Ubuntu 18.04 使用Systemd管理MySQL 5.6
Posted digdeep
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Ubuntu 18.04 使用Systemd管理MySQL 5.6相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/skykingf/article/details/45225981
如何用Systemd管理 general 包安装的mysql呢?
首先看看yum安装的MySQL提供的Systemd管理脚本
$ cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service # # Simple MySQL systemd service file # # systemd supports lots of fancy features, look here (and linked docs) for a full list: # http://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemd.exec.html # # Note: this file ( /usr/lib/systemd/system/mysql.service ) # will be overwritten on package upgrade, please copy the file to # # /etc/systemd/system/mysql.service # # to make needed changes. # # systemd-delta can be used to check differences between the two mysql.service files. # [Unit] Description=MySQL Community Server After=network.target After=syslog.target [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target Alias=mysql.service [Service] User=mysql Group=mysql # Execute pre and post scripts as root PermissionsStartOnly=true # Needed to create system tables etc. ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/mysql-systemd-start pre # Start main service ExecStart=/usr/bin/mysqld_safe # Don\'t signal startup success before a ping works ExecStartPost=/usr/bin/mysql-systemd-start post # Give up if ping don\'t get an answer TimeoutSec=600 Restart=always PrivateTmp=false
适当修改 /lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service 如下:
After=network.target After=syslog.target [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target Alias=mysql.service [Service] User=mysql Group=mysql PermissionsStartOnly=true ExecStart=/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe TimeoutSec=600 Restart=always PrivateTmp=false
然后
ln -s /lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service /etc/systemd/mysqld.service
ln -s /lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service /etc/systemd/mysqld.service
然后 使用 systemctl 设置 mysqld.service自动启动
systemctl enable mysqld.service
查看是否设置成:

systemctl 常见用法:
开机启动:
systemctl enable ***.service
停止开机启动:
systemctl disable ***.service
启动/停止/重启服务:
systemctl start/stop/restart ***.service
查询服务状态:
systemctl status ***.service
列出系统服务,-t后用tab键可以关联出所有支持的unit类型
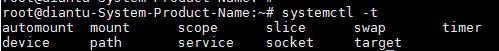
查询某项服务是否active,以sshd.serice为例
systemctl is-active sshd.service
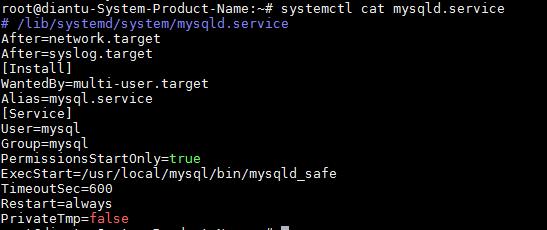
直接查看某项服务的配置文件,以mysqld.serice为例
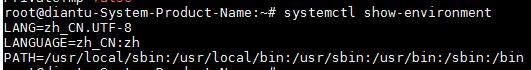
查看环境变量
以上是关于Ubuntu 18.04 使用Systemd管理MySQL 5.6的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章