C语言里int和short型变量的区别是啥??
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C语言里int和short型变量的区别是啥??相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我手里的一本谭浩强的C语言上说,这两种变量在内存中都是用两字节来表示。可表示的数字范围都是-32767——37678。
有点糊涂,那为什么还要把两种变量分开呢??
1、占用字节根据机型不同会有不同:
在一般的电脑中,int占用4字节,32比特,在之前的微型机中,int占用2字节,16比特。在32位平台下如windows(32位)中short一般为16位。
2、数值范围不同:
int在一般的电脑中,数据范围为-2147483648~2147483647[-2^31~2^31-1],在之前的微型机中,int数据范围为-32768~32767[-2^15~2^15-1]。C++ & C short为一种数据类型,范围-32768~+32767。

扩展资料:
整型数据的其它分类:
1、长整型:类型说明符为long int或long,在内存中占4个字节。
2、无符号型:类型说明符为unsigned。无符号型又可与上述三种类型匹配而构成:
3、无符号基本型:类型说明符为unsigned int或unsigned。
4、无符号短整型:类型说明符为unsigned short。
5、无符号长整型:类型说明符为unsigned long。
short长度规则:依据程序编译器的不同short定义的字节数不同。标准定义short短整型变量不得低于16位,即两个字节。编译器头文件夹里面的limits.h定义了short能表示的大小:SHRT_MIN~SHRT_MAX。在32位平台下如windows(32位)中short一般为16位。
参考资料来源:百度百科-INT
参考资料来源:百度百科-short
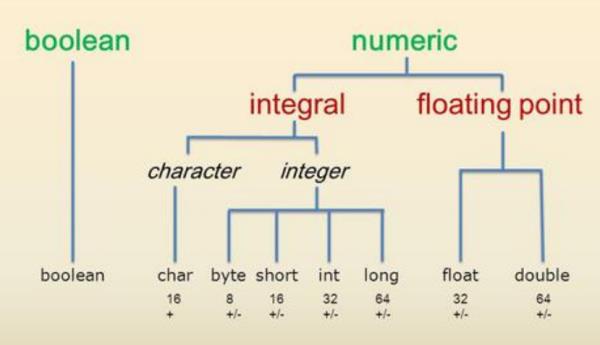
参考技术A一、字节数不同
1、int:int占用32字节,32比特。
2、short:短整型变量不得低于16位,即两个字节。
二、范围不同
1、int:数据范围为-2147483648~2147483647[-2^31~2^31-1]。
2、short:数据范围为范围-32768~+32767。
三、特点不同
1、int:除了int类型之外,还有short、long、long long类型可以表示整数。
2、short:依据程序编译器的不同short定义的字节数不同。
参考资料来源:百度百科-short
参考资料来源:百度百科-INT
参考技术B 区别如下:1 占用空间不同。
int占4个字节,short占2个字节。
2 可以表示数的范围不同。
int 的范围为-2147483648~ 2147483647;
short的范围为 -32768~ 32767。
3 用来输入输出的格式字符不同。
int用%d, short用%h。
用来输出的时候,short可以用%d。除此以外,不能混用。 参考技术C
C++标准规定,int占一个机器字长。在32位系统中int占32位,也就是4个字节,而在老式的16位系统中,int占16位,即2个字节。而C++标准中只限制规定short int不能超过int的长度,具体长度的可以由C++编译器的实现厂商自行决定。目前流行的32位C++编译器中,通常int占4字节,short int占2字节。其中short int可以简写为short。类似地,C++标准只限制了long int不得小于int的长度,具体也没有作出限制。
参考技术D 谭浩强的书太脑残,他那些东西都应该进博物馆int一般都是4字节(32位)或者8字节(64位)
short一般是2字节(16位)相当于word或者int16
不过有个别操作系统或者编译器略有不同本回答被提问者采纳
c语言的37个关键字都是啥
32个关键字吧。auto :声明自动变量
double :声明双精度变量或函数
int: 声明整型变量或函数
struct:声明结构体变量或函数
break:跳出当前循环
else :条件语句否定分支(与 if 连用)
long :声明长整型变量或函数
switch :用于开关语句
case:开关语句分支
enum :声明枚举类型
register:声明寄存器变量
typedef:用以给数据类型取别名
char :声明字符型变量或函数
extern:声明变量是在其他文件正声明
return :子程序返回语句(可以带参数,也可不带参数)
union:声明共用数据类型
const :声明只读变量
float:声明浮点型变量或函数
short :声明短整型变量或函数
unsigned:声明无符号类型变量或函数
continue:结束当前循环,开始下一轮循环
for:一种循环语句
signed:声明有符号类型变量或函数
void :声明函数无返回值或无参数,声明无类型指针
default:开关语句中的“其他”分支
goto:无条件跳转语句
sizeof:计算数据类型长度
volatile:说明变量在程序执行中可被隐含地改变
do :循环语句的循环体
while :循环语句的循环条件
static :声明静态变量
if:条件语句 参考技术A 都好乱·····
32个关键字的是ANSI1989年提出的。
37个关键字的是ANSI1999年提出的。
注意这是针对C语言的。
C99在C89的基础上增加了5个关键字:-Bool -Imaginary restrict -Complex inline
加上32个刚好37个 参考技术B 和英语单词的意思有点像,但又有点不同,关键字的意思好比是中国文言文中出现的字的意思.这中东西慢慢地就会习惯,不用刻意的去了解,程序编多了自然 参考技术C 和英语单词的意思有点像,但又有点不同,关键字的意思好比是中国文言文中出现的字的意思.这中东西慢慢地就会习惯,不用刻意的去了解,程序编多了自然就能理解其中的意思
参考技术D C++关键字不止37个
(1)asm
asm已经被__asm替代了,用于汇编语言嵌入在C/C++程序里编程,从而在某些方面优化代码.虽然用asm关键
字编译时编译器不会报错,但是asm模块的代码是没有意义的.
(2)auto
这个这个关键字用于声明变量的生存期为自动,即将不在任何类、结构、枚举、联合和函数中定义的变量
视为全局变量,而在函数中定义的变量视为局部变量。这个关键字不怎么多写,因为所有的变量默认就是
auto的。
(3)bad_cast,const_cast,dynamic_cast,reinterpret_cast,static_cast
关于异常处理的,还不是太了解..
(4)bad_typeid
也是用于异常处理的,当typeid操作符的操作数typeid为Null指针时抛出.
(5)bool
不用多说了吧,声明布尔类型的变量或函数.
(6)break
跳出当前循环.The break statement terminates the execution of the nearest enclosing loop or
conditional statement in which it appears.
(7)case
switch语句分支.Labels that appear after the case keyword cannot also appear outside a
switchstatement.
(8)catch,throw,try
都是异常处理的语句,The try, throw, and catch statements implement exception handling.
(9)char
声明字符型变量或函数.
(10)class
声明或定义类或者类的对象.The class keyword declares a class type or defines an object of a
class type.
(11)const
被const修饰的东西都受到强制保护,可以预防意外的变动,能提高程序的健壮性。它可以修饰函数的参
数、返回值,甚至函数的定义体。
作用:
1.修饰输入参数
a.对于非内部数据类型的输入参数,应该将“值传递”的方式改为“const引用传递”,目的是提
高效率。例如将void Func(A a) 改为void Func(const A &a)。
b.对于内部数据类型的输入参数,不要将“值传递”的方式改为“const引用传递”。否则既达不
到提高效率的目的,又降低了函数的可理解性。例如void Func(int x) 不应该改为void Func(const int
&x)。
2.用const修饰函数的返回值
a.如果给以“指针传递”方式的函数返回值加const修饰,那么函数返回值(即指针)的内容不能
被修改,该返回值只能被赋给加const修饰的同类型指针。
如对于:const char * GetString(void);
如下语句将出现编译错误:
char *str = GetString();//cannot convert from 'const char *' to 'char *';
正确的用法是:
const char *str = GetString();
b.如果函数返回值采用“值传递方式”,由于函数会把返回值复制到外部临时的存储单元中,加
const修饰没有任何价值。 如不要把函数int GetInt(void) 写成const int GetInt(void)。
3.const成员函数的声明中,const关键字只能放在函数声明的尾部,表示该类成员不修改对象.
说明:
const type m; //修饰m为不可改变
示例:
typedef char * pStr; //新的类型pStr;
char string[4] = "abc";
const char *p1 = string;
p1++; //正确,上边修饰的是*p1,p1可变
const pStr p2 = string;
p2++; //错误,上边修饰的
是p2,p2不可变,*p2可变
同理,const修饰指针时用此原则判断就不会混淆了。
const int *value; //*value不可变,value可变
int* const value; //value不可变,*value可变
const (int *) value; //(int *)是一种type,value不可变,*value可变
//逻辑上这样理解,编译不能通过,需要tydef int* NewType;
const int* const value;//*value,value都不可变
(12)continue
结束当前循环,开始下一轮循环.Forces transfer of control to the controlling expression of the
smallest enclosing do, for, or while loop.
(13)default
switch语句中的默认分支.None of the constants match the constants in the case labels;
adefault label is present.Control is transferred to the default label.
常量的无匹配情况下标签的常量;
adefault标签present.Control转移到默认的标签。
(14)delete
经常用于动态内存分配的语句,Deallocates a block of memory.
(15)do
在do-while循环结构中开始循环体.Executes a statement repeatedly until the specified
termination condition (the expression) evaluates to zero.
(16)double
声明双精度变量或函数.
(17)else
条件语句否定分支(与 if 连用).
(18)enum
声明枚举类型.The name of each enumerator is treated as a constant and must be unique within
the scope where the enum is defined.
(19)explicit
This keyword is a declaration specifier that can only be applied to in-class constructor
declarations. An explicit constructor cannot take part in implicit conversions. It can only
be used to explicitly construct an object.
这个关键字声明说明符,可以只适用于同类构造函数声明。显式构造函数不能在隐式转换的一部分。它只
能用于显式构造一个对象
(20)export
MSDN只说The export keyword is not supported on templates.一种导出语句吧..
(21)extern
extern 意为“外来的”···它的作用在于告诉编译器:有这个变量,它可能不存在当前的文件中,但
它肯定要存在于工程中的某一个源文件中或者一个Dll的输出中。声明变量是在其他文件中声明(也可以看
做是引用变量).Objects and variables declared as extern declare an object that is defined in
another translation unit or in an enclosing scope as having external linkage.
(22)false,true
bool类型的两个枚举值.
(23)float
声明浮点型变量或函数.
(24)for
一种循环语句(可意会不可言传).Use the for statement to construct loops that must execute a
specified number of times.
(25)friend
声明友元函数或者类.The friend keyword allows a function or class to gain access to the
private and protected members of a class.
(26)goto
无条件跳转语句.Performs an unconditional transfer of control to the named label.
(27)if
条件语句.Controls conditional branching.常与else一起用.
(28)inline
声明定义内联函数,编译时将所调用的代码嵌入到主函数中.The inline specifiers instruct the
compiler to insert a copy of the function body into each place the function is called.
(29)int
声明整型变量或函数.
(30)long
声明长整型变量或函数.
(31)mutable
This keyword can only be applied to non-static and non-const data members of a class. If a
data member is declared mutable, then it is legal to assign a value to this data member from
aconst member function.
这个关键字只适用于非静态和非const数据类成员。如果一个
声明数据成员是可变的,那么它是合法的赋值从这个数据成员
aconst成员函数
(32)namespace
Dynamically imports an element behavior into a document.
动态导入到文档中的元素行为
c++中using namespace std
(33)new
动态内存分配.Allocates memory for an object or array of objects of type-name from the free
store and returns a suitably typed, nonzero pointer to the object.
分配内存的对象或数组类型的对象从自由的名义
存储和返回一个适当类型,非零对象的指针
(34)operator
The operator keyword declares a function specifying what operator-symbol means when applied
to instances of a class.
经营者关键字声明一个函数指定经营什么符号意味着当应用
对一类的实例
(35)private
类私有函数和数据成员的标示.When preceding a list of class members, the private keyword
specifies that those members are accessible only from member functions and friends of the
class. This applies to all members declared up to the next access specifier or the end of
the class.
当上一类的成员,私人关键字列表
指定这些成员只能从成员的职能和朋友访问
类。这适用于所有成员宣布了下一个访问符或结束
类
(36)protected
The protected keyword specifies access to class members in the member-list up to the next
access specifier (public or private) or the end of the class definition.
受保护的关键字指定访问类成员的成员名单,直至下一个
访问说明符(公共或私营)或类定义结束
(37)public
访问方式:When preceding a list of class members, the public keyword specifies that those
members are accessible from any function. This applies to all members declared up to the
next access specifier or the end of the class.
当上一类成员,市民关键字列表指定的
成员可以从任何功能。这适用于所有成员宣布到
明年访问符或类的结束
(38)register
声明积存器变量.The register keyword specifies that the variable is to be stored in a machine
register, if possible.这个关键字命令编译器尽可能的将变量存在CPU内部寄存器中,而不是通过内存寻
址访问,从而提高效率。
登记册关键字指定变量是要在计算机中存储的
注册,如果可能的话
(39)return
子程序返回语句(可以带参数,也看不带参数),返回函数调用点.Terminates the execution of a
function and returns control to the calling function (or, in the case of the main function,
transfers control back to the operating system). Execution resumes in the calling function
at the point immediately following the call.
终止执行的
功能及控制返回给调用函数(或者,在主函数的情况,
传输控制返回给操作系统)。恢复执行在调用函数
在点后立即致电
(40)short
声明短整型变量或函数.
(41)signed,unsigned
声明有符号类型变量或函数;声明无符号类型变量或函数.
(42)static
声明静态变量.When modifying a variable, the static keyword specifies that the variable has
static durationinitializes it to 0 unless another value is specified.
当修改一个变量,static关键字指定的变量
静态durationinitializes为0,除非另一个指定值
(43)struct
声明结构体变量或函数.struct 类型是一种值类型,通常用来封装小型相关变量组.
struct hello文件名
(44)switch
Allows selection among multiple sections of code, depending on the value of an integral
expression.
允许选择多个之间的代码段,这取决于一个整体的价值
表达
(45)template
模板.The template declaration specifies a set of parameterized classes or functions.
该模板声明指定的类或函数的参数化设置
(46)this
The this pointer is a pointer accessible only within the nonstatic member functions of a
class,struct, or union type.
在该指针是一个指针访问只有在一个非静态成员函数
类,结构或联合类型
(47)typedef
用以给数据类型取别名.Introduces a name that, within its scope, becomes a synonym for the
type given by the type-declaration portion of the declaration.
引入了一个名称,在其范围内,成为一个同义词
该类型声明宣言的一部分给定类型
(48)typeid
typeid is used to get the Type for a type at compile time.
typeid用于获取一个类型的类型在编译时
(49)typename
Tells the compiler that an unknown identifier is a type.Use this keyword only in template
definitions.
告诉编译器是一个未知的标识符是一个type.Use这只是在模板中的关键字
定义
(50)union
声明联合数据类型.A union is a user-defined data or class type that, at any given time,
contains only one object from its list of members (although that object can be an array or a
class type).
阿联盟是一个用户定义的数据类型或类,在任何特定时间,
只包含其成员名单的对象(虽然这个对象可以是一个数组或
类类型)
(51)using
The using declaration introduces a name into the declarative region in which the
usingdeclaration appears.
使用声明的声明中引入了在该地区出现一个名称usingdeclaration
(52)virtual
声明虚基类或虚函数.The virtual keyword declares a virtual function or a virtual base class.
virtual关键字声明了一个虚函数或虚基类
(53)void
声明函数无返回值或无参数,声明无类型指针.
When used as a function return type, the void keyword specifies that the function does not
return a value. When used for a function's parameter list, void specifies that the function
takes no parameters. When used in the declaration of a pointer, void specifies that the
pointer is "universal."
(54)volatile
说明变量在程序执行中可被隐含地改变,表明某个变量的值可能在外部被改变,优化器在用到这个变量时
必须每次都小心地重新读取这个变量的值,而不是使用保存在寄存器里的备份。Thevolatile keyword is
a type qualifier used to declare that an object can be modified in the program by something
such as the operating system, the hardware, or a concurrently executing thread.
Thevolatile关键字
一个类型限定符用来声明一个对象可以在程序中修改的东西
如操作系统,硬件或并发执行线程。
(55)wchar_t
宽字.
(56)while
循环语句的循环条件
(57)class
类本回答被提问者和网友采纳
以上是关于C语言里int和short型变量的区别是啥??的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章