42.scrapy爬取数据入库mongodb
Posted 五杀摇滚小拉夫
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了42.scrapy爬取数据入库mongodb相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
scrapy爬虫采集数据存入mongodb
采集效果如图:
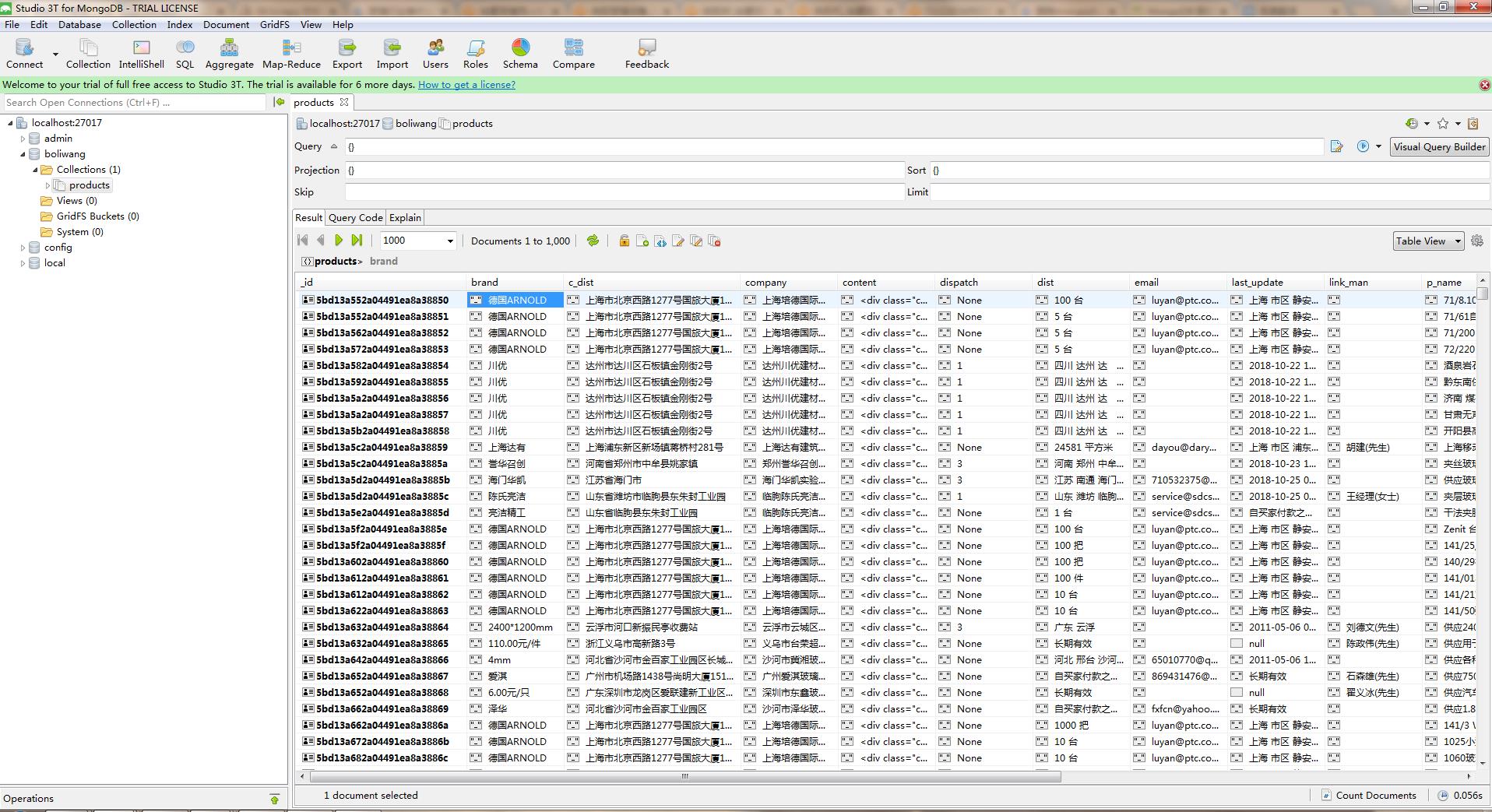
1.首先开启服务
切换到mongodb的bin目录下 命令:mongod --dbpath e:\\data\\db
另开黑窗口 命令:mongo.exe
2.连接可视化工具 studio—3t 建立本地连接
如图:
3.代码如下 采集的是玻璃网站产品数据 http://www.boliwang.com.cn/
boliwang.py # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy import re from boliwang_web.items import BoliwangWebItem class BoliwangSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = \'boliwang\' allowed_domains = [\'www.boliwang.com.cn\'] start_urls = [\'http://www.boliwang.com.cn/gy/index-htm-page-1.html\'] custom_settings = { \'DOWNLOAD_DELAY\': 0.5, "DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES": { \'boliwang_web.middlewares.BoliwangWebDownloaderMiddleware\': 500, }, } def parse(self, response): # print(response.text) # 获取当前页面url link_urls = response.xpath("//table//tr/td[4]/ul/li[1]/a/@href").extract() for link_url in link_urls: # print(link_url) yield scrapy.Request(url=link_url, callback=self.parse_detail) # print(\'*\'*100) #翻页 tag = response.xpath("//div[@class=\'pages\']/cite/text()").extract_first() # print(tag) p_num = tag.split(\'/\')[1].replace(\'页\',\'\') # print(p_num) for i in range(1, int(p_num)+1): url = \'http://www.boliwang.com.cn/gy/index-htm-page-{}.html\'.format(i) # print(url) yield scrapy.Request(url=url, callback=self.parse) def parse_detail(self, response): # 获取当前页面信息 item = BoliwangWebItem() # 产品名称 p_name = response.xpath("//table//tr[1]/td/h1[@id=\'title\']/text()").extract_first() item[\'p_name\'] = p_name # 品牌 brand = response.xpath("//table//tr[2]/td[3]/table//tr[1]/td[2]/text()").extract_first() item[\'brand\'] = brand # 单价 price = response.xpath("//table//tr[2]/td[@class=\'f_b f_orange\']/text()").extract_first() item[\'price\'] = price # 起订 set_up = response.xpath("//table//tr[3]/td[@class=\'f_b f_orange\']/text()").extract_first() item[\'set_up\'] = set_up # 供货总量 summation = response.xpath("//table//tr[4]/td[@class=\'f_b f_orange\']/text()").extract_first() item[\'summation\'] = summation # 发货期限 dispatch = response.xpath("//table//tr[5]/td[2]/span[@class=\'f_b f_orange\']/text()").extract_first() dispatch = \'{}\'.format(dispatch) item[\'dispatch\'] = dispatch # 所在地区 dist = response.xpath("//table//tr[6]/td[2]/text()").extract_first() item[\'dist\'] = dist # 有效期 term_of_valid = response.xpath("//table//tr[7]/td[2]/text()").extract_first() item[\'term_of_valid\'] = term_of_valid # 最后更新 last_update = response.xpath("//table//tr[8]/td[2]/text()").extract_first() item[\'last_update\'] = last_update # 详情信息 content = response.xpath("//div[@class=\'box_body\']/div[@id=\'content\']").extract_first() item[\'content\'] = content # 公司名称 company = response.xpath("//li[@class=\'f_b t_c\']/a/text()").extract_first() item[\'company\'] = company # 联系人 try: link_man = re.findall("<span>联系人</span>(.*?)  ", response.text) link_man = link_man[0] except: link_man = \'\' item[\'link_man\'] = link_man # 邮件 try: email = re.findall(\'<li><span>邮件</span>(.*?)</li>\', response.text) email = email[0] except: email = \'\' item[\'email\'] = email # 电话 try: tel = re.findall(\'<li><span>电话</span>(.*?)</li>\', response.text) tel = tel[0] except: tel = \'\' item[\'tel\'] = tel # 手机 try : phone = re.findall(\'<li><span>手机</span>(.*?)</li>\', response.text) phone = phone[0] except: phone = \'\' item[\'phone\'] = phone # 公司地址 try: c_dist = re.findall(\'<span>地址</span>(.*?)</li></ul>\',response.text) c_dist = c_dist[0] except: c_dist = \'\' item[\'c_dist\'] = c_dist yield item print(\'*\'*100)
items.py # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your scraped items # # See documentation in: # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html import scrapy class BoliwangWebItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # name = scrapy.Field() collection = table = \'products\' # 产品名称 p_name = scrapy.Field() # 品牌 brand = scrapy.Field() # 单价 price = scrapy.Field() # 起订 set_up = scrapy.Field() # 供货总量 summation = scrapy.Field() # 发货期限 dispatch = scrapy.Field() # 所在地区 dist = scrapy.Field() # 有效期 term_of_valid = scrapy.Field() # 最后更新 last_update = scrapy.Field() # 详情信息 content = scrapy.Field() # 公司名称 company = scrapy.Field() # 联系人 link_man = scrapy.Field() # 邮件 email = scrapy.Field() # 电话 tel = scrapy.Field() # 手机 phone = scrapy.Field() # 公司地址 c_dist = scrapy.Field()
items.py # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your spider middleware # # See documentation in: # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html from scrapy import signals class BoliwangWebSpiderMiddleware(object): # Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined, # scrapy acts as if the spider middleware does not modify the # passed objects. @classmethod def from_crawler(cls, crawler): # This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders. s = cls() crawler.signals.connect(s.spider_opened, signal=signals.spider_opened) return s def process_spider_input(self, response, spider): # Called for each response that goes through the spider # middleware and into the spider. # Should return None or raise an exception. return None def process_spider_output(self, response, result, spider): # Called with the results returned from the Spider, after # it has processed the response. # Must return an iterable of Request, dict or Item objects. for i in result: yield i def process_spider_exception(self, response, exception, spider): # Called when a spider or process_spider_input() method # (from other spider middleware) raises an exception. # Should return either None or an iterable of Response, dict # or Item objects. pass def process_start_requests(self, start_requests, spider): # Called with the start requests of the spider, and works # similarly to the process_spider_output() method, except # that it doesn’t have a response associated. # Must return only requests (not items). for r in start_requests: yield r def spider_opened(self, spider): spider.logger.info(\'Spider opened: %s\' % spider.name) class BoliwangWebDownloaderMiddleware(object): # Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined, # scrapy acts as if the downloader middleware does not modify the # passed objects. @classmethod def from_crawler(cls, crawler): # This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders. s = cls() crawler.signals.connect(s.spider_opened, signal=signals.spider_opened) return s def process_request(self, request, spider): # Called for each request that goes through the downloader # middleware. # Must either: # - return None: continue processing this request # - or return a Response object # - or return a Request object # - or raise IgnoreRequest: process_exception() methods of # installed downloader middleware will be called return None def process_response(self, request, response, spider): # Called with the response returned from the downloader. # Must either; # - return a Response object # - return a Request object # - or raise IgnoreRequest return response def process_exception(self, request, exception, spider): # Called when a download handler or a process_request() # (from other downloader middleware) raises an exception. # Must either: # - return None: continue processing this exception # - return a Response object: stops process_exception() chain # - return a Request object: stops process_exception() chain pass def spider_opened(self, spider): spider.logger.info(\'Spider opened: %s\' % spider.name)
piplines.py # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here # # Don\'t forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting # See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html import pymongo class BoliwangWebPipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): return item class MongoPipeline(object): def __init__(self, mongo_uri, mongo_db): self.mongo_uri = mongo_uri self.mongo_db = mongo_db @classmethod def from_crawler(cls, crawler): return cls(mongo_uri=crawler.settings.get(\'MONGO_URI\'), mongo_db=crawler.settings.get(\'MONGO_DB\')) def open_spider(self, spider): self.client = pymongo.MongoClient(self.mongo_uri) self.db = self.client[self.mongo_db] def process_item(self, item, spider): self.db[item.collection].insert(dict(item)) return item def close_spider(self, spider): self.client.close()
settinngs.py # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Scrapy settings for boliwang_web project # # For simplicity, this file contains only settings considered important or # commonly used. You can find more settings consulting the documentation: # # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html BOT_NAME = \'boliwang_web\' SPIDER_MODULES = [\'boliwang_web.spiders\'] NEWSPIDER_MODULE = \'boliwang_web.spiders\' # Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent #USER_AGENT = \'boliwang_web (+http://www.yourdomain.com)\' # Obey robots.txt rules ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False MONGO_HOST = "localhost" MONGO_PORT = 27017 MONGO_DB = \'boliwang\' # Configure maximum concurrent requests performed by Scrapy (default: 16) #CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 32 # Configure a delay for requests for the same website (default: 0) # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html#download-delay # See also autothrottle settings and docs #DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 3 # The download delay setting will honor only one of: #CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN = 16 #CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP = 16 # Disable cookies (enabled by default) #COOKIES_ENABLED = False # Disable Telnet Console (enabled by default) #TELNETCONSOLE_ENABLED = False # Override the default request headers: #DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = { # \'Accept\': \'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8\', # \'Accept-Language\': \'en\', #} # Enable or disable spider middlewares # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html #SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = { # \'boliwang_web.middlewares.BoliwangWebSpiderMiddleware\': 543, #} # Enable or disable downloader middlewares # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = { \'boliwang_web.middlewares.BoliwangWebDownloaderMiddleware\': 543, } # Enable or disable extensions # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/extensions.html #EXTENSIONS = { # \'scrapy.extensions.telnet.TelnetConsole\': None, #} # Configure item pipelines # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html ITEM_PIPELINES = { \'boliwang_web.pipelines.MongoPipeline\': 300, } # Enable and configure the AutoThrottle extension (disabled by default) # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/autothrottle.html #AUTOTHROTTLE_ENABLED = True # The initial download delay #AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5 # The maximum download delay to be set in case of high latencies #AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY = 60 # The average number of requests Scrapy should be sending in parallel to # each remote server #AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY = 1.0 # Enable showing throttling stats for every response received: #AUTOTHROTTLE_DEBUG = False # Enable and configure HTTP caching (disabled by default) # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html#httpcache-middleware-settings #HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True #HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0 #HTTPCACHE_DIR = \'httpcache\' #HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = [] #HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = \'scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage\'
以上是关于42.scrapy爬取数据入库mongodb的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章

