geneID转换之org.Hs.eg.db包简介
Posted djx571
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了geneID转换之org.Hs.eg.db包简介相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1)安装载入
-------------------------------------------
if("org.Hs.eg.db" %in% rownames(installed.packages()) == FALSE) {source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R");biocLite("org.Hs.eg.db")}
suppressMessages(library(org.Hs.eg.db))
2)查看该包所有的对象
--------------------------------------------
ls("package:org.Hs.eg.db")

功能:可以用来进行基因ID的转换
org.Hs.egACCNUM:Map Entrez Gene identifiers to GenBank Accession Numbers(Entrez Gene identifiers 和genbank)
org.Hs.egALIAS2EG:Map between Common Gene Symbol Identifiers and Entrez Gene
org.Hs.eg.db:Bioconductor annotation data package
org.Hs.egCHR:Map Entrez Gene IDs to Chromosomes
org.Hs.egCHRLENGTHS:A named vector for the length of each of the chromosomes
org.Hs.egCHRLOC:Entrez Gene IDs to Chromosomal Location
org.Hs.egENSEMBL:Map Ensembl gene accession numbers with Entrez Gene identifiers
org.Hs.egENSEMBLPROT:Map Ensembl protein acession numbers with Entrez Gene identifiers
org.Hs.egENSEMBLTRANS:Map Ensembl transcript acession numbers with Entrez Gene identifiers
org.Hs.egENZYME:Map between Entrez Gene IDs and Enzyme Commission (EC) Numbers
org.Hs.egGENENAME:Map between Entrez Gene IDs and Genes
org.Hs.egGO:Maps between Entrez Gene IDs and Gene Ontology (GO) IDs
org.Hs.egMAP:Map between Entrez Gene Identifiers and cytogenetic:Maps/bands
org.Hs.egMAPCOUNTS Number of:Mapped keys for the:Maps in package org.Hs.eg.db
org.Hs.egOMIM:Map between Entrez Gene Identifiers and Mendelian Inheritance in Man (MIM) identifiers
org.Hs.egORGANISM:The Organism for org.Hs.eg
org.Hs.egPATH:Mappings between Entrez Gene identifiers and KEGG pathway identifiers
org.Hs.egPFAM:Maps between Manufacturer Identifiers and PFAM Identifiers
org.Hs.egPMID:Map between Entrez Gene Identifiers and PubMed Identifiers
org.Hs.egPROSITE:Maps between Manufacturer Identifiers and PROSITE Identifiers
org.Hs.egREFSEQ:Map between Entrez Gene Identifiers and RefSeq Identifiers
org.Hs.egSYMBOL:Map between Entrez Gene Identifiers and Gene Symbols
org.Hs.egUNIGENE:Map between Entrez Gene Identifiers and UniGene cluster identifiers
org.Hs.egUNIPROT:Map Uniprot accession numbers with Entrez Gene identifiers
org.Hs.eg_dbconn:Collect information about the package annotation DB
示例:
(用mget函数):
myEIDs <- c("1", "10", "100", "1000", "37690")
mySymbols <- mget(myEIDs, org.Hs.egSYMBOL, ifnotfound=NA) ####myEID是自己的ID,org.Hs.egSYMBOL是其中的一个对象
mySymbols <- unlist(mySymbols)
(用select函数):
myEIDs <- c("ENSG00000130720", "ENSG00000103257", "ENSG00000156414")
cols <- c("SYMBOL", "GENENAME")
select(org.Hs.eg.db, keys=myEIDs, columns=cols, keytype="ENSEMBL")#生成数据框,
原理:例如将 Entrez Gene identifiers( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=gene) 与 GenBank accession numbers进行简单的mapping。该map依据的数据库是Entrez Gene ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/DATA
以DATA其中的一个gene2ensembl文件为例来感受其实如何实现的:
wget ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/DATA/gene2ensembl.gz
解压后查看:
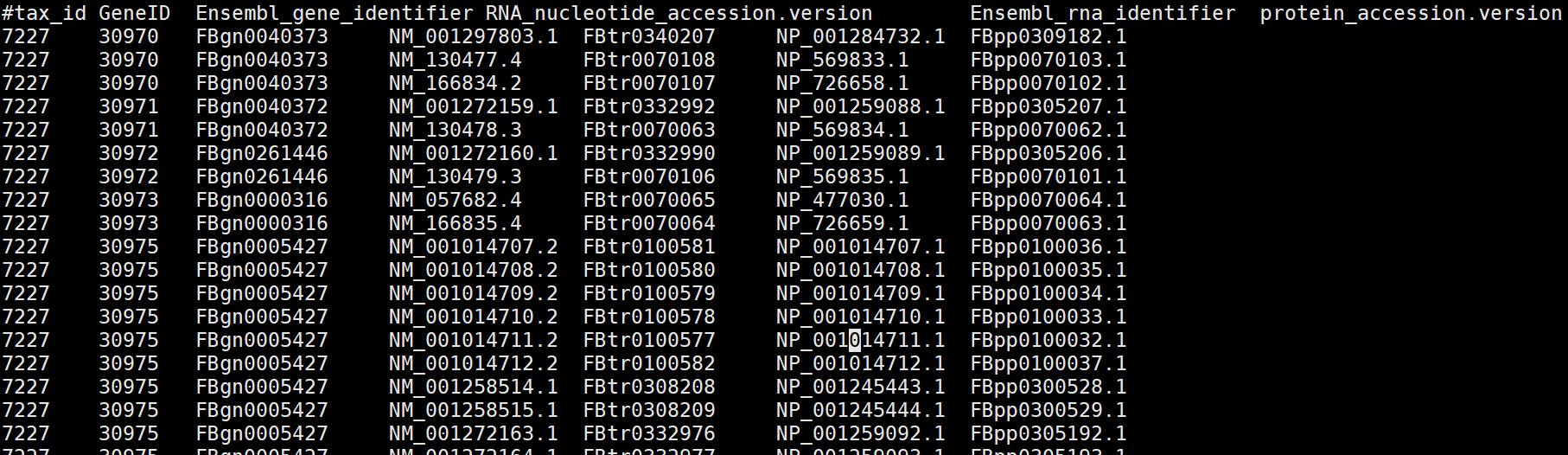
其中第一列是物种id,第二列是GeneID, 第三列是Ensemble_geneID,第四列是RNA_id,第五列是Ensemble_RNAid,第六列是protein_id。因此这些R包的功能极有可能就是利用NCBI或ensem等数据库中的这些文件信息,通过一系列的脚本实现了基因ID之间进行转换,因此如果对NCBI、Ensemble等网络架构熟悉的话,自己又会写脚本,就可以自己处理,而不用这些R包进行。当然别人写好了,为什么自己造轮子呢?自己造轮子是为了深刻的理解
3)各个对象的简单使用
-----------------------------------------------------------
3.1)org.Hs.egACCNUM(将Entrez Gene identifiers 与 GenBank Accession Numbers进行map
x <- org.Hs.egACCNUM ### Bimap interface
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x) ## Get the entrez gene identifiers that are mapped to an ACCNUM
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes]) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5] # Get the ACCNUM for the first five genes
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
#For the reverse map ACCNUM2EG:
xx <- as.list(org.Hs.egACCNUM2EG) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0){
xx[1:5] # Gets the entrez gene identifiers for the first five Entrez Gene IDs
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
3.2)org.Hs.egALIAS2EG(将 Common Gene Symbol Identifiers 和 Entrez Gene进行转换)
x <- org.Hs.egACCNUM ## Bimap interface:org.Hs.egALIAS2EG
xx <- as.list(org.Hs.egALIAS2EG) # Convert the object to a list
xx <- xx[!is.na(xx)] # Remove pathway identifiers that do not map to any entrez gene id
if(length(xx) > 0){
xx[1:2] # The entrez gene identifiers for the first two elements of XX
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
3.3) org.Hs.egCHR (将Entrez Gene IDs 和Chromosomes进行map)
x <- org.Hs.egCHR ## Bimap interface
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x) #Get entrez gene that are mapped to a chromosome
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes]) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5] # Get the CHR for the first five genes
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
3.4)org.Hs.egCHRLENGTHS (每个染色体的长度)
tt <- org.Hs.egCHRLENGTHS ## Bimap interface:
tt["1"] # Length of chromosome 1
for (i in c(1:22,\'X\',\'Y\')){print(tt[i])} #####打印每一个染色体的长度
3.5) org.Hs.egCHRLOC (Entrez Gene IDs在Chromosomal 上的定位)
x <- org.Hs.egCHRLOC ### Bimap interface
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x) #Get the entrez gene identifiers that are mapped to chromosome locations
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes]) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5] # Get the CHRLOC for the first five genes
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
3.6)org.Hs.egENSEMBL (将Ensembl gene accession numbers 与 Entrez Gene identifiers进行map)
x <- org.Hs.egENSEMBL ## Bimap interface
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x)# Get the entrez gene IDs that are mapped to an Ensembl ID
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes]) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5] # Get the Ensembl gene IDs for the first five genes
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
#For the reverse map ENSEMBL2EG:
xx <- as.list(org.Hs.egENSEMBL2EG) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0){
xx[1:5] # Gets the entrez gene IDs for the first five Ensembl IDs
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
x <- org.Hs.egENSEMBLPROT ## Bimap interface
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x) #Get the entrez gene IDs that are mapped to an Ensembl ID
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes]) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5] # Get the Ensembl gene IDs for the first five proteins
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
#For the reverse map ENSEMBLPROT2EG:
xx <- as.list(org.Hs.egENSEMBLPROT2EG) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0){
xx[1:5] # Gets the entrez gene IDs for the first five Ensembl IDs
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
x <- org.Hs.egENSEMBLTRANS ## Bimap interface:
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x) #entrez gene IDs that are mapped to an Ensembl ID
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes]) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5] # Get the Ensembl gene IDs for the first five proteins
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
#For the reverse map ENSEMBLTRANS2EG:
xx <- as.list(org.Hs.egENSEMBLTRANS2EG) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0){
xx[1:5] # Gets the entrez gene IDs for the first five Ensembl IDs
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
3.9)org.Hs.egGENENAME(将 Entrez Gene IDs 与 Genes进行mapping)
x <- org.Hs.egGENENAME ## Bimap interface
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x) #gene names that are mapped to an entrez gene identifier
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes]) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5] # Get the GENE NAME for the first five genes
xx[[1]] # Get the first one
}
3.10)org.Hs.egGO (Entrez Gene IDs与 Gene Ontology (GO) IDs进行mapping)
x <- org.Hs.egGO ## Bimap interface:
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x) # entrez gene identifiers that are mapped to a GO ID
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes]) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0) {
got <- xx[[1]] # Try the first one
got[[1]][["GOID"]]
got[[1]][["Ontology"]]
got[[1]][["Evidence"]]
}
# For the reverse map:
xx <- as.list(org.Hs.egGO2EG) # Convert to a list
if(length(xx) > 0){
goids <- xx[2:3] # Gets the entrez gene ids for the top 2nd and 3nd GO identifiers
goids[[1]] # Gets the entrez gene ids for the first element of goids
names(goids[[1]]) # Evidence code for the mappings
}
# For org.Hs.egGO2ALLEGS
xx <- as.list(org.Hs.egGO2ALLEGS)
if(length(xx) > 0){
goids <- xx[2:3] # Entrez Gene identifiers for the top 2nd and 3nd GO identifiers
goids[[1]] # Gets all the Entrez Gene identifiers for the first element of goids
names(goids[[1]]) # Evidence code for the mappings
}
3.11)org.Hs.egPATH (将Entrez Gene identifiers 与KEGG pathway identifiers进行mapping)
x <- org.Hs.egPATH ## Bimap interface:
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x)
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes])
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5]
xx[[1]]
}
# For the reverse map:
xx <- as.list(org.Hs.egPATH2EG)
xx <- xx[!is.na(xx)] # Remove pathway identifiers that do not map to any entrez gene id
if(length(xx) > 0){
xx[1:2]
xx[[1]]
}
x <- org.Hs.egREFSEQ
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x)
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes])
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5]
xx[[1]]
}
# For the reverse map:
x <- org.Hs.egREFSEQ2EG
mapped_seqs <- mappedkeys(x)
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_seqs])
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5]
xx[[1]]
}
3.13)org.Hs.egSYMBOL(将 Entrez Gene Identifiers 与Gene Symbols进行mapping)
x <- org.Hs.egSYMBOL
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x)
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes])
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5]
xx[[1]]
}
x <- org.Hs.egSYMBOL2EG
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x)
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes])
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5]
xx[[1]]
}
3.14)org.Hs.egUNIGENE (Entrez Gene Identifiers 与 UniGene cluster identifiers进行mapping)
x <- org.Hs.egUNIGENE
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x)
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes])
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5]
xx[[1]]
}
# For the reverse map:
x <- org.Hs.egUNIGENE2EG
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x)
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes])
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5]
xx[[1]]
}
3.15)org.Hs.egUNIPROT (Uniprot accession numbers与 Entrez Gene identifiers进行mapping)
x <- org.Hs.egUNIPROT
mapped_genes <- mappedkeys(x)
xx <- as.list(x[mapped_genes])
if(length(xx) > 0) {
xx[1:5]
xx[[1]]
}
希望大家通过上述教程的解析,能够理解,基因ID,名称等之间是如何转换,并通过这些对NCBI、ensemble、pfam等数据库有相应的一定认识。
以上是关于geneID转换之org.Hs.eg.db包简介的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章