基本类型包装类,,,System类,,,Math类,,,Arrays类,,,大数据运算
Posted wangmeihao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基本类型包装类,,,System类,,,Math类,,,Arrays类,,,大数据运算相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

基本数据类型对象包装类:java将基本数据类型值封装成了对象。
8种基本类型对应的包装类:
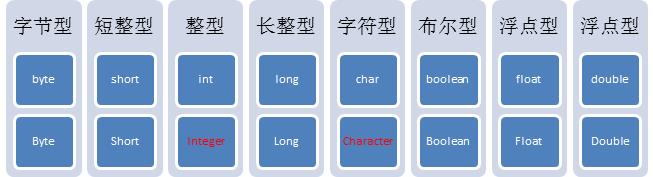
基本数据类型对象包装类特点:用于在基本数据和字符串之间进行转换。
l 将字符串转成基本类型:

System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("123") + 2);
//打印结果为 125
l 将基本数值转成字符串有3种方式:
1. 基本类型直接与””相连接即可;34+""
2. 调用String的valueOf方法;String.valueOf(34) ;
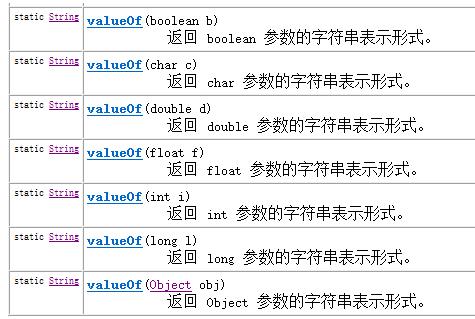
3。 调用包装类中的toString方法;Integer.toString(34) ;

package com.oracle.demo01; public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //字符串转基本数据类型 int i=Integer.parseInt("123"); //基本数据类型转字符串 //1.双引号:“”+基本数据类型 System.out.println("sum"+1+1); //2.调用String类中的valueof方法 String i=String.valueOf(12.3); //3.调用包装类中独有的tostring方法 String i=Double.toString(12.3);
基本类型和对象转换
l 基本数值---->包装对象

Integer i = new Integer(4);//使用构造函数函数 Integer ii = new Integer("4");//构造函数中可以传递一个数字字符串

Integer iii = Integer.valueOf(4);//使用包装类中的valueOf方法 Integer iiii = Integer.valueOf("4");//使用包装类中的valueOf方法
l 包装对象---->基本数值

int num = i.intValue();
自动装箱拆箱
l 自动拆箱:对象自动直接转成基本数值
l 自动装箱:基本数值自动直接转成对象
Integer i = 4;//自动装箱。相当于Integer i = Integer.valueOf(4); i = i + 5;//等号右边:将i对象转成基本数值(自动拆箱) i.intValue() + 5; 加法运算完成后,再次装箱,把基本数值转成对象。
l 自动装箱(byte常量池)细节的演示
当数值在byte范围之内时,进行自动装箱,不会新创建对象空间而是使用已有的空间。
Integer a = new Integer(3); Integer b = new Integer(3); System.out.println(a==b);//false System.out.println(a.equals(b));//true
System.out.println("---------------------");
Integer x = 127;
Integer y = 127;
//在jdk1.5自动装箱时,如果数值在byte范围之内,不会新创建对象空间而是使用原来已有的空间。
System.out.println(x==y); //true
System.out.println(x.equals(y)); //true
System类

l currentTimeMillis() 获取当前系统时间与1970年01月01日00:00点之间的毫秒差值
l exit(int status) 用来结束正在运行的Java程序。参数传入一个数字即可。通常传入0记为正常状态,其他为异常状态
l gc() 用来运行JVM中的垃圾回收器,完成内存中垃圾的清除。
l getProperty(String key) 用来获取指定键(字符串名称)中所记录的系统属性信息

l arraycopy方法,用来实现将源数组部分元素复制到目标数组的指定位置
public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());//毫秒,当前时间 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ if(i==5){ System.exit(0);//结束程序 }else{ System.out.println(i); } } }
public class Person { protected void finalize() throws Throwable { super.finalize(); System.out.println("我被清理了"); }//当我这个对象被清理的时候调用 } public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { new Person(); new Person(); new Person(); new Person(); new Person(); System.gc(); } }
public class Demo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr={1,2,3,4,5,6}; int[] brr={0,0,0,0,0,0,0}; System.arraycopy(arr, 1, brr, 3, 2);//把arr下标为1开始的值替换给brr下标为3长度为2的数 for(int i=0;i<brr.length;i++){ System.out.println(brr[i]); } } }
1.1 System类的方法练习
l 练习一:验证for循环打印数字1-9999所需要使用的时间(毫秒)
public class Demo01 { /*验证for循环打印数字1-9999所需要使用的时间(毫秒)*/ public static void main(String[] args) { Long kaishi=System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i=1;i<1000;i++){ System.out.print(i); } Long jieshu=System.currentTimeMillis(); Long time=jieshu-kaishi; System.out.println(); System.out.println(time); } }
l 练习二:将src数组中前3个元素,复制到dest数组的前3个位置上
复制元素前:src数组元素[1,2,3,4,5],dest数组元素[6,7,8,9,10]
复制元素后:src数组元素[1,2,3,4,5],dest数组元素[1,2,3,9,10]
public class Demo02 { /*将src数组中前3个元素,复制到dest数组的前3个位置上 复制元素前:src数组元素[1,2,3,4,5],dest数组元素[6,7,8,9,10] 复制元素后:src数组元素[1,2,3,4,5],dest数组元素[1,2,3,9,10] */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] src={1,2,3,4,5}; int[] dest={6,7,8,9,10}; System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, 3); for(int i=0;i<dest.length;i++){ System.out.print(dest[i]+"\\t"); } } }
l 练习三:循环生成100-999之间的的三位数并进行打印该数,当该数能被10整除时,结束运行的程序
package com.oracle.demo001; import java.util.Random; public class Demo03 { /*循环生成100-999之间的的三位数并进行打印该数,当该数能被10整除时,结束运行的程序*/ public static void main(String[] args) { Random aa=new Random(); while(1==1){ int shu=aa.nextInt(900)+100; if(shu%10==0){ System.exit(0); }else{ System.out.println(shu); } } } }
Math类
工具类,代表能够完成一系列功能的类,在使用它们时,不用创建对象,该类中方法为静态方法
1.1 常用方法

package com.oracle.demo02; public class Dmath { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Math.abs(-9.9));//绝对值 System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.1));//向上取整 System.out.println(Math.floor(12.1));//向下取整 System.out.println(Math.max(12.1,12.9));//比较最大值 System.out.println(Math.min(12.1,12.9));//比较最小值 System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 10));//求次幂2的10次方 System.out.println(Math.random());//求【0-1)内的随机数 System.out.println(Math.round(12.5));//四舍五入 } }
Arrays类
此类包含用来操作数组(比如排序和搜索)的各种方法。
1.1 常用方法
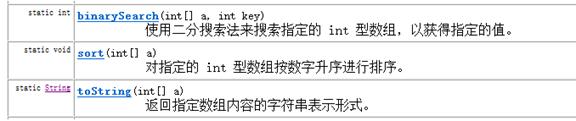
l sort方法,用来对指定数组中的元素进行排序(元素值从小到大进行排序)
//源arr数组元素{1,5,9,3,7}, 进行排序后arr数组元素为{1,3,5,7,9} int[] arr = {1,5,9,3,7}; Arrays.sort( arr );
l toString方法,用来返回指定数组元素内容的字符串形式
int[] arr = {1,5,9,3,7}; String str = Arrays.toString(arr); // str的值为[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
l binarySearch方法,在指定数组中,查找给定元素值出现的位置。若没有查询到,返回位置为-1。要求该数组必须是个有序的数组。
int[] arr = {1,3,4,5,6}; int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 4); //index的值为2 int index2= Arrasy.binarySearch(arr, 2); //index2的值为-1 public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr={11,68,32,79,55}; //排序 Arrays.sort(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); //方法前提,必须有序 //如果查找的元素在数组中不存在,那么返回负的钙元素应该在的下标减一 int index=Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 41);//查找元素在数组中的位置 System.out.println(index); } }
Arrays类的方法练习
l 练习一:定义一个方法,接收一个数组,数组中存储10个学生考试分数,该方法要求返回考试分数最低的后三名考试分数。
package com.oracle.demo001; import java.util.Arrays; public class Demo04 { /*定义一个方法,接收一个数组, * 数组中存储10个学生考试分数,该方法要求返回考试分数最低的后三名考试分数。*/ public static void main(String[] args) { double[] arr={60,70,80,90,99,24,43,56,34,22}; double[] brr=fangfa(arr); for(int i=0;i<brr.length;i++){ System.out.println(brr[i]); } } public static double[] fangfa(double[] arr){ Arrays.sort(arr); double[] xin=new double[3]; System.arraycopy(arr, 0, xin, 0, 3); return xin; } }
大数据运算
BigInteger
在Java的世界中,超过long型的整数已经不能被称为整数了,它们被封装成BigInteger对象.在BigInteger类中,实现四则运算都是方法来实现,并不是采用运算符.
BigInteger类的构造方法:

四则运算
package com.oracle.demo02; import java.math.BigInteger; public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) {
//大数据封装为BigInteger对象
BigInteger b1=new BigInteger("10000000000000000000"); BigInteger b2=new BigInteger("90000000000000000000"); System.out.println(b1.add(b2));//加 System.out.println(b2.subtract(b1));//减 System.out.println(b1.multiply(b2));//乘 System.out.println(b2.divide(b1));//除 } }
BigDecimal

public static void main(String[] args) { //大数据封装为BigDecimal对象 BigDecimal big1 = new BigDecimal("0.09"); BigDecimal big2 = new BigDecimal("0.01"); //add实现加法运算 BigDecimal bigAdd = big1.add(big2); BigDecimal big3 = new BigDecimal("1.0"); BigDecimal big4 = new BigDecimal("0.32"); //subtract实现减法运算 BigDecimal bigSub = big3.subtract(big4); BigDecimal big5 = new BigDecimal("1.105"); BigDecimal big6 = new BigDecimal("100"); //multiply实现乘法运算 BigDecimal bigMul = big5.multiply(big6);
对于浮点数据的除法运算,和整数不同,可能出现无限不循环小数,因此需要对所需要的位数进行保留和选择舍入模式

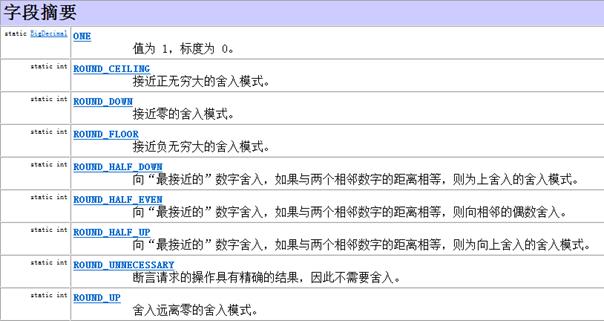
以上是关于基本类型包装类,,,System类,,,Math类,,,Arrays类,,,大数据运算的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章