在linux操作系统中,怎样挂载U盘。
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了在linux操作系统中,怎样挂载U盘。相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A方法如下:
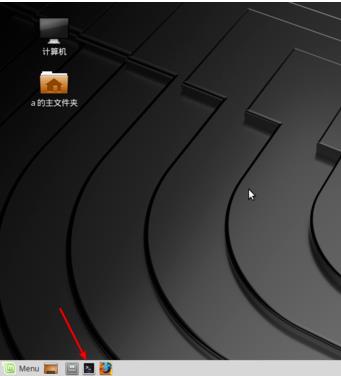
1、先一步把U盘插入到电脑上,然后点击任务栏上的图标,终端的图标,把它打开了的,如图二为打开状态。
2、此时输入命令:【sudo fdisk -l】,注意后面的为小写的l不是i。然后知道这U盘的分区名字为【sdb1】,然后输入命令【sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt】,那么回车。

3、那么看到图一的提示,说明挂载成功了,然后输入命令:【cd /mnt】,那么相当于进入到U盘里面的。如果这个方法管理不方便的话,那么看下面的步骤。

4、或者是打开这个计算机,然后打开这个文件系统,如图所示。

5、然后里面有个mnt文件夹,打开后,看到它的容量为5g,那么说明这个就是U盘了的。那么你可以把文件或者是其他的东西搬运进入即可,相当于搬运到了的U盘上的。

怎样在linux下对U盘进行格式化和分区
说明,为了不做无用功,首先必须卸载要分区的设备,分区才能执行成功。通过命令umount /media/?? 或者umount /mnt/???
看你的实际情况,这一步必不可少。
1、首先通过命令fdisk -l 在root命令下查看U盘的分区信息。
1、首先通过命令fdisk -l 在root命令下查看U盘的分区信息。
2、通过fdisk命令对挂载的设备进行分区操作,命令如下:fdisk /dev/sdb (可能不一定是这样,按照实际情况而定)。
3、输入fdisk /dev/sdb 会有提示命令,输入m就会列出来,如下所示:
[email protected]:~# fdisk /dev/sdb
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition‘s system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help):
4、输入p可以浏览当前设备的分区信息,如下所示:
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition‘s system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help):
4、输入p可以浏览当前设备的分区信息,如下所示:
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 7948 MB, 7948206080 bytes
245 heads, 62 sectors/track, 1021 cylinders, total 15523840 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x13561963
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 268287 133120 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 268288 15523839 7627776 83 Linux
Command (m for help):
5、可以看到上面有两个分区,现在我删除这两个分区,d命令:
Disk /dev/sdb: 7948 MB, 7948206080 bytes
245 heads, 62 sectors/track, 1021 cylinders, total 15523840 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x13561963
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 268287 133120 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 268288 15523839 7627776 83 Linux
Command (m for help):
5、可以看到上面有两个分区,现在我删除这两个分区,d命令:
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-4): 1
Command (m for help): d
Selected partition 2
Command (m for help):
6、确定是否分区被删除了,在通过p命令:
Partition number (1-4): 1
Command (m for help): d
Selected partition 2
Command (m for help):
6、确定是否分区被删除了,在通过p命令:
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 7948 MB, 7948206080 bytes
245 heads, 62 sectors/track, 1021 cylinders, total 15523840 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x13561963
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
Command (m for help):
可以看出没有了分区信息,删除分区成功。
Disk /dev/sdb: 7948 MB, 7948206080 bytes
245 heads, 62 sectors/track, 1021 cylinders, total 15523840 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x13561963
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
Command (m for help):
可以看出没有了分区信息,删除分区成功。
7、现在新建分区,两个分区:
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p):
Using default response p
Partition number (1-4, default 1):
Using default value 1
First sector (2048-15523839, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-15523839, default 15523839): +200M //设定此分区的大小
Command (m for help):
第一个分区已经新建完毕。
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p):
Using default response p
Partition number (1-4, default 1):
Using default value 1
First sector (2048-15523839, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-15523839, default 15523839): +200M //设定此分区的大小
Command (m for help):
第一个分区已经新建完毕。
现在第二个分区:
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p):
Using default response p
Partition number (1-4, default 2):
Using default value 2
First sector (411648-15523839, default 411648):
Using default value 411648
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (411648-15523839, default 15523839): //没有写,就表示剩下的空间都是此分区的。
Using default value 15523839
Command (m for help):
按照默认的就可以了,这样分区就完成了。
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p):
Using default response p
Partition number (1-4, default 2):
Using default value 2
First sector (411648-15523839, default 411648):
Using default value 411648
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (411648-15523839, default 15523839): //没有写,就表示剩下的空间都是此分区的。
Using default value 15523839
Command (m for help):
按照默认的就可以了,这样分区就完成了。
8、退出分区操作:
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
这一步有可能出错(如下),出错的原因是现有设备挂载了。首先必须卸载此设备,上面的操作才能执行成功。
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: 设备或资源忙.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at
the next reboot or after you run partprobe(8) or kpartx(8)
Syncing disks.
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: 设备或资源忙.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at
the next reboot or after you run partprobe(8) or kpartx(8)
Syncing disks.
上面分区成功,但是我们想要自己的文件系统,比如分区1是fat格式的,分区2是ext2格式的,这样怎样处理呢?非常重要的命令mkfs
其有很多种命令:
mkfs mkfs.cramfs mkfs.ext3 mkfs.ext4dev mkfs.msdos mkfs.vfat
mkfs.bfs mkfs.ext2 mkfs.ext4 mkfs.minix mkfs.ntfs
mkfs.bfs mkfs.ext2 mkfs.ext4 mkfs.minix mkfs.ntfs
1、分区1为fat格式:
mkfs.vfat -F 32 -n vfat /dev/sdb1 //后面的vfat是自己起的设备的命令
[email protected]:~# mkfs.vfat -F 32 -n fat /dev/sdb1
mkfs.vfat 3.0.12 (29 Oct 2011)
[email protected]:~# mkfs.vfat -F 32 -n fat /dev/sdb1
mkfs.vfat 3.0.12 (29 Oct 2011)
2、分区2为ext2格式:
mkfs.ext2 -F -L ext2 /dev/sdb2 //同上,这个会格式化,时间依据空间的大小不定
[email protected]:~# mkfs.ext2 -F -L ext2 /dev/sdb2
mke2fs 1.42 (29-Nov-2011)
文件系统标签=ext2
OS type: Linux
块大小=4096 (log=2)
分块大小=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
472352 inodes, 1889024 blocks
94451 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
第一个数据块=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1937768448
58 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8144 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632
Allocating group tables: 完成
正在写入inode表: 完成
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information:
完成
[email protected]:~#
[email protected]:~# mkfs.ext2 -F -L ext2 /dev/sdb2
mke2fs 1.42 (29-Nov-2011)
文件系统标签=ext2
OS type: Linux
块大小=4096 (log=2)
分块大小=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
472352 inodes, 1889024 blocks
94451 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
第一个数据块=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1937768448
58 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8144 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632
Allocating group tables: 完成
正在写入inode表: 完成
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information:
完成
[email protected]:~#
如果命令不知道,通过man mkfs.vfat查看,一目了然。
完成。
以上是关于在linux操作系统中,怎样挂载U盘。的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章