Ⅰ、总览
- S行级共享锁
lock in share mode - X行级排它锁
增删改 - IS意向共享锁
- IX意向排他锁
- AI自增锁
Ⅱ、锁之间的兼容性
| 兼 | X | IX | S | IS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | × | × | × | × |
| IX | × | √ | × | √ |
| S | × | × | √ | √ |
| IS | × | √ | √ | √ |
2.1 意向锁
意向锁揭示了下一层级请求的锁类型,意向锁全兼容
- IS:事务想要获得一张表中某几行的共享锁
- IX:事务想要获得一张表中某几行的排它锁
InnoDB存储引擎中意向锁都是表锁,是不是读下来很懵逼?
如果没有意向锁,当你去锁一张表的时候,你就需要对表下的所有记录都进行加锁操作,且对其他事务刚刚插入的记录(游标已经扫过的范围)就没法在上面加锁了,此时就没有实现锁表的功能
对一棵树加锁的概念:
从上往下的,先加意向锁再加记录锁,内存操作,很快,释放操作则是从记录锁开始从下往上进行释放
假设数据库四个层级,库,表,页,记录
假如此时有事务tx1需要在记录A上进行加X锁:
1. 在该记录所在的数据库上加一把意向锁IX
2. 在该记录所在的表上加一把意向锁IX
3. 在该记录所在的页上加一把意向锁IX
4. 最后在该记录A上加上一把X锁
假如此时有事务tx2需要对记录B(假设和记录A在同一个页中)加S锁:
1. 在该记录所在的数据库上加一把意向锁IS
2. 在该记录所在的表上加一把意向锁IS
3. 在该记录所在的页上加一把意向锁IS
4. 最后在该记录B上加一把S锁
假如此时有事务tx3需要在记录A上进行加S锁:
1. 在该记录所在的数据库上加一把意向锁IS
2. 在该记录所在的表上加一把意向锁IS
3. 在该记录所在的页上加一把意向锁IS
4. 发现该记录被锁定(tx1的X锁),那么tx3需要等待,直到tx1进行committips:
-
共享锁和排它锁不是说只能加在记录级别上,是可以加在各个级别上的
innodb表锁的获取:lock table l read; lock table l write; unlock tables; 这是server层的锁(mdl锁)
从原理上讲innodb也是可以对表加X锁的,但是没有一个具体的命令来触发,也可以把lock table l read; 理解为加X锁通常来说不需要加表级别的锁,mysqldump都不加,ddl不支持online的时候就是先对一张表先加一个S锁,现在不一样了
-
为什么意向锁都是互相兼容的?因为在当前级别上并没有加锁啊
但是在MySQL中没有数据库级别的锁和页级别的锁,这就意味着一共就两层,所有的意向锁都是表锁,意向锁是innodb层级的
tips:
MySQL8.0中所有的锁都在innodb层,现在的锁一部分在innodb层一部分在server层,server层的不好理解
Ⅱ、自增锁
- 一个表一个自增列,自增锁做自增并发处理
- auto_increment pk 代表这个列的自增有一把锁
- 在事务提交前释放
其他锁在事务提交时才释放 - Think about
insert ... select ...
tips:
MySQL的自增存在一个回溯的问题,5.7版本之前都是非持久化的,都是服务启动时候执行下面这个sql获取自增值,从下个位置开始继续自增,如果数据库重启了,之前的自增值可能被重复使用,8.0已解决,这个值会被写到元数据表(innodb引擎)中。
select max(auto_inc_col) from t for update;2.1 自增列的约束
(root@localhost) [test]> create table t (a int auto_increment, b int) engine = innodb;
ERROR 1075 (42000): Incorrect table definition; there can be only one auto column and it must be defined as a key
(root@localhost) [test]> create table t (a int auto_increment, b int, key(b,a)) engine = innodb;
ERROR 1075 (42000): Incorrect table definition; there can be only one auto column and it must be defined as a key
(root@localhost) [test]> create table t (a int auto_increment, b int, key(a,b)) engine = innodb;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)InnoDB自增列必须被定义为一个key,且必须是这个key的开始部分
WHY?
select max(auto_inc_col) from t for update;避免重启执行上面这句的时候扫全表 ,myisam是非聚集索引的,不是用这个方式来采集自增值的,8.0虽然持久化了,但还是有这个限制
经测试,myisam自增列也需要被定义为一个key,但是不需要是key的开始部分
2.2 自增的参数
(root@localhost) [test]> show variables like \'auto_increment%\';
+--------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------+-------+
| auto_increment_increment | 1 | -- 步长
| auto_increment_offset | 1 | --初始值
+--------------------------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)多节点全局唯一
N台服务器:A:[offset = 1, increment=N] , B:[offset = 2, increment=N] , C:[offset = 3, increment=N]...N:[offset = N, increment=N]
注意,这不能用来做多主,如果有额外的唯一索引就保证不了全局唯一了
2.3 自增锁分析
session1:
(root@localhost) [test]> create table t_ai_l(a int auto_increment, b int, primary key(a));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> insert into t_ai_l values(NULL, 10);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
事务不提交session2:
(root@localhost) [test]> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> insert into t_ai_l values(NULL, 20);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)咦?没等待耶,amazing!
AI锁在事务提交前就释放了,类似latch,使用完就释放了
session1&2:
(root@localhost) [test]> rollback;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)session1:
(root@localhost) [test]> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> insert into t_ai_l values(NULL, 30);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> commit;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> select * from t_ai_l;
+---+------+
| a | b |
+---+------+
| 3 | 30 |
+---+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)可以看到虽然rollback,但AI锁是提交过了的,自增值不会跟着回滚,这样自增值就不连续,但连续也没什么用
也就是说,仅仅是这条sql执行的这段时间里,其他session是不可以对这个表操作的,插入过程太长,对insert也会阻塞
执行这条sql的时候,自增是被锁住的,所以插进去之后都是连续的值
2.4 利用sleep()分析自增锁
session1:
(root@localhost) [test]> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> insert into t_ai_l (a,b) select NULL, sleep(1) from tmp limit 10000;
~~~
session2:
(root@localhost) [test]> show engine innodb status\\G
...
LIST OF TRANSACTIONS FOR EACH SESSION:
---TRANSACTION 421958478908128, not started
0 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 0 row lock(s)
---TRANSACTION 31217775, ACTIVE 10 sec
mysql tables in use 2, locked 2
4 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 11 row lock(s), undo log entries 10
MySQL thread id 2255, OS thread handle 140482757068544, query id 3006342 localhost root User sleep
insert into t_ai_l (a,b) select NULL, sleep(1) from tmp limit 10000
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`tmp` trx id 31217775 lock mode IS
RECORD LOCKS space id 1408 page no 4 n bits 624 index PRIMARY of table `test`.`tmp` trx id 31217775 lock mode S
Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 4; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd15db; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex d4000001760110; asc v ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 4; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd15dc; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex d5000001300110; asc 0 ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;;
...
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`t_ai_l` trx id 31217775 lock mode AUTO-INC
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`t_ai_l` trx id 31217775 lock mode IX
...插入数据过程分析:
- tmp表被加了IS锁,表中记录被加S锁,注意不会一次性所有记录加锁,是被查到的记录就被锁住,最终事务结束后释放所有锁
- t_ai_l表上有两个锁AUTO-INC和IX
session2:
(root@localhost) [test]> insert into t_ai_l (a,b) select NULL, sleep(1) from tmp limit 10000;
~~~
session3:
(root@localhost) [test]> show engine innodb status\\G
...
LIST OF TRANSACTIONS FOR EACH SESSION:
---TRANSACTION 421958478909040, not started
0 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 0 row lock(s)
---TRANSACTION 31218060, ACTIVE 15 sec setting auto-inc lock
mysql tables in use 2, locked 2
LOCK WAIT 3 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 1 row lock(s)
MySQL thread id 2255, OS thread handle 140482757068544, query id 3006385 localhost root Sending data
insert into t_ai_l (a,b) select NULL, b from tmp limit 10000
------- TRX HAS BEEN WAITING 15 SEC FOR THIS LOCK TO BE GRANTED:
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`t_ai_l` trx id 31218060 lock mode AUTO-INC waiting
------------------
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`tmp` trx id 31218060 lock mode IS
RECORD LOCKS space id 1408 page no 4 n bits 624 index PRIMARY of table `test`.`tmp` trx id 31218060 lock mode S
Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 4; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd15db; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex d4000001760110; asc v ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`t_ai_l` trx id 31218060 lock mode AUTO-INC waiting
---TRANSACTION 31218051, ACTIVE 40 sec
mysql tables in use 2, locked 2
4 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 40 row lock(s), undo log entries 39
MySQL thread id 2254, OS thread handle 140482756536064, query id 3006383 localhost root User sleep
insert into t_ai_l (a,b) select NULL, sleep(1) from tmp limit 10000
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`tmp` trx id 31218051 lock mode IS
RECORD LOCKS space id 1408 page no 4 n bits 624 index PRIMARY of table `test`.`tmp` trx id 31218051 lock mode S
Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 4; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd15db; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex d4000001760110; asc v ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 4; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd15dc; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex d5000001300110; asc 0 ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;;
...insert into t_ai_l (a,b) select NULL, b from tmp limit 10000 在等待三个锁
- t_ai_l表上的AUTO-INC锁
- tmp表上的IS锁
- tmp表中第一条记录上的S锁
这样设计的初衷是希望批量插入的自增值是连续的,但实际上是牺牲了并发度的
2.5 自增锁的分类
| - | 说明 |
|---|---|
| insert-like | 所有插入语句都属于此类 |
| simple inserts | 插入之前能确定插入多少行(insert into table_1 values(NULL, 1), (NULL, 2);) |
| bulk inserts | 插入之前不确定插入多少行(insert into table_1 select * from t;) |
| mixed-mode inserts | 插入内容部分自增部分确定(insert ... on duplicate key update不推荐) |
2.6 如何提升自增并发度
(root@localhost) [test]> show variables like \'innodb_autoinc_lock_mode\';
+--------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------+-------+
| innodb_autoinc_lock_mode | 1 |
+--------------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)此参数可设置为[0|1|2]
- 0 sql语句执行完释放AI锁,若数据量大sql执行完之前其他事务是无法插入的,保证了在此sql语句内插入的数据自增值是连续的
- 1(default,大部分情况用1) 对于bulk inserts,和设置0一样
simple inserts则可以并发插入,在sql运行完之前确定自增值之后就可以释放AI锁了
+
bulk inserts | simple inserts
|
+-------------------------------------------------------+
|
acquire AI_Lock | acquire AI_Lock
|
insert ... select ... | ai = ai + M
|
ai = ai + N | release AI_Lock
|
release AI_Lock | insert ... select ...
+
bulk inserts不知道要插入多少行,所以只能等insert结束后,才知道N的值,然后一次性(ai + N)
simple inserts知道插入的行数(M),所以可以先(ai + M),然后将锁释放掉,给别的事务用,然后自己慢慢插入数据- 2 所有自增都可以并发(不同于Simple inserts的方式 ) 同一sql语句自增可能不连续
row-based binlog
for (i = ai; until_no_rec; i++) {
acquire AI_Lock # 插入前申请锁
insert one record... # 只插入一条记录
ai = ai + 1 # 自增值+1
release AI_Lock # 释放锁
}并发度增加了,但性能不一定变好,尤其是单线程的时候,频繁申请和释放锁会导致开销大
虽然不连续,但插入进去至少是单调递增所以基本满足业务需求tips:
这种情况严格意义上是不连续,但由于并发度不够再加上limit是预先批量申请分配这种不阻塞不是很好演示,所以看上去是连续的,其实不是,limit大一点应该是可以的,但等待时间太长了,也可以通过mysqlslap测测
InnoDB中锁的查看
Ⅰ、 show engine innodb status\\G
1.1 实力分析一波
锁介绍的那篇中已经提到了这个命令,现在我们开一个参数,更细致的分析一下这个命令
(root@localhost) [(none)]> set global innodb_status_output_locks=1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)(root@localhost) [test]> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> delete from l where a = 2;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> update l set b = b + 1 where a = 4;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
(root@localhost) [test]> show engine innodb status\\G
...
LIST OF TRANSACTIONS FOR EACH SESSION:
---TRANSACTION 30217412, ACTIVE 37 sec
2 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 2 row lock(s), undo log entries 2
MySQL thread id 355, OS thread handle 140483080300288, query id 1263 localhost root starting
show engine innodb status
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`l` trx id 30217412 lock mode IX
RECORD LOCKS space id 1358 page no 3 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `test`.`l` trx id 30217412 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap
Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 32
0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd14c4; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex 2400000fc21499; asc $ ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000004; asc ;;
4: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;;
5: len 4; hex 80000008; asc ;;
Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000004; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd14c4; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex 2400000fc214c8; asc $ ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000007; asc ;;
4: len 4; hex 80000008; asc ;;
5: len 4; hex 8000000a; asc ;;
...解析:
- table lock IX 意向排他锁(意向锁都是表锁)
- record locks 记录锁
-->space id 表空间
-->page no 第几个页,所有的记录开始写都是从表的第四个页开始写,第四个页也是聚集索引的root page
-->index PRIMARY 表示在主键上加了一把锁
-->lock_mode 锁的模式
-->locks rec but not gap 这个先不看
-->heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6 锁住记录的heap no为2的物理记录,这个记录一共6个列
-->compact format 这条记录的存储格式是compact(dynamic也是compact)
-->info bits 0表示这条记录没有被删除;非0表示被修改或者被删除(32)
Q? 表中是四个列,为什么这把是6个列?
- 如果没有主键的话,会多一个隐藏列row_id,这里有主键row_id就是主键那不谈
- 6个字节的表示事务id,7个字节表示回滚指针,这两个列就是隐藏列
1.2、趁热打铁,分析一下等待的情况
session1:
(root@localhost) [test]> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> delete from l where a = 2;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)session2:
(root@localhost) [test]> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> select * from l where a=2 for update;
hang住了session3:
...
LIST OF TRANSACTIONS FOR EACH SESSION:
---TRANSACTION 421958478909040, not started
0 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 0 row lock(s)
---TRANSACTION 30217455, ACTIVE 1741 sec starting index read
mysql tables in use 1, locked 1
LOCK WAIT 2 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 2 row lock(s)
MySQL thread id 396, OS thread handle 140483215816448, query id 2340 localhost root statistics
select * from l where a=2 for update
------- TRX HAS BEEN WAITING 27 SEC FOR THIS LOCK TO BE GRANTED:
RECORD LOCKS space id 1358 page no 3 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `test`.`l` trx id 30217455 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap waiting
Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 32
0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd14ee; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex 230000013d27d5; asc # =\' ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000004; asc ;;
4: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;;
5: len 4; hex 80000008; asc ;;
------------------
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`l` trx id 30217455 lock mode IX
RECORD LOCKS space id 1358 page no 3 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `test`.`l` trx id 30217455 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap waiting
Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 32
0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd14ee; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex 230000013d27d5; asc # =\' ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000004; asc ;;
4: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;;
5: len 4; hex 80000008; asc ;;
---TRANSACTION 30217454, ACTIVE 1821 sec
2 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 1 row lock(s), undo log entries 1
MySQL thread id 355, OS thread handle 140483080300288, query id 2339 localhost root
TABLE LOCK table `test`.`l` trx id 30217454 lock mode IX
RECORD LOCKS space id 1358 page no 3 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `test`.`l` trx id 30217454 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap
Record lock, heap no 2 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 32
0: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000001cd14ee; asc ;;
2: len 7; hex 230000013d27d5; asc # =\' ;;
3: len 4; hex 80000004; asc ;;
4: len 4; hex 80000006; asc ;;
5: len 4; hex 80000008; asc ;;
...- 找到LOCK WAIT
LOCK WAIT 2 lock struct(s), heap size 1136, 1 row lock(s) 两个锁结构,一个记录锁 - 找到TRX HAS BEEN WAITING 27 SEC FOR THIS LOCK TO BE GRANTED
等的是主键是2的这条记录上的锁,锁的类型是排他锁 - 再往下看,找到hold住2这条记录的事务,根据thread id 355可以找到对应的线程
这个355就是show processlist;对应的id,我们去session1上看下便知
(root@localhost) [test]> show processlist;
+-----+------+-----------+------+---------+------+----------+------------------+
| Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info |
+-----+------+-----------+------+---------+------+----------+------------------+
| 355 | root | localhost | test | Query | 0 | starting | show processlist |
| 396 | root | localhost | test | Sleep | 1321 | | NULL |
+-----+------+-----------+------+---------+------+----------+------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注意再thread_id表中就不一样了,是对应proceelist_id
(root@localhost) [test]> select thread_id,processlist_id,thread_os_id from performance_schema.threads where processlist_id is not NULL;
+-----------+----------------+--------------+
| thread_id | processlist_id | thread_os_id |
+-----------+----------------+--------------+
| 27 | 1 | 10574 |
| 381 | 355 | 18745 |
| 422 | 396 | 10592 |
+-----------+----------------+--------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
分别表示内部线程号(自增的),对应show processlist里的id,进程号Ⅱ、简单点,上面是不是太专业了
2.1 利用三张表写一个sql脚本
重复之前的步骤,一边开一个事务删除2这条记录不提交,另一边用for update查2这条记录
(root@localhost) [(none)]> SELECT
-> r.trx_id waiting_trx_id,
-> r.trx_mysql_thread_id waiting_thread,
-> r.trx_query wating_query,
-> b.trx_id blocking_trx_id,
-> b.trx_mysql_thread_id blocking_thread,
-> b.trx_query blocking_query
-> FROM
-> information_schema.innodb_lock_waits w
-> INNER JOIN
-> information_schema.innodb_trx b ON b.trx_id = w.blocking_trx_id
-> INNER JOIN
-> information_schema.innodb_trx r ON r.trx_id = w.requesting_trx_id;
+----------------+----------------+--------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------+
| waiting_trx_id | waiting_thread | wating_query | blocking_trx_id | blocking_thread | blocking_query |
+----------------+----------------+--------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------+
| 30217455 | 396 | select * from l where a=2 for update | 30217454 | 355 | NULL |
+----------------+----------------+--------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.02 sec)2.2 走sys库看一把,更简单
5.7才有sys库,不过5.6也可以自行把sys库弄进去
(root@localhost) [(none)]> select * from sys.innodb_lock_waits\\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
wait_started: 2018-06-03 00:52:01
wait_age: 00:00:14
wait_age_secs: 14
locked_table: `test`.`l`
locked_index: PRIMARY
locked_type: RECORD
waiting_trx_id: 30217455
waiting_trx_started: 2018-06-03 00:11:13
waiting_trx_age: 00:41:02
waiting_trx_rows_locked: 5
waiting_trx_rows_modified: 0
waiting_pid: 396
waiting_query: select * from l where a=2 for update
waiting_lock_id: 30217455:1358:3:2
waiting_lock_mode: X
blocking_trx_id: 30217454
blocking_pid: 355
blocking_query: NULL
blocking_lock_id: 30217454:1358:3:2
blocking_lock_mode: X
blocking_trx_started: 2018-06-03 00:09:53
blocking_trx_age: 00:42:22
blocking_trx_rows_locked: 1
blocking_trx_rows_modified: 1
sql_kill_blocking_query: KILL QUERY 355
sql_kill_blocking_connection: KILL 355
1 row in set, 3 warnings (0.09 sec)tips:
- waiting_lock_id: 30217455:1358:3:2 这个东西表示 事务ID:space:page_No:heap_no,其他得比较简单不用说了
- blocking_query是null,waiting_query是知道的,为什么?
因为blocking的语句已经执行结束了,只是事务没提交罢了
线上大部分时间是看不到这个blocking_query的
即使show engine innodb status\\G也是只能看到在等待哪条记录上的锁释放,而看不到是哪条sql导致的这个问题 - 最下面的KILL QUERY和KILL的区别是?
KILL QUERY是杀这个查询,KILL是直接杀连接
Ⅲ、锁超时
刚才模拟锁等待过程中出现了下面得报错
(root@localhost) [test]> select * from l where a=2 for update;
ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction这叫锁等待超时,开发人员通常把这个和死锁混为一谈
lock持有的时间是以事务为单位的,事务提交后才会把事务里所有的锁释放,这是无法避免的,不过可以通过一个参数来控制超时时间
(root@localhost) [test]> show variables like \'innodb_lock_wait_timeout\';
+--------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------+-------+
| innodb_lock_wait_timeout | 50 |
+--------------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)默认50s,建议设置为3s左右即可
Ⅲ、强行分析heap no
innodb中页里面的记录是逻辑有序的
一个页中,第一条插入的记录heap no是2,后面插入的heap no递增,这样在堆中就是有序的了,但是记录之间又是逻辑有序的,通过指针连接
heap no表示插入时的顺序,用来表示一个page中的record是什么时候插入的,所以加锁的定位是space->page_no->heap_no
一个page中,一条记录都没有,innodb默认会生成两条虚拟伪记录,min和max,min的heap_no是0,max的heap_no是1,所以用户插入的记录heap_no都是从2开始
max上是可以加锁的,min上面通常不加锁
Ⅳ、InnoDB中锁的管理
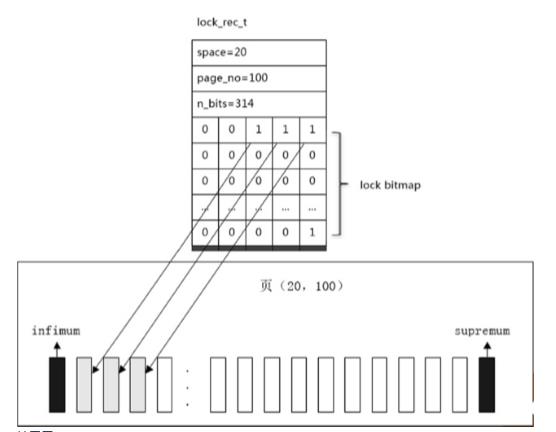
- 每个事务每个page(不是每条记录)有一个锁的对象,通过位图(lock bitmap )的方式来管理,位图是基于每个page的
page里面哪条record加锁了,就会把这条record的heap_no设置为1,heap_no就表示一个位图,表示第几位,所以innodb的锁是占用内存的,但是不是一个锁一个锁来管理锁的存储的(mysql上一个page的锁差不多30个字节就够了,网上都说的是100) - 没有锁升级(like oracle)
sqlserver有锁升级,sqlserver是每个锁一个锁对象,innodb是每个page一个锁对象,所以锁的空间占用上,oracle<mysql<sqlserver
补充sqlserver和innodb全表更新对比
sqlserver每个记录一个锁对象
如果占用10字节,300w个page,每个page100条记录
InnoDB:300M(300w*100/1000/1000)
sqlserver:3G(300w10010/1000/1000)
tips:
- sqlserver锁升级
一个事务持有5000(默认)行锁升级到表锁,锁升级也不是一点都不好,毕竟内存变小了
InnoDB中锁的算法(1)
Ⅰ、InnoDB锁算法的介绍
首先明确一点,锁锁住的是什么?锁锁住的是索引
- Record Lock
单个行记录上的锁 - Gap Lock
锁定一个范围,但不包含记录本身 - Next-key Lock
Gap Lock + Record Lock 锁定一个范围,并且锁定记录本身
Ⅱ、模拟加锁场景
(root@localhost) [test]> desc l;
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| a | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| b | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | |
| c | int(11) | YES | UNI | NULL | |
| d | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> select * from l;
+---+------+------+------+
| a | b | c | d |
+---+------+------+------+
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
| 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
+---+------+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.02 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [test]> select * from l where a = 2 for update;
+---+------+------+------+
| a | b | c | d |
+---+------+------+------+
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
+---+------+------+------+
1 row in set (0.03 sec)
对主键为2的这条记录加锁,这里可以表示三个意思
①record lock:对2加X锁
②gap lock:对(负无穷,2)加X锁
thd1:hold 2 x gap
thd2:hold 2 x record
上面两个是兼容的,也就是说,thd2直接操作2这条记录是可以操作的,不需要等待
thd3:insert 1,这个线程就要wait,因为1在这个范围内
③next-key lock 锁住(负无穷,2]
oralce中只有record lock,没有别的意思一般来说,此处我们根据不同事务隔离级别来分析这个加锁情况如下:
- rc
所有某条记录的加锁都是record锁,所有insert不用等待,并发度更好
--->lock_mode X locks rec but not gap - rr
所有对某条记录加锁都用的next-key locking,insert 并行性能或许有点差
--->lock_mode X
特殊情况:
会
以上是关于InnoDB中锁的模式,锁的查看,算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章