MySQL之唯一索引外键的变种SQL语句数据行操作补充
Posted zh_小猿
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL之唯一索引外键的变种SQL语句数据行操作补充相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
0、唯一索引
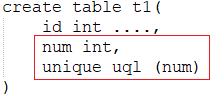
unique对num进行唯一限制,表示num是独一无二的,uql是唯一索引名称
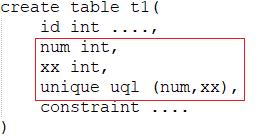
上面为联合索引:num和xx不能完全一样

1、外键的变种
a. 用户表和部门表
用户:
1 alex 1
2 root 1
3 egon 2
4 laoyao 3
部门:
1 服务
2 保安
3 公关
===》 一对多
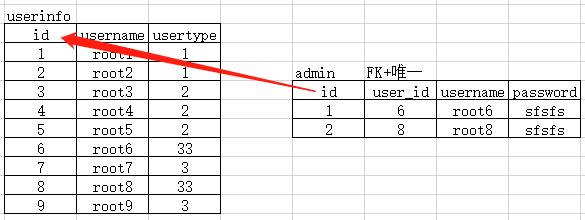
b. 用户表和博客表
用户表:
1 alex
2 root
3 egon
4 laoyao
博客表:
FK() + 唯一
1 /yuanchenqi/ 4
2 /alex3714/ 1
3 /asdfasdf/ 3
4 /ffffffff/ 2
===> 一对一
程序代码:
create table userinfo1( id int auto_increment primary key, name char(10), gender char(10), email varchar(64) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
create table admin( id int not null auto_increment primary key, username varchar(64) not null, password VARCHAR(64) not null, user_id int not null, unique uq_u1 (user_id), CONSTRAINT fk_admin_u1 FOREIGN key (user_id) REFERENCES userinfo1(id) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
c.多对多
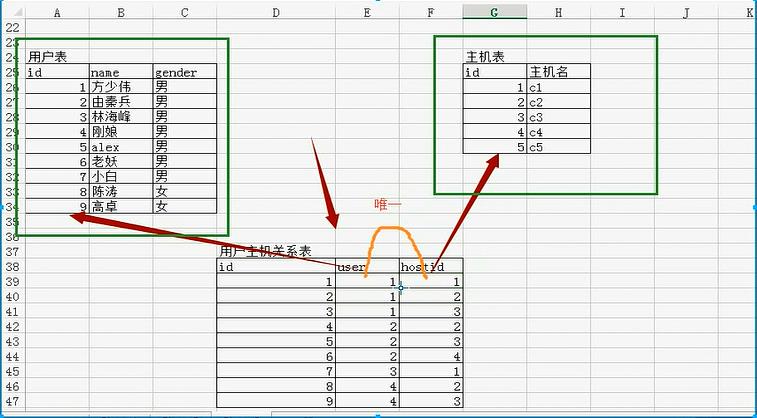
create table userinfo2( id int auto_increment primary key, name char(10), gender char(10), email varchar(64) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table host( id int auto_increment primary key, hostname char(64) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table user2host( id int auto_increment primary key, userid int not null, hostid int not null, unique uq_user_host (userid,hostid), CONSTRAINT fk_u2h_user FOREIGN key (userid) REFERENCES userinfo2(id), CONSTRAINT fk_u2h_host FOREIGN key (hostid) REFERENCES host(id) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
3、SQL语句数据行操作补充
3.1 增
insert into tb11(name,age) values(\'alex\',12); #往tb11中插入一条数据 insert into tb11(name,age) values(\'alex\',12),(\'root\',18); #往tb11中插入多条数据 insert into tb12(name,age) select name,age from tb11; #把tb11中的数据复制到tb12中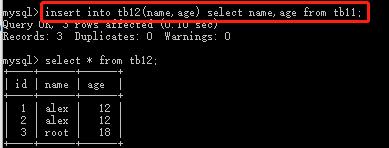
3.2 删
delete from tb12; delete from tb12 where id !=2 delete from tb12 where id =2 delete from tb12 where id > 2 delete from tb12 where id >=2 delete from tb12 where id >=2 or name=\'alex\'
3.3 改
update tb12 set name=\'alex\' where id>12 and name=\'xx\' update tb12 set name=\'alex\',age=19 where id>12 and name=\'xx\'
3.4 查
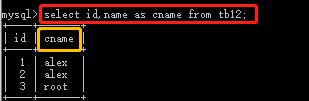
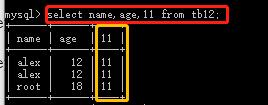
select * from tb12; select id,name from tb12; select id,name from tb12 where id > 10 or name =\'xxx\'; select name as cname,age from tb12; #查数据,并把表头的name改为cname select id,name as cname from tb12 where id > 10 or name =\'xxx\'; select name,age,11 from tb12; #多出一列,数据全部为11
其他:
select * from tb12 where id != 1 select * from tb12 where id in (1,5,12); #取id为1、5、12的数据 select * from tb12 where id not in (1,5,12); #取id不为1、5、12的数据 select * from tb12 where id in (select id from tb11) #先把tb11的id取出来,作为tb12要查的id select * from tb12 where id between 5 and 12; #取id为5到12的数据(闭区间)
通配符:
select * from tb12 where name like "a%" #查name以a为开头的数据 select * from tb12 where name like "%a%" #查name中带a的数据 select * from tb12 where name like "a_" #查name以a开头,后面只带一位的数据,比如 ab、ag
分页:
select * from tb12 limit 10; #查看前10条 select * from tb12 limit 0,10; #从第0行开始读取,读取10行; select * from tb12 limit 10,10; #从第10行开始读取,读取10行; select * from tb12 limit 20,10; #从第20行开始读取,读取10行; select * from tb12 limit 10 offset 20; #从第20行开始读取,读取10行; #结合Python分页: page = input(\'请输入要查看的页码\') page = int(page) (page-1) * 10 select * from tb12 limit 0,10; #查看第1页数据 select * from tb12 limit 10,10;2 #查看第2页数据
排序:
select * from tb12 order by id desc; #id从大到小排 select * from tb12 order by id asc; #id从小到大排 select * from tb12 order by age desc,id desc; #age从大到小排,id从大到小排(如果age数相同,就按照id从大到小排) select * from tb12 order by id desc limit 10; #取后10条数据
创建部门与员工表:
create table department5(
id int auto_increment primary key,
title varchar(32)
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
insert into department5(title) values(\'经理\'),(\'销售\'),(\'管理\'),(\'财务\');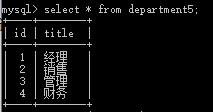
create table userinfo5( id int auto_increment primary key, name varchar(32), part_id int, CONSTRAINT fk_user_part FOREIGN key (part_id) REFERENCES department5(id) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
insert into userinfo5(name,part_id) values(\'杨涵\',2),(\'大波\',1),(\'高月\',2),(\'送气\',3),(\'小白\',4);
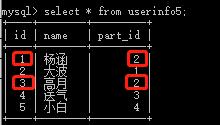
分组:
max:#按par_id进行分类,如果part_id相同,就取id最大的那个进行分类
count:此外还有min、sum、avg
如果对于聚合函数结果进行二次筛选时?必须使用having 例如果想筛选出id大于1的part_id: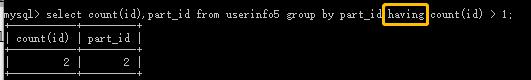
也可以用where,但后面不能加聚合函数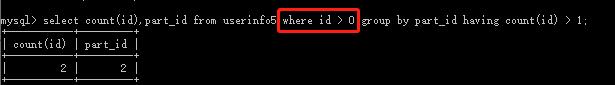
连表操作:
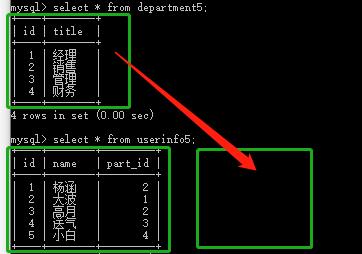
做法:select * from userinfo5,department5 where userinfo5.part_id = department5.id
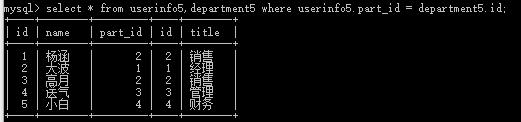
推荐下面写法:
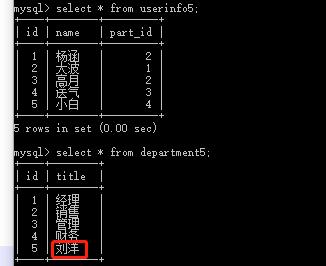
(1)select * from userinfo5 left join department5 on userinfo5.part_id = department5.id; #userinfo5左边全部显示,因为userinfo5中没有对应department5中的刘洋,所以不显示刘洋
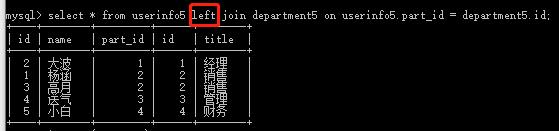
(2) select * from userinfo5 right join department5 on userinfo5.part_id = department5.id; #department5右边全部显示
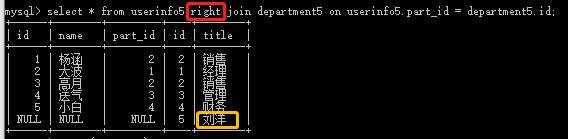
(3)select * from userinfo5 innder join department5 on userinfo5.part_id = department5.id; #将出现null时的一行隐藏
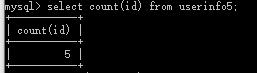
(4)select count(id) from userinfo5; #统计userinfo5中的数据个数
cmd中导出现有数据库数据:
mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 数据库名称 >导出文件路径 #结构+数据
mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 -d数据库名称 >导出文件路径 #结构
导出现有数据库数据:
mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 数据库名称 <文件路径
4、相关知识
1、临时表:把查出来的数据用()括起来,加上as+名称就能生成临时表
select * from (select * from tb where id<10) as B; #这里 (select * from tb where id<10) as B 就是一个临时表,名称为B
2、指定映射:
select id,name,1,sum(x)/count()
3、条件:
case when id>8 then xx else xx end
4、三元运算:
if(isnull(xx),0,1) #如果xx为空取0,否则取1
5、union
join执行的是左右连表,union执行的是上下连表
# 自动去重 select id,name from tb1 union select num,sname from tb2 # 不去重 select sid,sname from student UNION ALL select sid,sname from student
注:group by,having语句中可以存在where,但where要放到group by, having的前面,表示先进行一次筛选,在筛选出的结果中再执行group by,having
以上是关于MySQL之唯一索引外键的变种SQL语句数据行操作补充的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章