Redis实现分布式锁(设计模式应用实战)
Posted 引路的风
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Redis实现分布式锁(设计模式应用实战)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
笔者看过网络上各种各样使用redis实现分布式锁的代码,要么错误,要么片段化,没有一个完整的例子,借这个周末给大家总结一下redis实现分布式锁的两种机制
自旋锁和排他锁
鉴于实现锁的方式不同,那么这里使用策略模式来组织代码
一、自旋锁
分布式锁抽象策略接口
package com.srr.lock; /** * @Description 分布式锁的接口 */ abstract public interface DistributedLock { /** * 获取锁 */ boolean lock(); /** * 解锁 */ void unlock(); }
自旋锁策略抽象类,使用模板方法模式构建
package com.srr.lock; /** * 自旋锁策略模板 */ public abstract class SpinRedisLockStrategy implements DistributedLock { private static final Integer retry = 50; //默认重试5次 private static final Long sleeptime = 100L; protected String lockKey; protected String requestId; protected int expireTime; private SpinRedisLockStrategy(){} public SpinRedisLockStrategy(String lockKey, String requestId, int expireTime){ this.lockKey=lockKey; this.requestId=requestId; this.expireTime=expireTime; } /** * 模板方法,搭建的获取锁的框架,具体逻辑交于子类实现 */ @Override public boolean lock() { Boolean flag = false; try { for (int i=0;i<retry;i++){ flag = tryLock(); if(flag){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取锁成功"); break; } Thread.sleep(sleeptime); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return flag; } /** * 尝试获取锁,子类实现 */ protected abstract boolean tryLock() ; /** * 解锁:删除key */ @Override public abstract void unlock(); }
自旋锁实现子类
package com.srr.lock; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; import java.util.Collections; /** * 自旋锁 */ public class SpinRedisLock extends SpinRedisLockStrategy{ private static final Long RELEASE_SUCCESS = 1L; private static final String LOCK_SUCCESS = "OK"; private static final String SET_IF_NOT_EXIST = "NX"; private static final String SET_WITH_EXPIRE_TIME = "PX"; public SpinRedisLock(String lockKey, String requestId, int expireTime) { super(lockKey,requestId, expireTime); } @Override protected boolean tryLock() { Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379); //创建客户端,1p和端口号 String result = jedis.set(lockKey, requestId, SET_IF_NOT_EXIST, SET_WITH_EXPIRE_TIME, expireTime); if (LOCK_SUCCESS.equals(result)) { return true; } return false; } @Override public void unlock() { Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379); //创建客户端,1p和端口号 String script = "if redis.call(\'get\', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call(\'del\', KEYS[1]) else return 0 end"; Object result = jedis.eval(script, Collections.singletonList(lockKey), Collections.singletonList(requestId)); if (RELEASE_SUCCESS.equals(result)) { System.out.println("lock is unlock"); } } }
至此,自旋锁方式实现分布式锁就完成了,下面来看排他锁阻塞的方式实现
二、排他锁
在实现之前需要大家搞懂一个概念,也就是redis的事件通知:
/**
* 键空间通知,所有通知以 keyspace@ 为前缀
* 键事件通知,所有通知以 keyevent@ 为前缀
* 所有命令都只在键真的被改动了之后,才会产生通知,比如删除foo会产生
* 键空间通知
* “pmessage”,"__ key*__ : * “,”__ keyspace@0__:foo",“set”
* 和键事件通知
* “pmessage”,"__ key*__ : *","__ keyevent@0__:set",“foo”
*/
搞懂概念之后,需要在redis的配置文件redis.conf中将其 notify-keyspace-events "KEA",默认为notify-keyspace-events "",这样才能启动redis的事件监听机制。
排它锁策略抽象类
package com.srr.lock; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; /** * @Description 阻塞获取锁,模板类 */ public abstract class BlockingRedisLockStrategy implements DistributedLock { protected String lockKey; protected String requestId; protected int expireTime; private BlockingRedisLockStrategy(){} public BlockingRedisLockStrategy(String lockKey, String requestId,int expireTime){ this.lockKey=lockKey; this.requestId=requestId; this.expireTime=expireTime; } /** * 模板方法,搭建的获取锁的框架,具体逻辑交于子类实现 * @throws Exception */ @Override public final boolean lock() { //获取锁成功 if (tryLock()){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取锁成功"); return true; }else{ //获取锁失败 //阻塞一直等待 waitLock(); //递归,再次获取锁 return lock(); } } /** * 尝试获取锁,子类实现 */ protected abstract boolean tryLock() ; /** * 等待获取锁,子类实现 */ protected abstract void waitLock(); /** * 解锁:删除key */ @Override public abstract void unlock(); }
排他锁实现子类
package com.srr.lock; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; import java.util.Collections; /** * 排他锁,阻塞 */ public class BlockingRedisLock extends BlockingRedisLockStrategy { private static final Long RELEASE_SUCCESS = 1L; private static final String LOCK_SUCCESS = "OK"; private static final String SET_IF_NOT_EXIST = "NX"; private static final String SET_WITH_EXPIRE_TIME = "PX"; public BlockingRedisLock(String lockKey, String requestId, int expireTime) { super(lockKey,requestId, expireTime); } /** * 尝试获取分布式锁 * @return 是否获取成功 */ @Override public boolean tryLock() { Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379); //创建客户端,1p和端口号 String result = jedis.set(lockKey, requestId, SET_IF_NOT_EXIST, SET_WITH_EXPIRE_TIME, expireTime); if (LOCK_SUCCESS.equals(result)) { return true; } return false; } @Override public void waitLock() { //判断key是否存在 Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379); //创建客户端,1p和端口号 KeyExpiredListener keyExpiredListener = new KeyExpiredListener(); /** * 键空间通知,所有通知以 keyspace@ 为前缀 * 键事件通知,所有通知以 keyevent@ 为前缀 * 所有命令都只在键真的被改动了之后,才会产生通知,比如删除foo会产生 * 键空间通知 * “pmessage”,"__ key*__ : * “,”__ keyspace@0__:foo",“set” * 和键事件通知 * “pmessage”,"__ key*__ : *","__ keyevent@0__:set",“foo” */ //如果要监听某个key的执行了什么操作,就订阅__ keyspace@0__,监听某种操作动了哪些key,就订阅__ keyevent@0__ //这里我们需要监听分布式锁的键被删除了,所以要监听删除动作"__keyspace@0__:"+key jedis.psubscribe(keyExpiredListener, "__keyspace@0__:"+lockKey); System.out.println("over"); } /** * 释放分布式锁 * @return 是否释放成功 */ @Override public void unlock() { Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379); //创建客户端,1p和端口号 String script = "if redis.call(\'get\', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call(\'del\', KEYS[1]) else return 0 end"; Object result = jedis.eval(script, Collections.singletonList(lockKey), Collections.singletonList(requestId)); if (RELEASE_SUCCESS.equals(result)) { System.out.println("lock is unlock"); } } }
redis事件监听类
package com.srr.lock; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPubSub; /** * redis 事件监听器 */ public class KeyDelListener extends JedisPubSub { public KeyDelListener(){ } // 初始化订阅时候的处理 @Override public void onPSubscribe(String pattern, int subscribedChannels) { } // 取得订阅的消息后的处理 @Override public void onPMessage(String pattern, String channel, String message) { System.out.println("message == "+message); this.punsubscribe(); System.out.println("unsubscribe == "+message); } }
到这里排他锁的完整代码就写完了,其实对比一下,两者的区别在于lock的实现方式不同,笔者为了确保代码完整性就全部贴上了。
代码写完了那么给一个场景测试一下我们的代码有没有问题,请看下面的测试代码:
这里我们构建一个Lock工具类:
package com.srr.lock; /** * 锁工具类 */ public class Lock { /** * 获取锁 */ boolean lock(DistributedLock lock) { return lock.lock(); }; /** * 释放锁 */ void unlock(DistributedLock lock) { lock.unlock(); }; }
测试类:
package com.srr.lock; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; /** * 测试场景 * count从1加到101 * 使用redis分布式锁在分布式环境下保证结果正确 */ public class T { volatile int count = 1; public void inc(){ for(int i = 0;i<100;i++){ try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } count++; System.out.println("count == "+count); } } public int getCount(){ return count; } public static void main(String[] args) { final T t = new T(); final Lock lock = new Lock(); //final RedisLock redisLock = new BlockingRedisLock("","1",100000,jedis); final DistributedLock distributedLock = new SpinRedisLock("test","1",100000); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { if(lock.lock(distributedLock)){ t.inc(); System.out.println("t1 running"); System.out.println("t1 == count == "+ t.getCount()); lock.unlock(distributedLock); } } }); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { if(lock.lock(distributedLock)) { t.inc(); System.out.println("t2 running"); System.out.println("t2 == count == " + t.getCount()); lock.unlock(distributedLock); } } }); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
测试结果:
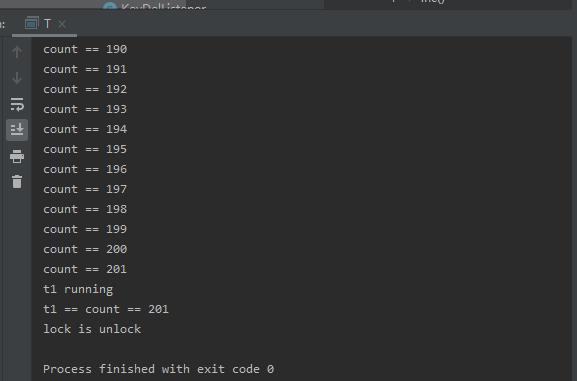
到这里,全部代码就完成了,如果想使用zookeeper实现分布式锁只需要抽象出一个策略类实现DistributedLock接口即可。是不是很方便呢。
原创不易,多多关注!
以上是关于Redis实现分布式锁(设计模式应用实战)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章