请教一下这个数据结构作业怎么编程序。7个城市A,B,C,D,E,F,G的公路网如图11.3所示。
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了请教一下这个数据结构作业怎么编程序。7个城市A,B,C,D,E,F,G的公路网如图11.3所示。相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
弧上的数字表示该段公路的长度。问有一批货物要从城市A运到城市G走哪条路最短?输出最短路径及其长度。是否还有其他最短路径?若有,如何求出其他的最短路径?
要求用c语言程序,用迪杰克斯特拉算法求解。

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxnum = 100;
const int maxint = 999999;
void Dijkstra(int n, int v, int *dist, int *prev, int c[maxnum][maxnum])
bool s[maxnum]; // 判断是否已存入该点到S集合中
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
dist[i] = c[v][i];
s[i] = 0; // 初始都未用过该点
if(dist[i] == maxint)
prev[i] = 0;
else
prev[i] = v;
dist[v] = 0;
s[v] = 1;
// 依次将未放入S集合的结点中,取dist[]最小值的结点,放入结合S中
// 一旦S包含了所有V中顶点,dist就记录了从源点到所有其他顶点之间的最短路径长度
for(int i=2; i<=n; ++i)
int tmp = maxint;
int u = v;
// 找出当前未使用的点j的dist[j]最小值
for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j)
if((!s[j]) && dist[j]<tmp)
u = j; // u保存当前邻接点中距离最小的点的号码
tmp = dist[j];
s[u] = 1; // 表示u点已存入S集合中
// 更新dist
for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j)
if((!s[j]) && c[u][j]<maxint)
int newdist = dist[u] + c[u][j];
if(newdist < dist[j])
dist[j] = newdist;
prev[j] = u;
void searchPath(int *prev,int v, int u)
int que[maxnum];
int tot = 1;
que[tot] = u;
tot++;
int tmp = prev[u];
while(tmp != v)
que[tot] = tmp;
tot++;
tmp = prev[tmp];
que[tot] = v;
for(int i=tot; i>=1; --i)
if(i != 1)
cout << que[i] << " -> ";
else
cout << que[i] << endl;
int main()
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// 各数组都从下标1开始
int dist[maxnum]; // 表示当前点到源点的最短路径长度
int prev[maxnum]; // 记录当前点的前一个结点
int c[maxnum][maxnum]; // 记录图的两点间路径长度
int n, line; // 图的结点数和路径数
// 输入结点数
cin >> n;
// 输入路径数
cin >> line;
int p, q, len; // 输入p, q两点及其路径长度
// 初始化c[][]为maxint
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j)
c[i][j] = maxint;
for(int i=1; i<=line; ++i)
cin >> p >> q >> len;
if(len < c[p][q]) // 有重边
c[p][q] = len; // p指向q
c[q][p] = len; // q指向p,这样表示无向图
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
dist[i] = maxint;
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j)
printf("%8d", c[i][j]);
printf("\\n");
Dijkstra(n, 1, dist, prev, c);
// 最短路径长度
cout << "源点到最后一个顶点的最短路径长度: " << dist[n] << endl;
// 路径
cout << "源点到最后一个顶点的路径为: ";
searchPath(prev, 1, n);
追问

错误。。。
请问怎么改?
用更高版本的编译器 比如说VS2010 不要用VC6.0
追问忽然发现。。。你这是c++的吧。。。我只是学了c语言的耶。。。难怪里面好多我都看不懂。。。
而且我只是普通学习程序的,没有那么高级的VS2010版本的
这个和语言没关系啊 。 这个就是 dijkstra算法 可以直接运行的 你如果这个程序都编译不通过 应该就是编译器的问题了
参考技术A 沿着ACFDG走?数据结构(陈越) 作业题 第三周
03-1. 二分法求多项式单根
二分法求函数根的原理为:如果连续函数f(x)在区间[a, b]的两个端点取值异号,即f(a)f(b)<0,则它在这个区间内至少存在1个根r,即f(r)=0。
二分法的步骤为:
- 检查区间长度,如果小于给定阈值,则停止,输出区间中点(a+b)/2;否则
- 如果f(a)f(b)<0,则计算中点的值f((a+b)/2);
- 如果f((a+b)/2)正好为0,则(a+b)/2就是要求的根;否则
- 如果f((a+b)/2)与f(a)同号,则说明根在区间[(a+b)/2, b],令a=(a+b)/2,重复循环;
- 如果f((a+b)/2)与f(b)同号,则说明根在区间[a, (a+b)/2],令b=(a+b)/2,重复循环;
本题目要求编写程序,计算给定3阶多项式f(x)=a3x3+a2x2+a1x+a0在给定区间[a, b]内的根。
输入格式:
输入在第1行中顺序给出多项式的4个系数a3、a2、a1、a0,在第2行中顺序给出区间端点a和b。题目保证多项式在给定区间内存在唯一单根。
输出格式:
在一行中输出该多项式在该区间内的根,精确到小数点后2位。
输入样例:3 -1 -3 1 -0.5 0.5
输出样例:0.33
此题比较简单,有两个点要注意。
1.输入完之后,应该先判断两个端点是否是根,如果是直接输出,否则再用二分法来查找
2.输出时精确到小数点后2位,所以应该保证精确解和近似解相差不超0.001,所以循环终止条件为找到根,或者|b-a|<0.001
1 //一是如何判断精度,二是如何设置输出的小数点后位数 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<iomanip> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 double a[4]; 7 double f(double); 8 9 int main() 10 { 11 cin >> a[0] >> a[1] >> a[2] >> a[3]; 12 13 double a,b; 14 cin >> a >> b; 15 16 double left=a,right=b,mid=(a+b)/2.0; 17 18 if (f(left)==0.) 19 cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << left << endl; 20 else if (f(right)==0.) 21 cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << right << endl; 22 else 23 { 24 while ( f(mid) && (right-left)>0.001 ) 25 { 26 if ( f(left)*f(mid) < 0 ) 27 right = mid; 28 else 29 left = mid; 30 mid = (left+right)/2.0; 31 } 32 cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << mid << endl; 33 } 34 35 return 0; 36 } 37 38 double f (double x) 39 { 40 double results=a[0]*x+a[1]; 41 42 for (int i=2;i<4;i++) 43 { 44 results = results*x+a[i]; 45 } 46 return results; 47 }
03-2. List Leaves
Given a tree, you are supposed to list all the leaves in the order of top down, and left to right.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (<=10) which is the total number of nodes in the tree -- and hence the nodes are numbered from 0 to N-1. Then N lines follow, each corresponds to a node, and gives the indices of the left and right children of the node. If the child does not exist, a "-" will be put at the position. Any pair of children are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line all the leaves‘ indices in the order of top down, and left to right. There must be exactly one space between any adjacent numbers, and no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:8 1 - - - 0 - 2 7 - - - - 5 - 4 6Sample Output:
4 1 5
本题的第一个关键点是,如何找出树的根结点。很简单,输入的每一行分别是每个结点的左右孩子,因此输入中不出现的那个结点就是根结点,很容易理解。输入完之后构建树,构建完之后用队列进行层序遍历,输出的条件是判断结点是叶结点。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<fstream> 3 #include<queue> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct node 7 { 8 int data; 9 node* left; 10 node* right; 11 }; 12 13 int main() 14 { 15 int N; 16 char left,right; 17 cin >> N; 18 19 node **tree = new node* [N]; 20 int *flag = new int [N]; 21 22 for (int i=0;i<N;i++) 23 { 24 tree[i] = new node; 25 tree[i]->data = i; 26 flag[i]=1; 27 } 28 29 for (int i=0;i<N;i++) 30 { 31 cin >> left; 32 if (left == ‘-‘) 33 tree[i]->left = nullptr; 34 else 35 { 36 tree[i]->left = tree[left-‘0‘]; 37 flag[left-‘0‘]=0; 38 } 39 40 cin >> right; 41 if (right == ‘-‘) 42 tree[i]->right = nullptr; 43 else 44 { 45 tree[i]->right = tree[right-‘0‘]; 46 flag[right-‘0‘]=0; 47 } 48 } 49 50 int head=0; 51 for (int i=0;i<N;i++) 52 if (flag[i] == 1) 53 head = i; 54 55 //开始层序遍历输出叶节点 56 queue<node*> Q; 57 Q.push(tree[head]); 58 node *temp_node; 59 int output_flag=0; 60 61 while (!Q.empty()) 62 { 63 temp_node = Q.front(); 64 Q.pop(); 65 if (!temp_node->left && !temp_node->right ) 66 { 67 if (output_flag) 68 cout << ‘ ‘ << temp_node->data; 69 else 70 { 71 cout << temp_node->data; 72 output_flag=1; 73 } 74 } 75 76 if (temp_node->left) 77 Q.push(temp_node->left); 78 if (temp_node->right) 79 Q.push(temp_node->right); 80 } 81 82 return 0; 83 }
03-3. Tree Traversals Again
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
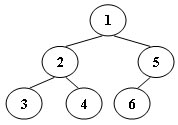
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<=30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:6 Push 1 Push 2 Push 3 Pop Pop Push 4 Pop Pop Push 5 Push 6 Pop PopSample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
这题我的做法是,根据输入中的操作和序号,来构建树。从第一个操作开始,相邻的两个操作有4种可能,push-push,push-pop,pop-pop,pop-push,根据这四种可能来构建树。构建完之后用后序遍历输出即可。值得注意的是,后序遍历可以递归,可以非递归,建议大家两种都写一下,让自己更熟悉。我自己第一遍写后序遍历的非递归程序的过程就比较麻烦了。
1 #include<string> 2 #include<stack> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<fstream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 struct node 8 { 9 int data; 10 node *left; 11 node *right; 12 int flag; 13 }; 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 int N; 18 cin >> N; 19 20 string *operation = new string [N*2]; 21 int *num = new int [N*2]; 22 string temp_op; 23 24 for (int i=0;i<2*N;i++) 25 { 26 cin >> temp_op; 27 if (temp_op == "Push") 28 { 29 operation[i] = "Push"; 30 cin >> num[i]; 31 } 32 else 33 { 34 operation[i] = "Pop"; 35 num[i]=-1; 36 } 37 } 38 39 node **tree = new node* [N+1]; 40 for (int i=1;i<N+1;i++) 41 { 42 tree[i] = new node; 43 tree[i]->data = i; 44 tree[i]->left = nullptr; 45 tree[i]->right = nullptr; 46 tree[i]->flag=0; 47 } 48 49 int head=num[0]; 50 stack<int> sta; 51 int temp=0; 52 for (int i=0;i<2*N-1;i++) 53 { 54 if (operation[i] == "Push") 55 sta.push(num[i]); 56 else 57 { 58 temp = sta.top(); 59 sta.pop(); 60 } 61 62 if (operation[i] == "Push" && operation[i+1] == "Push" ) 63 { 64 tree[num[i]]->left = tree[num[i+1]]; 65 } 66 else if (operation[i] == "Push" && operation[i+1] == "Pop" ) 67 { 68 tree[num[i]]->left = nullptr; 69 } 70 else if (operation[i] == "Pop" && operation[i+1] == "Push" ) 71 { 72 tree[temp]->right = tree[num[i+1]]; 73 } 74 else //pop pop 75 tree[temp]->right = nullptr; 76 } 77 78 //开始后序输出 79 stack<node*> out; 80 node *T=tree[head]; 81 82 while (T || !out.empty()) 83 { 84 while (T) 85 { 86 out.push(T); 87 T = T->left; 88 } 89 90 if (!out.empty()) 91 { 92 T = out.top(); 93 94 if (T->flag) 95 { 96 cout << T->data << ‘ ‘; 97 out.pop(); 98 T=out.top(); 99 } 100 else 101 { 102 T->flag = 1; 103 T=T->right; 104 } 105 } 106 } 107 108 return 0; 109 }
以上是关于请教一下这个数据结构作业怎么编程序。7个城市A,B,C,D,E,F,G的公路网如图11.3所示。的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章