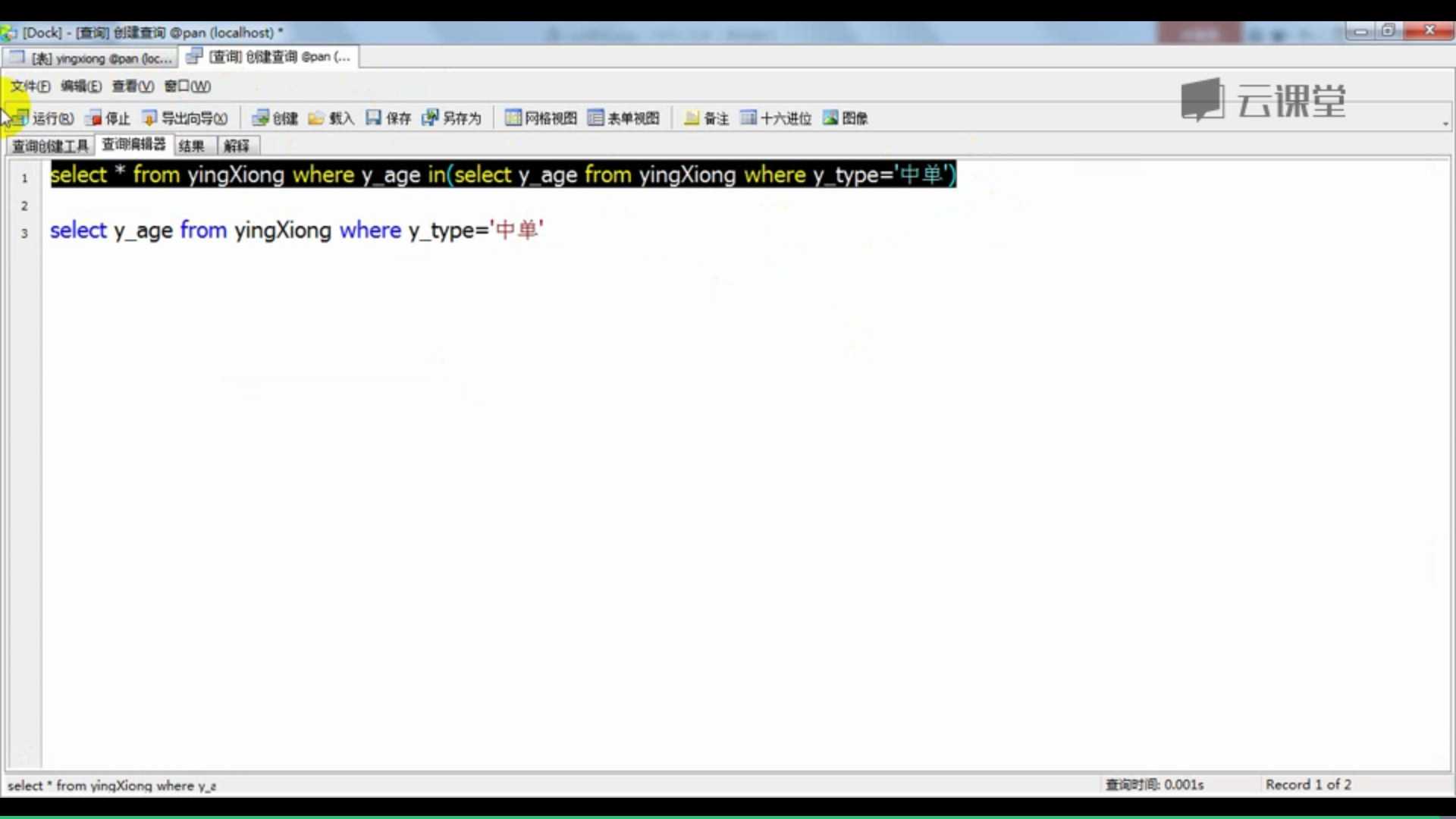
子条件查询
定义:用查询处理的结果作为查询的条件来继续查询
个人理解 :找出分数不是最高分的记录
以上是关于mysql的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章