大数据技术之MapReduce中多表合并案例
Posted Frankdeng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了大数据技术之MapReduce中多表合并案例相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
MapReduce中多表合并案例
一.案例需求
订单数据表t_order:
|
id |
pid |
amount |
|
1001 |
01 |
1 |
|
1002 |
02 |
2 |
|
1003 |
03 |
3 |
订单数据order.txt
1001 01 1 1002 02 2 1003 03 3 1004 01 4 1005 02 5 1006 03 6
商品信息表t_product
|
pid |
pname |
|
01 |
小米 |
|
02 |
华为 |
|
03 |
格力 |
商品数据pd.txt
01 小米 02 华为 03 格力
将商品信息表中数据根据商品pid合并到订单数据表中。
最终数据形式:
|
id |
pname |
amount |
|
1001 |
小米 |
1 |
|
1004 |
小米 |
4 |
|
1002 |
华为 |
2 |
|
1005 |
华为 |
5 |
|
1003 |
格力 |
3 |
|
1006 |
格力 |
6 |
二.reduce端表合并(数据倾斜)
通过将关联条件作为map输出的key,将两表满足join条件的数据并携带数据所来源的文件信息,发往同一个reduce task,在reduce中进行数据的串联。
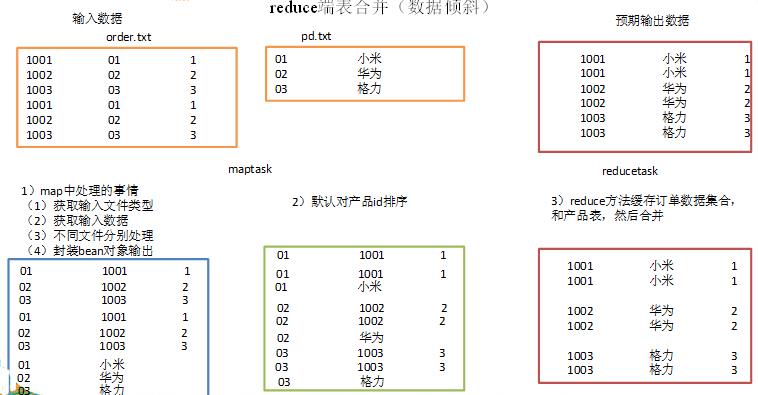
1)创建商品和订合并后的bean类
package com.xyg.mapreduce.table; import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable; public class TableBean implements Writable { private String order_id; // 订单id private String p_id; // 产品id private int amount; // 产品数量 private String pname; // 产品名称 private String flag;// 表的标记 public TableBean() { super(); } public TableBean(String order_id, String p_id, int amount, String pname, String flag) { super(); this.order_id = order_id; this.p_id = p_id; this.amount = amount; this.pname = pname; this.flag = flag; } public String getFlag() { return flag; } public void setFlag(String flag) { this.flag = flag; } public String getOrder_id() { return order_id; } public void setOrder_id(String order_id) { this.order_id = order_id; } public String getP_id() { return p_id; } public void setP_id(String p_id) { this.p_id = p_id; } public int getAmount() { return amount; } public void setAmount(int amount) { this.amount = amount; } public String getPname() { return pname; } public void setPname(String pname) { this.pname = pname; } @Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeUTF(order_id); out.writeUTF(p_id); out.writeInt(amount); out.writeUTF(pname); out.writeUTF(flag); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { this.order_id = in.readUTF(); this.p_id = in.readUTF(); this.amount = in.readInt(); this.pname = in.readUTF(); this.flag = in.readUTF(); } @Override public String toString() { return order_id + "\\t" + pname + "\\t" + amount + "\\t" ; } }
2)编写TableMapper程序
package com.xyg.mapreduce.table; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit; public class TableMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, TableBean>{ TableBean bean = new TableBean(); Text k = new Text(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 1 获取输入文件类型 FileSplit split = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit(); String name = split.getPath().getName(); // 2 获取输入数据 String line = value.toString(); // 3 不同文件分别处理 if (name.startsWith("order")) {// 订单表处理 // 3.1 切割 String[] fields = line.split(","); // 3.2 封装bean对象 bean.setOrder_id(fields[0]); bean.setP_id(fields[1]); bean.setAmount(Integer.parseInt(fields[2])); bean.setPname(""); bean.setFlag("0"); k.set(fields[1]); }else {// 产品表处理 // 3.3 切割 String[] fields = line.split(","); // 3.4 封装bean对象 bean.setP_id(fields[0]); bean.setPname(fields[1]); bean.setFlag("1"); bean.setAmount(0); bean.setOrder_id(""); k.set(fields[0]); } // 4 写出 context.write(k, bean); } }
3)编写TableReducer程序
package com.xyg.mapreduce.table;
import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; public class TableReducer extends Reducer<Text, TableBean, TableBean, NullWritable> { @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<TableBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 1准备存储订单的集合 ArrayList<TableBean> orderBeans = new ArrayList<>(); // 2 准备bean对象 TableBean pdBean = new TableBean(); for (TableBean bean : values) { if ("0".equals(bean.getFlag())) {// 订单表 // 拷贝传递过来的每条订单数据到集合中 TableBean orderBean = new TableBean();` try { BeanUtils.copyProperties(orderBean, bean); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } orderBeans.add(orderBean); } else {// 产品表 try { // 拷贝传递过来的产品表到内存中 BeanUtils.copyProperties(pdBean, bean); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } // 3 表的拼接 for(TableBean bean:orderBeans){ bean.getPname(pdBean.getPname()); // 4 数据写出去 context.write(bean, NullWritable.get()); } } }
4)编写TableDriver程序
package com.xyg.mapreduce.table; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class TableDriver { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 1 获取配置信息,或者job对象实例 Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration); // 2 指定本程序的jar包所在的本地路径 job.setJarByClass(TableDriver.class); // 3 指定本业务job要使用的mapper/Reducer业务类 job.setMapperClass(TableMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(TableReducer.class); // 4 指定mapper输出数据的kv类型 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(TableBean.class); // 5 指定最终输出的数据的kv类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(TableBean.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); // 6 指定job的输入原始文件所在目录 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); // 7 将job中配置的相关参数,以及job所用的java类所在的jar包, 提交给yarn去运行 boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(result ? 0 : 1); } }
3)运行程序查看结果
1001 小米 1 1001 小米 1 1002 华为 2 1002 华为 2 1003 格力 3 1003 格力 3
缺点:这种方式中,合并的操作是在reduce阶段完成,reduce端的处理压力太大,map节点的运算负载则很低,资源利用率不高,且在reduce阶段极易产生数据倾斜
解决方案: map端实现数据合并
三.map端表合并(Distributedcache)
1.分析
适用于关联表中有小表的情形;
可以将小表分发到所有的map节点,这样,map节点就可以在本地对自己所读到的大表数据进行合并并输出最终结果,可以大大提高合并操作的并发度,加快处理速度。

2.实操案例
(1)先在驱动模块中添加缓存文件
package test;
import java.net.URI; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class DistributedCacheDriver { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 1 获取job信息 Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration); // 2 设置加载jar包路径 job.setJarByClass(DistributedCacheDriver.class); // 3 关联map job.setMapperClass(DistributedCacheMapper.class); // 4 设置最终输出数据类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); // 5 设置输入输出路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); // 6 加载缓存数据 job.addCacheFile(new URI("file:///e:/inputcache/pd.txt")); // 7 map端join的逻辑不需要reduce阶段,设置reducetask数量为0 job.setNumReduceTasks(0); // 8 提交 boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(result ? 0 : 1); } }
(2)读取缓存的文件数据
package test;
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; public class DistributedCacheMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>{ Map<String, String> pdMap = new HashMap<>(); @Override protected void setup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 1 获取缓存的文件 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("pd.txt"),"UTF-8")); String line; while(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line = reader.readLine())){ // 2 切割 String[] fields = line.split("\\t"); // 3 缓存数据到集合 pdMap.put(fields[0], fields[1]); } // 4 关流 reader.close(); } Text k = new Text(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 1 获取一行 String line = value.toString(); // 2 截取 String[] fields = line.split("\\t"); // 3 获取产品id String pId = fields[1]; // 4 获取商品名称 String pdName = pdMap.get(pId); // 5 拼接 k.set(line + "\\t"+ pdName); // 6 写出 context.write(k, NullWritable.get()); } }
以上是关于大数据技术之MapReduce中多表合并案例的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章