oracle 03-03 数据库实例管理
Posted 世界树
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了oracle 03-03 数据库实例管理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Managing the Database Instance
Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
• Start and stop the Oracle database instance and
components启动和关闭Oracle实例以及相关组成部件
• Modify database initialization parameters初始化参数
• Describe the stages of database startup数据库启动过程
• Describe database shutdown options数据库关闭选项
• View the alert log查看预警日制
• Access dynamic performance views如何访问动态视图
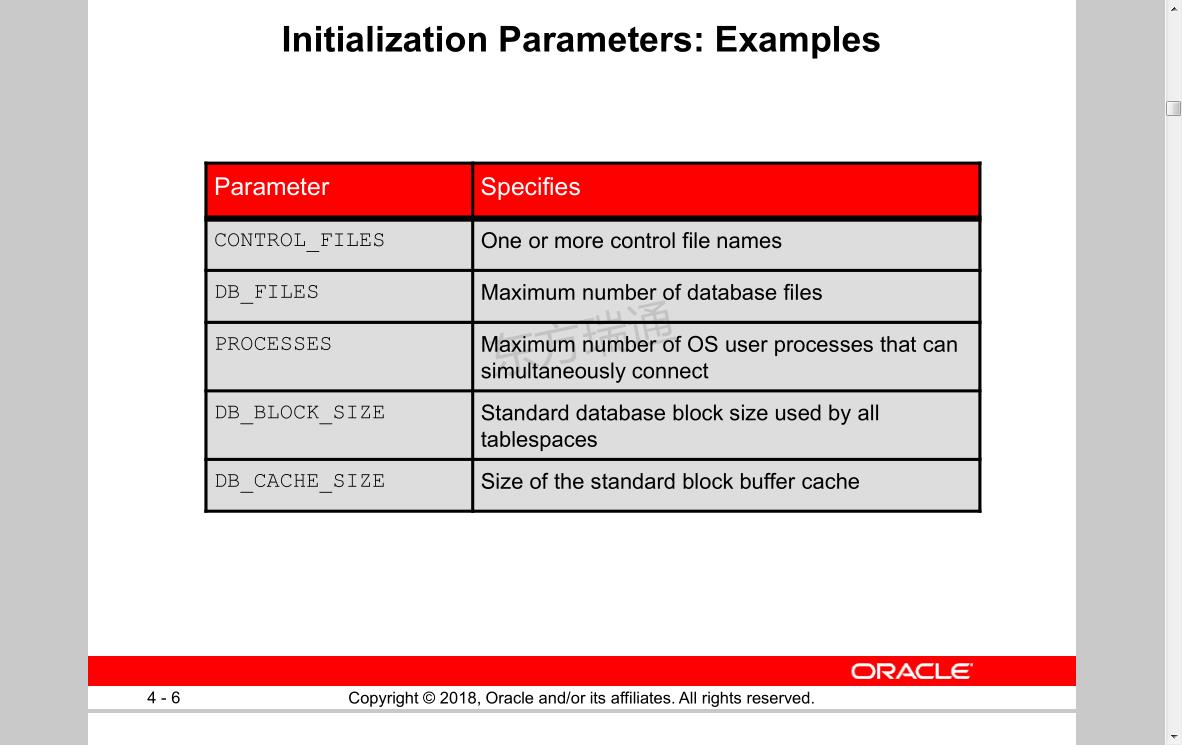
Initialization Parameters: Examples
Parameter Specifies
CONTROL_FILES控制文件 One or more control file names
DB_FILES Maximum number of database files数据库允许的最大文件个数
PROCESSES Maximum number of OS user processes that can
simultaneously connect最大后台进程及后台进程的个数
DB_BLOCK_SIZE Standard database block size used by all
tablespaces标准数据库块大小
DB_CACHE_SIZE 数据库告诉缓冲池Size of the standard block buffer cache
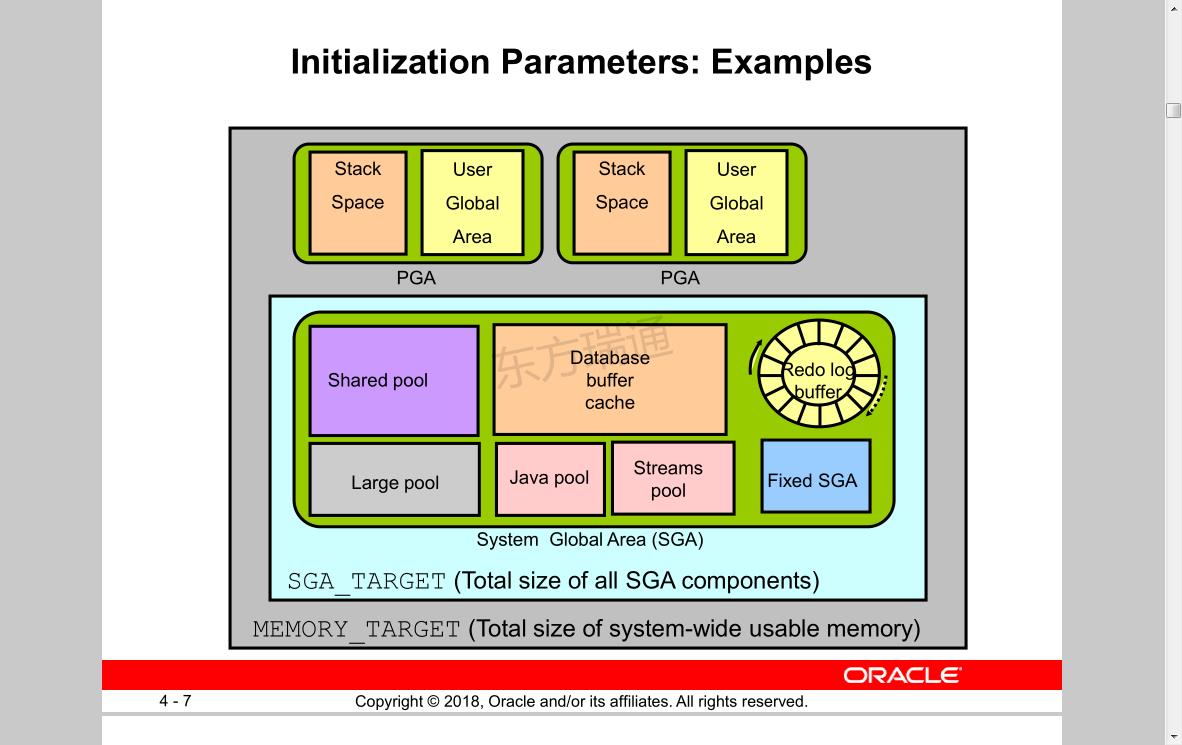
内存大小设置
SGA_TARGET (Total size of all SGA components)
MEMORY_TARGET (Total size of system-wide usable memory)
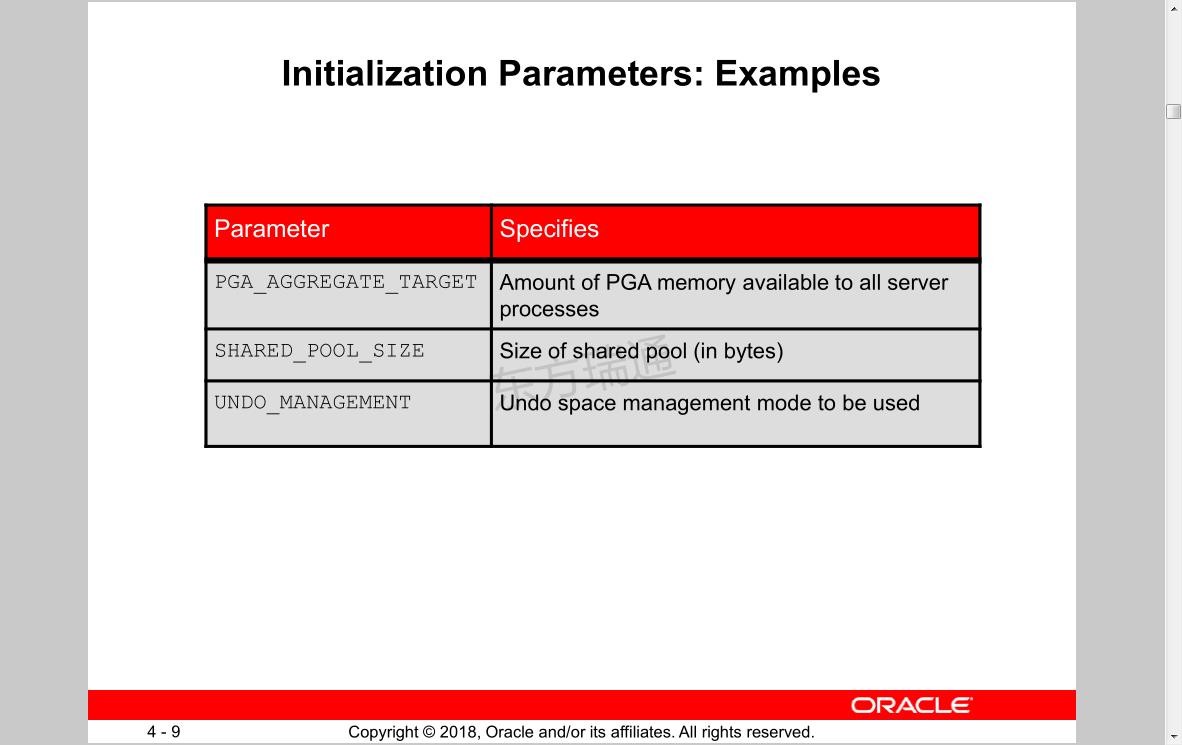
Parameter Specifies
PGA_AGGREGATE_TARGET Amount of PGA memory available to all server
processes设置PGA内存大小
SHARED_POOL_SIZE 设定共享池大小Size of shared pool (in bytes)
UNDO_MANAGEMENT Undo space management mode to be used默认AUTO方式
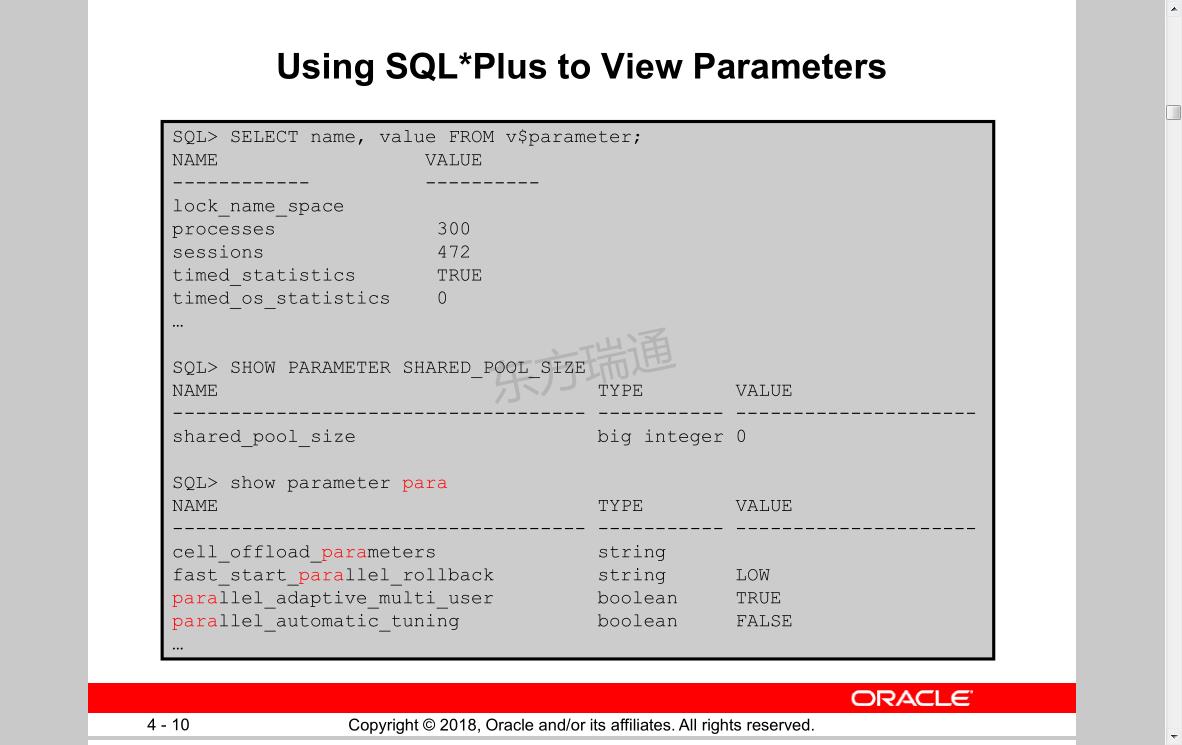
查看参数命令
SQL>show parameter
SQL> show parameter process查看进程参数
Changing Initialization Parameter Values
• Static parameters: 静态参数
– Can be changed only in the parameter file
– Require restarting the instance before taking effect
• Dynamic parameters: 动态参数 修改后不需要重新启动实例即可生效
– Can be changed while database is online
– Can be altered at:
— Session level
— System level
– Are valid for duration of session or based on SCOPE setting
– Are changed by using the ALTER SESSION and ALTER
SYSTEM commands
如何区分静态参数与动态参数
尝试修改某一参数(下面三句意义一样)
SQL> alter system set processes=400
SQL> alter system set processes=400 scope=both;
SQL> alter system set processes=400 scope=memory+sqfiel;
静态参数无法对内存直接修改,需要重新启动实例后才能生效
SQL> alter system set processes=400 scope=sqfiel; 换成只对sqfiel文件修改才能成功
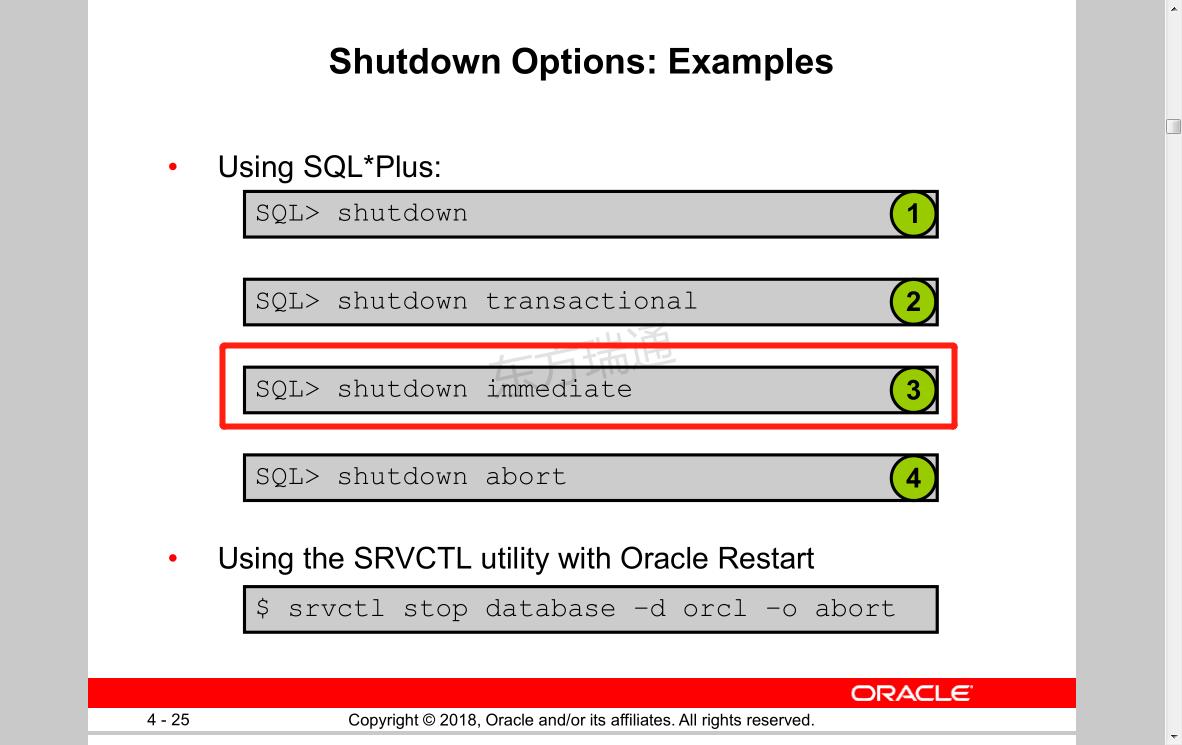
SQL>shut immediate; 关闭后重启数据库后才能生效
SQL>startup
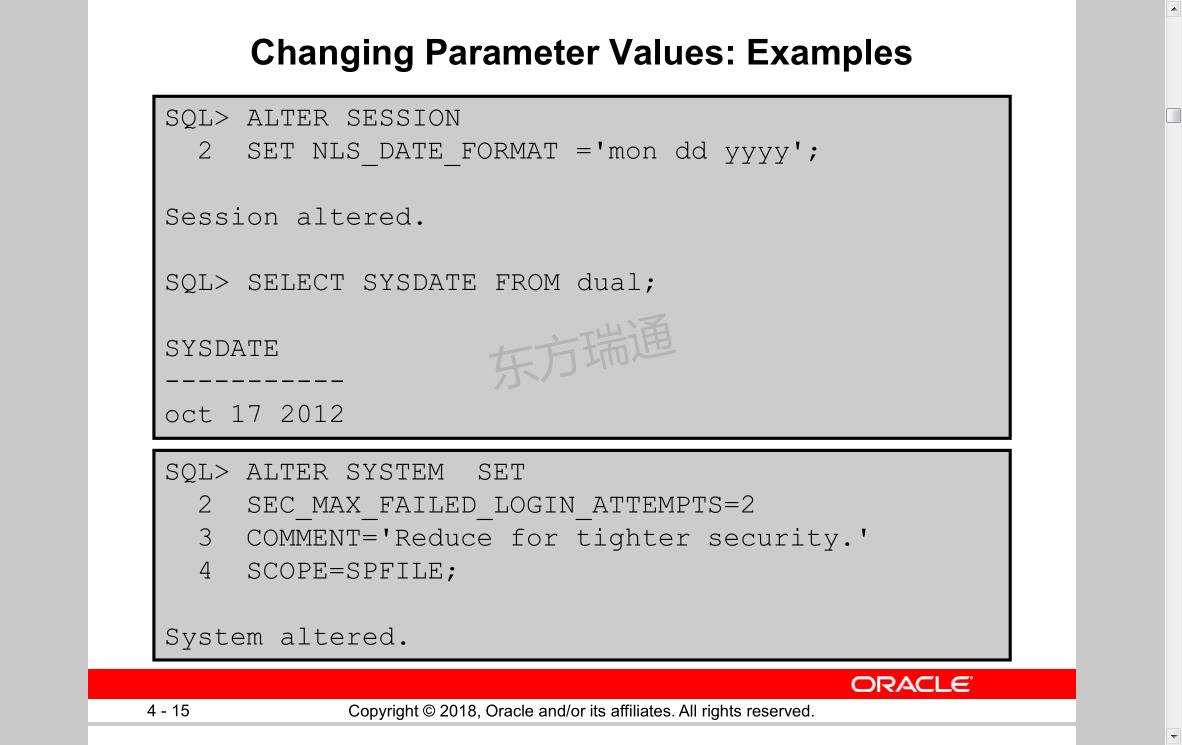
SQL> ALTER SESSION 只对本会话期生效
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET 对整个系统生效 重启后永久生效
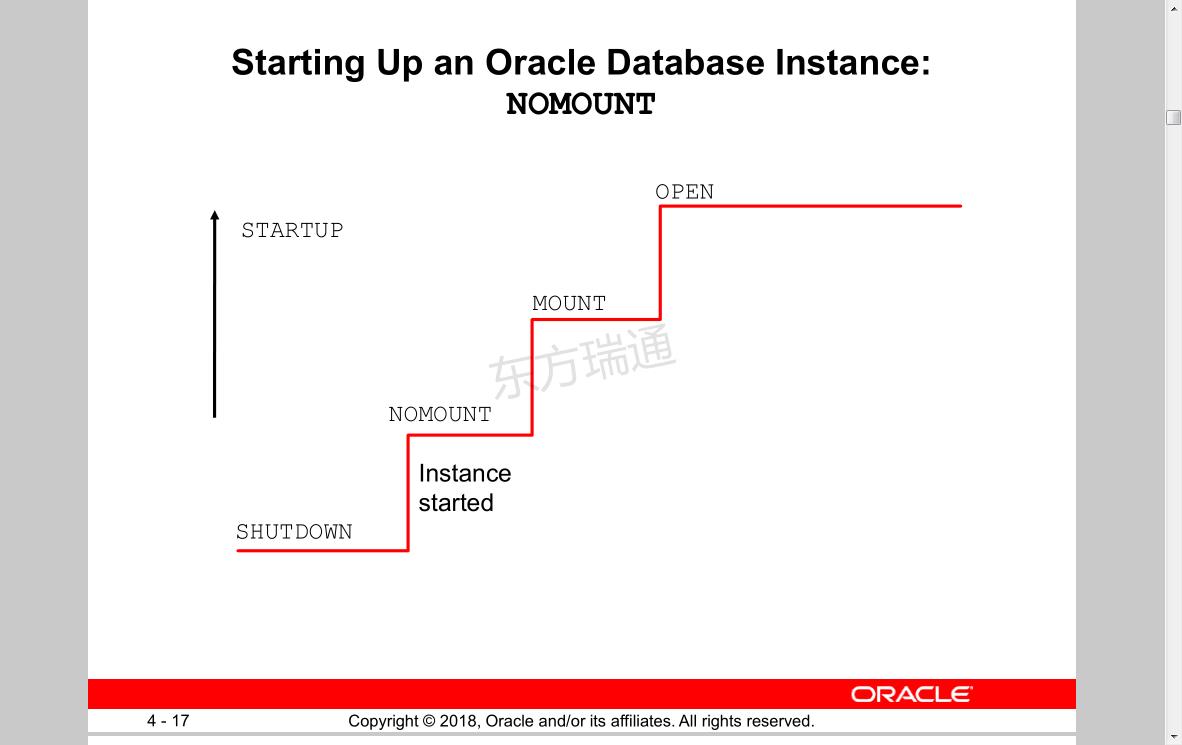
状态0:shutdown 关闭状态
状态1:nomount instance started 实例启动命令 SQL>statup nomount;
状态2:mount control file opened for this instance 对控制文件进行装载,装载命令 SQL>alter database mount; 可用于数据库恢复,从备份卷中恢复控制文件
状态3:open all files opened as described by the control file for this instance 打开在线日志文件redo和数据文件。 打开命令 SQL>alter database open;
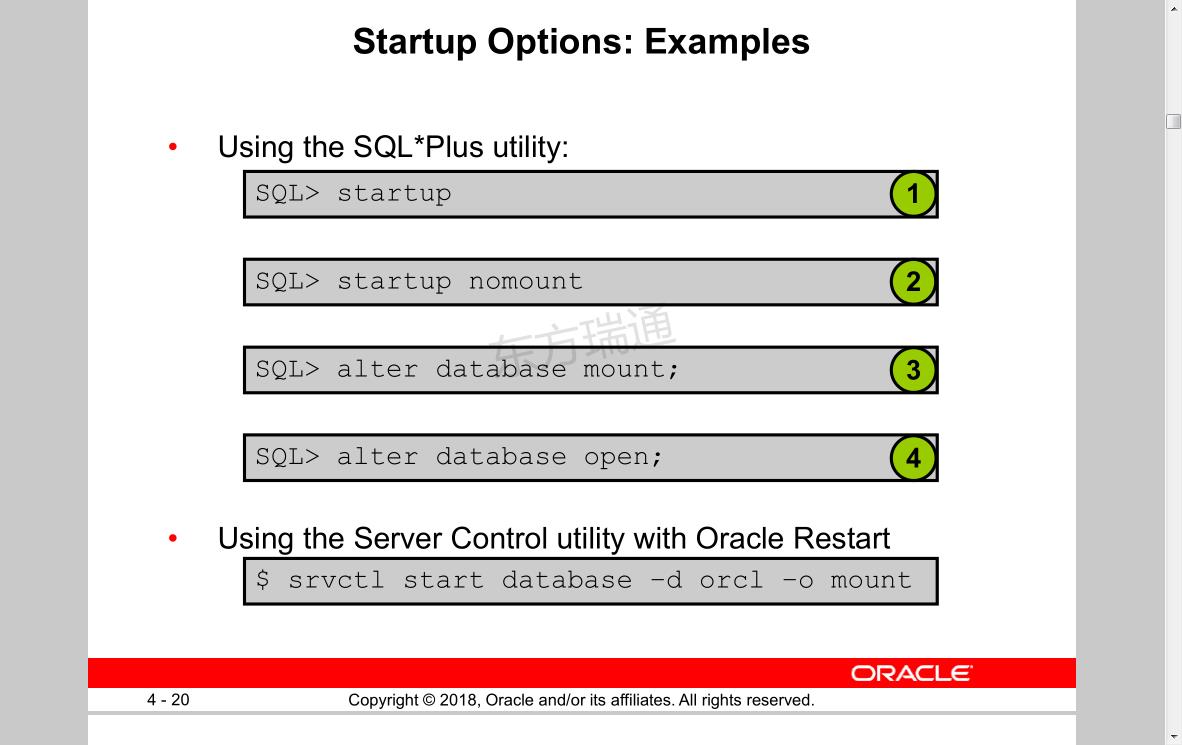
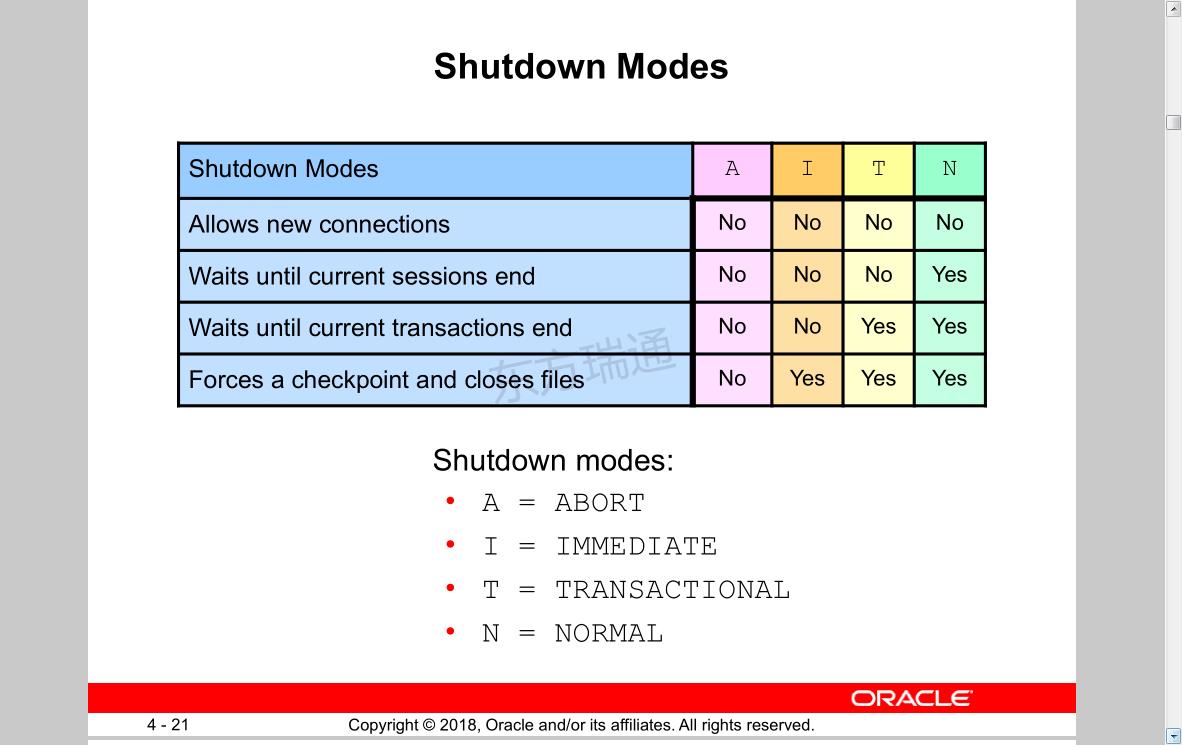
Shutdown modes:
• A = ABORT 强制终止,备份不可用,需要修复数据库
• I = IMMEDIATE 对为完成事物回退
• T = TRANSACTIONAL 等待事物完成
• N = NORMAL
Allows new connections 建立新的链接
No No No No
Waits until current sessions end 等待当前会话期结束
No No No Yes
Waits until current transactions end 等待事物完成
No No Yes Yes
Forces a checkpoint and closes files 强制检查点并关闭文件,确保数据可用
No Yes Yes Yes
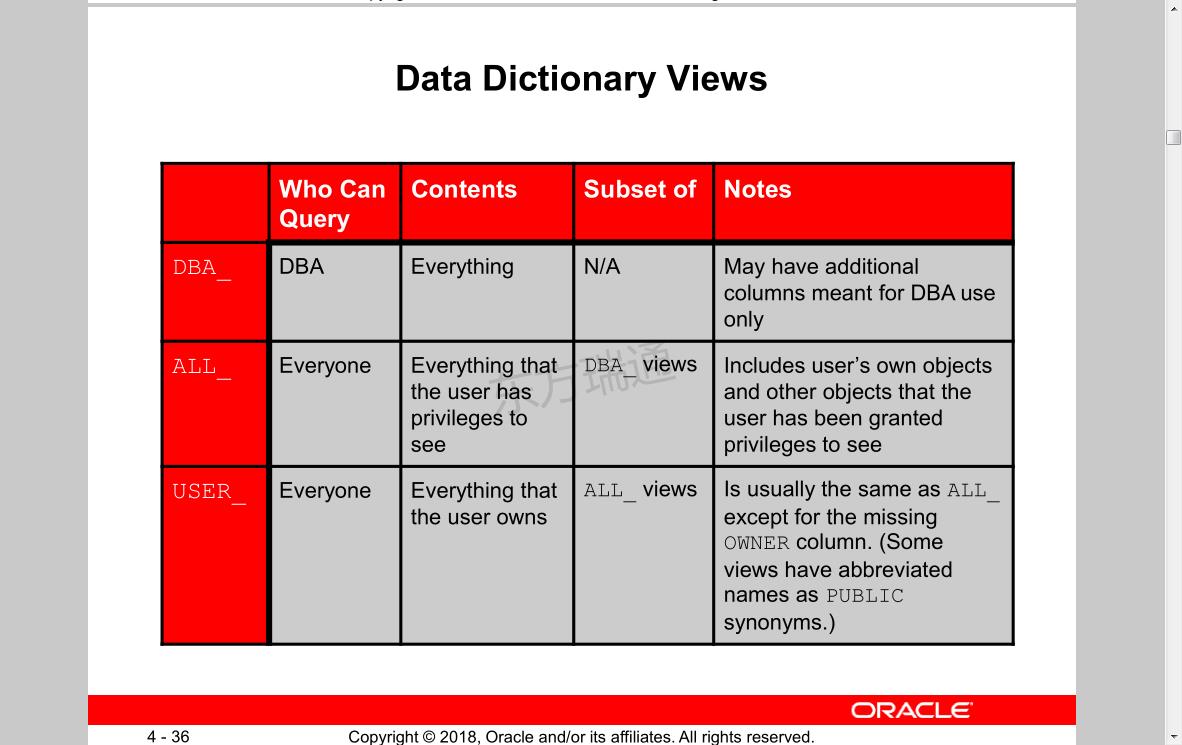
Dynamic Performance Views: Considerations
• These views are owned by the SYS user.
• Different views are available at different times:
– The instance has been started.
– The database is mounted.
– The database is open.
• You can query V$FIXED_TABLE to see all the view names.
• These views are often referred to as “v-dollar views.”
• Read consistency is not guaranteed on these views
because the data is dynamic.
查看数据库视图
SQL>desc v$instance;
SQL>select status from v$instance; 查看status视图是否打开
SQL>desc v$database
SQL>select open_Moed from v$database; 查看open_Moed视图状态
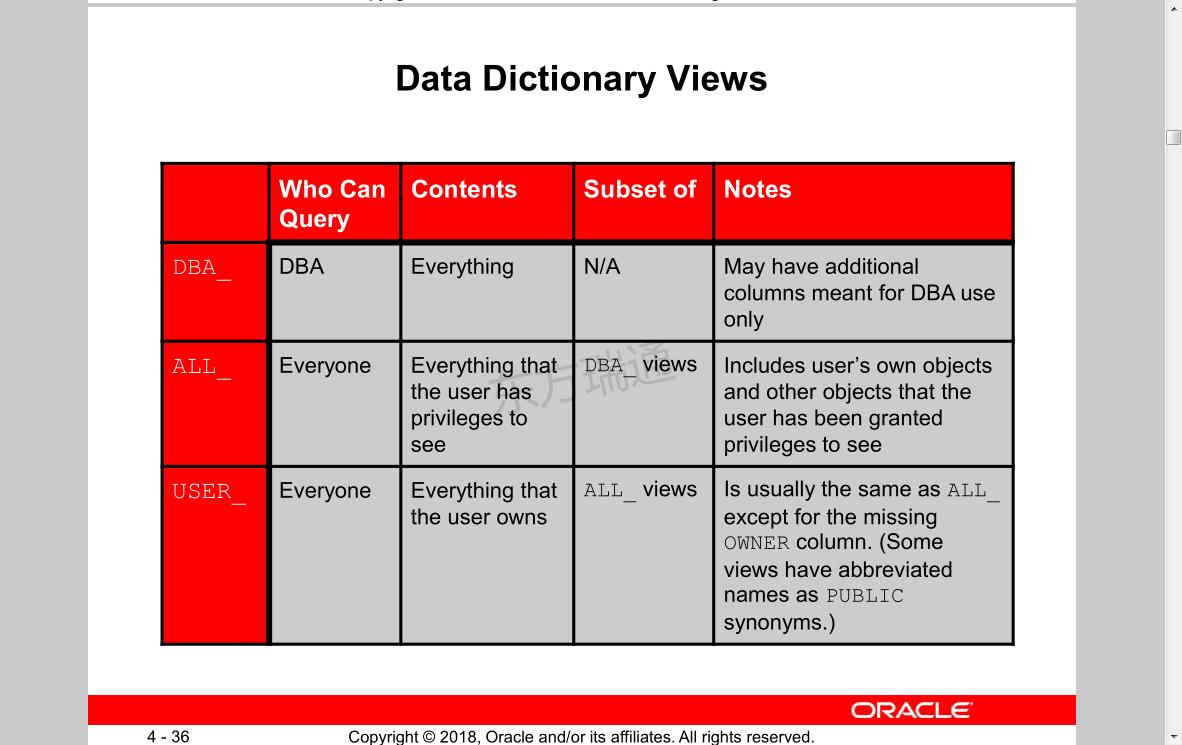
SQL>desc 查看表结构命令
SQL> connect hr/hr
或
SQL> conn hr/hr 登陆用户hr
SQL>show user 查看当前用户
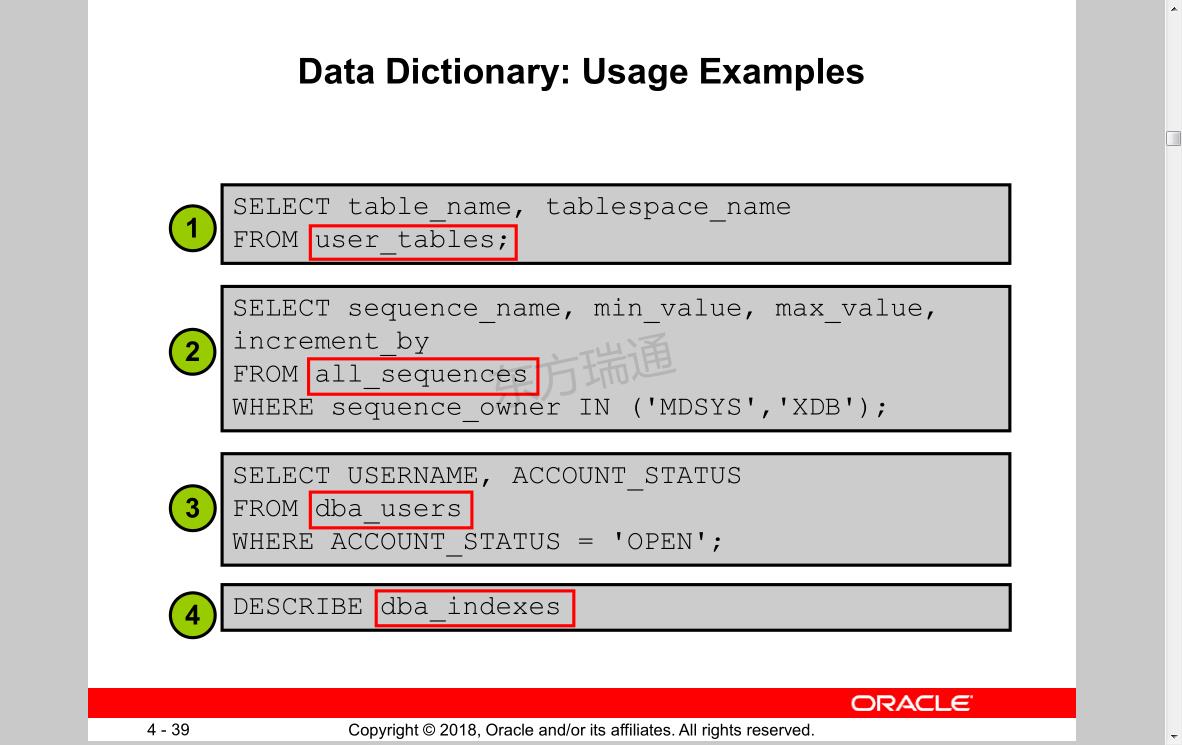
SQL>desc user_tables; 查看当前用户的所有表格
SQL>select table_name from user_tables; 查看所有属于hr用户表的名称
SQL>select * from all_tables; 查看改用户所有表格,含被授权的表格
SQL>conn / as sysdba 切换到超级用户sysdba
SQL>desc dba_tables;
SQL>seletc count(*) from dba_tables; 查看表的数量seletc count(*)
以上是关于oracle 03-03 数据库实例管理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章