安卓启动流程(一) - rc文件初步解析
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了安卓启动流程(一) - rc文件初步解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A init进程的一个核心部分,是通过解析rc文件,执行Action和启动Service。在分析init进程前,有必要先学习rc文件的配置和解析的原理。/system/core/init/init.cpp
/system/core/init/init.cpp
通过 CreateParser , 创建了 Parser 解析器对象,其解析规则如下:
然后开始执行解析过程
最后调用 Parser 解析器的 ParseConfig 函数执行解析。
下一篇: 安卓启动流程(二) - Parser解析器
Android 7.0系统启动流程分析
随着Android版本的升级,aosp项目中的代码也有了些变化,本文基于Android 7.0分析Android系统启动流程.当我们按下电源键后,整个Android设备大体经过了一下过程:
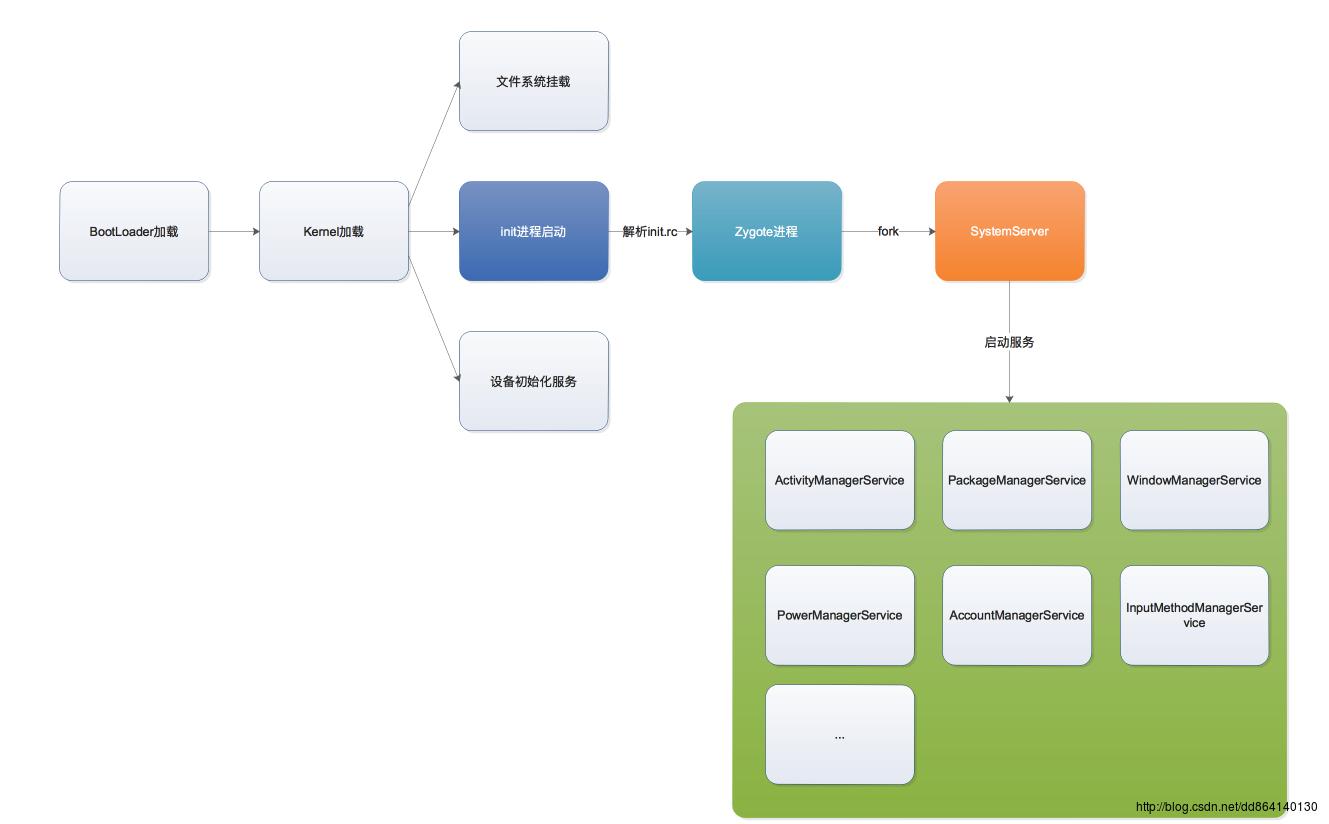
今天我们只想来分析init进程及其后的过程,也就是下图所示部分:

init进程
init进程会解析init.rc文件(关于init.rc中的语法,可以参见之前写的深入分析AIL语言及init.rc文件),加载相关分区,并启动相关服务.
init进程在/system/core/init/init.cpp
init.rc文件在/system/core/rootdir下
init.rc文件由parser.cpp解析,在/system/core/init/init_parser.cpp
在init.rc中,Zygote进程被启动.Zygote进程是其他所有进程的孵化器.init.rc通过include引入init.zygote.rc,这里以init.zygote64.rc为例:
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks对个脚本简单分析:
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64:service命令告诉init进程要创建一个名字为zygote的进程,这个zygote进程执行的程序是/system/bin/app_process64,后面是传给app_process64程序的参数.socket zygote stream 660 root system:表示zygote进程需要一个名为”zygote”的socket,该socket用来实现进程间的通信.当新启动一个应用时,ActivityManagerService想向该Socket发起请求,请求zygote进程fork出一个新的进程.- 后面的onrestart表示zygote重启时需要执行的动作.
Zygote进程启动
上面说到init进程会根据init.rc执行相关的操作,其中有一项就是创建Zygote进程.Zygote进程所对应的程序是/system/bin/app_process,
位于/frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp,其入口函数是main():
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
if (prctl(PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS, 1, 0, 0, 0) < 0)
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS failed: %s", strerror(errno));
if (!LOG_NDEBUG)
String8 argv_String;
for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i)
argv_String.append("\\"");
argv_String.append(argv[i]);
argv_String.append("\\" ");
ALOGV("app_process main with argv: %s", argv_String.string());
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
const char* spaced_commands[] = "-cp", "-classpath" ;
bool known_command = false;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++)
if (known_command == true)
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
ALOGV("app_process main add known option '%s'", argv[i]);
known_command = false;
continue;
for (int j = 0;
j < static_cast<int>(sizeof(spaced_commands) / sizeof(spaced_commands[0]));
++j)
if (strcmp(argv[i], spaced_commands[j]) == 0)
known_command = true;
ALOGV("app_process main found known command '%s'", argv[i]);
if (argv[i][0] != '-')
break;
if (argv[i][1] == '-' && argv[i][2] == 0)
++i; // Skip --.
break;
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
ALOGV("app_process main add option '%s'", argv[i]);
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
while (i < argc)
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0)
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0)
//init.zygote64.rc中接受的参数,表示启动SystemServer组件
startSystemServer = true;
else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0)
application = true;
else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0)
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0)
className.setTo(arg);
break;
else
--i;
break;
Vector<String8> args;
if (!className.isEmpty())
args.add(application ? String8("application") : String8("tool"));
runtime.setClassNameAndArgs(className, argc - i, argv + i);
if (!LOG_NDEBUG)
String8 restOfArgs;
char* const* argv_new = argv + i;
int argc_new = argc - i;
for (int k = 0; k < argc_new; ++k)
restOfArgs.append("\\"");
restOfArgs.append(argv_new[k]);
restOfArgs.append("\\" ");
ALOGV("Class name = %s, args = %s", className.string(), restOfArgs.string());
else
// We're in zygote mode.
maybeCreateDalvikCache();
if (startSystemServer)
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (property_get(ABI_LIST_PROPERTY, prop, NULL) == 0)
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: Unable to determine ABI list from property %s.",
ABI_LIST_PROPERTY);
return 11;
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag);
// In zygote mode, pass all remaining arguments to the zygote
// main() method.
for (; i < argc; ++i)
args.add(String8(argv[i]));
if (!niceName.isEmpty())
runtime.setArgv0(niceName.string(), true /* setProcName */);
if (zygote)
//此处见到了我们熟悉的ZygoteInit,但该方法的具体实现在//AndroidRuntime.start()
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
else if (className)
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
else
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
上述代码总体比较简单,主要是处理相关参数,并创建AppRuntime,由于在init.rc文件中,app_process启动参数被设置为--zygote --start-system-server,因此会执行runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote),现在我们来看看AppRuntime的具体实现,它同样在
在/frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp:
class AppRuntime : public AndroidRuntime
public:
AppRuntime(char* argBlockStart, const size_t argBlockLength)
: AndroidRuntime(argBlockStart, argBlockLength)
, mClass(NULL)
void setClassNameAndArgs(const String8& className, int argc, char * const *argv)
mClassName = className;
for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i)
mArgs.add(String8(argv[i]));
virtual void onVmCreated(JNIEnv* env)
if (mClassName.isEmpty())
return; // Zygote. Nothing to do here.
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(mClassName.string());
mClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (mClass == NULL)
ALOGE("ERROR: could not find class '%s'\\n", mClassName.string());
free(slashClassName);
mClass = reinterpret_cast<jclass>(env->NewGlobalRef(mClass));
virtual void onStarted()
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\\n");
proc->startThreadPool();
AndroidRuntime* ar = AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
ar->callMain(mClassName, mClass, mArgs);
IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess();
virtual void onZygoteInit()
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\\n");
proc->startThreadPool();
virtual void onExit(int code)
if (mClassName.isEmpty())
// if zygote
IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess();
AndroidRuntime::onExit(code);
String8 mClassName;
Vector<String8> mArgs;
jclass mClass;
;AppRuntime继承AndroidRuntime,而AndroidRuntime位于
/frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp.
而start()方法便是定义在AndroidRuntime的虚方法:
//这里的className的值就是com.android.intrnal.os.ZygoteInit
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
//...省略多行代码
static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i)
if (options[i] == startSystemServer)
/* track our progress through the boot sequence */
const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START, ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (rootDir == NULL)
rootDir = "/system";
if (!hasDir("/system"))
LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /android does not exist.");
return;
setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
//1. 启动虚拟机
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0)
return;
onVmCreated(env);
//2. 调用startReg()注册JNI方法
if (startReg(env) < 0)
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\\n");
return;
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i)
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL)
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\\n", slashClassName);
else
//3. 本质就是调用com.android.intrnal.os.ZygoteInit类的main函数
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL)
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\\n", className);
/* keep going */
else
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
free(slashClassName);
// 省略多行代码
在start()方法中主要做三件事情:
1. 调用startVM()函数启动虚拟机
2. 调用startReg()注册JNI方法
3. 调用com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.java类的main函数.
走进ZygoteInit
关于前两者就不细说了,重点来关注我们熟悉的ZygoteInit.java.它在
rameworks/base/core/Java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java,我们直接来看他的main方法:
public static void main(String argv[])
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer();
ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
try
Os.setpgid(0, 0);
catch (ErrnoException ex)
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
try
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.enableDdms();
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++)
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i]))
startSystemServer = true;
else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG))
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG))
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
else
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
if (abiList == null)
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
//创建名为zygote的socket
zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "ZygotePreload");
//省略多行参数
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PostZygoteInitGC");
gcAndFinalize();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false);
Zygote.nativeUnmountStorageOnInit();
ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
//由于在init.rc中设置了start-system-server参数,因此
//这里将启动SystemServer,可见SystemServer由Zygote创 //建的第一个进程
if (startSystemServer)
//启动SystemServer组件
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
//等待ActivityManagerService请求
zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
catch (Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller caller)
caller.run();
catch (Throwable ex)
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
这里的main()方法中主要做了三件事情
1. 通过registerServerSocket()来创建Socket,它将作为服务端用来和作为客户端的ActivityManagerService进行通信
2. 通过startSystemServer()方法来启动SystemServer
3. 最后通过通过runSelectLoop方法使得刚才创建的Socket进入无限循环,以等待来自ActivityManagerService请求
Zygote中Socket创建
首先来看resiterServerSocket()它在:
void registerServerSocket(String socketName)
if (mServerSocket == null)
int fileDesc;
final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName;
try
String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName);
//从环境变量env中获取文件描述符,
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
catch (RuntimeException ex)
throw new RuntimeException(fullSocketName + " unset or invalid", ex);
try
//通过文件描述符创建socket,该描述符代表/dev/socket/zygote文件.
FileDescriptor fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.setInt$(fileDesc);
mServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(fd);
catch (IOException ex)
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
方法主要通过文件描述符创建socket,该文件描述代表/dev/socket/zygote文件,现在看看开头init.rc中的配置:socket zygote stream 660 root system
Zygote启动SystemServer
现在来看startSystemServer()方法:
private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName, ZygoteServer zygoteServer)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException
long capabilities = posixCapabilitiesAsBits(
OsConstants.CAP_IPC_LOCK,
OsConstants.CAP_KILL,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_ADMIN,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BROADCAST,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_RAW,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_MODULE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_NICE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_RESOURCE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TIME,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG,
OsConstants.CAP_WAKE_ALARM
);
if (!SystemProperties.getBoolean(PROPERTY_RUNNING_IN_CONTAINER, false))
capabilities |= posixCapabilitiesAsBits(OsConstants.CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND);
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] =
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
;
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
//创建子进程
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex)
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
//pid=0表示子进程,此处就是SystemServer进程
if (pid == 0)
//用于处理系统中有两个Zygote进程的情况,由于通常我们不会配置两个Zygote,因此暂时不关注
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList))
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
//Zygote创建的子进程(此处就是SystemServer)不需要使用Zygote中创建的Socket文件描述符,因此通过closeServerSocket()关闭它.
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
return true;
这里首先通过Zygote.forkSystemServer()创建一个系统服务进程.与该方法相似还有forkAndSpecialize(),用于创建一个普通应用进程.进程创建成功后返回pid为0.由于此处生成的新进程和Zygote进程一模一样,也就是说这个新进程中同样包含了刚才创建的Socket,但是该Socket在此处无效,因此要将其关闭.接下来调用handleSystemServerProcess()处理刚才新建的进程即SystemServer进程,需要注意此时已经工作在SystemServer进程中了:
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller
//省略多行代码,此处invokeWith为null
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null)
String[] args = parsedArgs.remainingArgs;
if (systemServerClasspath != null)
//省略多行代码
else
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null)
//为SysteServer进程创建PathClassLoader类加载器
cl = createSystemServerClassLoader(systemServerClasspath,
parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion);
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
该函数继续调用RuntimeInit.zygoteInit()进一步执行启动SystemServer组件的操作.继续来看 RuntimeInit.zygoteInit()的具体实现,它在
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java文件中:
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller
//...省略多行代码
commonInit();
nativeZygoteInit();
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
在该方法中主要调用了三个方法:
- commonInit():为当前进程的VM设置未捕获异常处理器
- nativeZygoteInit():Binder驱动初始化,该方法完成后,就可以通过该Binder进行进程通信
- applicationInit():主要用调用com.android.server.SystemServer类的main()方法
由于commonInit()方法比较简单,在此就不做分析.
nativeZygoteInit()是一个本地方法,其对应实现在frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp中:
static void com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeZygoteInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
gCurRuntime->onZygoteInit();
这里的gCurRuntime是AppRuntime的指针,在frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp中定义,并在AndroidRuntime的够赞函数中初始化:
//定义
static AndroidRuntime* gCurRuntime = NULL;
...
//在frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp的main()方法中被调用
AndroidRuntime::AndroidRuntime(char* argBlockStart, const size_t argBlockLength) :
mExitWithoutCleanup(false),
mArgBlockStart(argBlockStart),
mArgBlockLength(argBlockLength)
SkGraphics::Init();
mOptions.setCapacity(20);
assert(gCurRuntime == NULL);
gCurRuntime = this;
继续来看onZygoteInit():
virtual void onZygoteInit()
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\\n");
proc->startThreadPool();
这里调用ProcessState::startThreadPool()方法启动线程池,这个线程池就是用来和Binder驱动程序进程交互的.(Binder驱动本质就是一个文件,位于/dev/binder),关于线程池具体创建的过程暂不做说明.
现在来看applicationInit():
private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller
//省略多行代码
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
这里继续调用了invokeStaticMain()进行后续工作:
private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller
Class<?> cl;
try
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex)
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
Method m;
try
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] String[].class );
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex)
//...
catch (SecurityException ex)
//...
// 省略多行代码
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
此时要执行的是com.android.server.SystemServer的中mian()方法.此外真正执行的过程是在Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller的run()方法中:
public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception
implements Runnable
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs;
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args)
mMethod = method;
mArgs = args;
public void run()
try
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] mArgs );
catch (IllegalAccessException ex)
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
catch (InvocationTargetException ex)
//省略多行代码
MethodAndArgsCaller继承Exception并实现Runnable接口,作为一个异常他被ZygoteInit.main()捕获并处理:
public static void main(String argv[])
// ...
try
//...省略多行代码
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller)
caller.run();
catch (Throwable ex)
//...
现在SystemServer的main()已经被调用,我们顺着来看一下实现:
public class SystemServer
public static void main(String[] args)
new SystemServer().run();
private void run()
try
//...省略一些初始化操作
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
//初始化主线程Looper
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
//创建SystemServiceManager对象
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
finally
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
// 启动关键服务
startBootstrapServices();
//启动核心服务
startCoreServices();
//启动其他服务
startOtherServices();
//...省略多行代码
//启动消息循环
Looper.loop();
在main()方法中调用了run()方法继续启动操作.在run方法中这三个方法非常重要:
- startBootstrapServices():启动引导服务,比如AMS,PMS等
- startCoreServices():启动核心服务,比如BatteryService等
- startOtherServices():启动其他服务,比如NetworkStatsService等.
关于SystemService的具体执行过程,在此不做细解.
Socket循环监听
到目前为止,关于ZygoteServer.registerServerSocket()和startSystemServer()的大体流程我们已经弄清除,接下来就是ZygoteServer.runSelectLoop()方法:
void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
fds.add(mServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
while (true)
StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i)
pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
try
Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
catch (ErrnoException ex)
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i)
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0)
continue;
if (i == 0)
//监听Socket链接,如果你做过Socket编程就发现此处充当了服务端Socket
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
else
//重点关注runOnce()方法
boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce(this);
if (done)
peers.remove(i);
fds.remove(i);
该方法非常简单:不断的处理来自客户端AMS的请求,然后交给runOnce().此处可见Android 7.0应用启动流程分析
到现在为止,整个SystemServer进程的启动流程已经明确看,用一张顺序图大体的表示上述的整个流程:

总结
- 系统启动时init进程会创建Zygote进程,Zygote进程负责后续Android应用框架层的其他进程的创建和启动.
- Zygote进程会首先创建一个SystemSever进程,然后由SystemServer负责启动系统关键服务,如ActivityManagerService或者PackageManagerService等.
以上是关于安卓启动流程(一) - rc文件初步解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章