day13 MySQL 及数据库相关
Posted Spurs
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了day13 MySQL 及数据库相关相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Author:相忠良
Email: ugoood@163.com
起始于:May 16, 2018
最后更新日期:May 26, 2018
声明:本笔记依据传智播客方立勋老师 Java Web 的授课视频内容记录而成,中间加入了自己的理解。本笔记目的是强化自己学习所用。若有疏漏或不当之处,请在评论区指出。谢谢。
涉及的图片,文档写完后,一次性更新。
day13 mysql 及数据库相关
1. MySQL 的安装
参照MySQL安装图解,下载后,把rar改为doc即可。https://files.cnblogs.com/files/ZhongliangXiang/MySQL安装图解.rar
2. 数据库的创建细节
练习下面内容即可:
mysql管理员的用户名和密码:root root
创建一个名称为mydb1的数据库
create database mydb1;
show databases;
创建一个使用utf-8字符集的mydb2数据库。
create database mydb2 character set utf8;
创建一个使用utf-8字符集,并带校对规则的mydb3数据库。
create database mydb3 character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;
查看前面创建的mydb2数据库的定义信息
show create database mydb2;
删除前面创建的mydb1数据库
drop database mydb1;
查看服务器中的数据库,并把其中某一个库的字符集修改为gb2312;
alter database mydb2 character set gb2312;
show create database mydb2;
演示恢复和备份
create database tt;
use tt;
create table a
(
name varchar(20)
);
insert into a(name) values(\'aaaa\');
select * from a;
-----看到a表有数据
对tt作备份操作,启动一个window命令行窗口,执行如下命令
mysqldump -uroot -p tt>c:\\tt.sql
演示恢复
1.先删除库
drop database tt;
2.恢复tt库(1)
2.1 为恢复库,要先创建库 create database tt;
2.2 再恢复tt库
use tt;
source c:\\tt.sql (source:可以执行一个 sql脚本)
3.恢复tt库(2)
2.1 为恢复库,要先创建库 create database tt;
2.2 恢复库 mysql -uroot -proot tt<c:\\1.sql; (window命令)
3. 创建表的细节
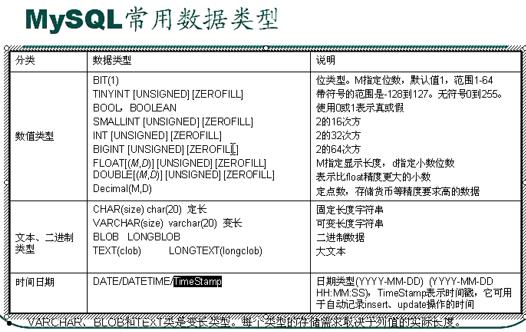
创建一个员工表
use mydb2;
create table employee
(
id int,
name varchar(40),
sex varchar(4),
birthday date,
entry_date date,
job varchar(40),
salary decimal(8,2),
resume text
);
show tables; 查看库的所有表
show create table employee; 查看表的创建细节
desc employee; 看表结构
在上面员工表的基本上增加一个image列。
alter table employee add image blob;
修改job列,使其长度为60。
alter table employee modify job varchar(60);
删除sex列
alter table employee drop sex;
表名改为user。
rename table employee to user;
修改表的字符集为utf-8
alter table user character set utf8;
列名name修改为username
alter table user change column name username varchar(40);
删除表
drop table user;
4. 增删改语句
使用insert语句向表中插入三个员工的信息。
rename table user to employee;
insert into employee(id,username,birthday,entry_date,job,salary,resume) values(1,\'aaa\',\'1980-09-09\',\'1980-09-09\',\'bbb\',90,\'aaaaa\');
select * from employee;
插入数据的细节1
insert into employee values(1,\'aaa\',\'1980-09-09\',\'1980-09-09\',\'bbb\',90,\'aaaaa\');
插入数据的细节2
insert into employee values(\'1\',\'aaa\',\'1980-09-09\',\'1980-09-09\',\'bbb\',\'90\',\'aaaaa\');
插入数据的时候都用单引号引起来,省的数据报错,如果ID引起来的话,mysql会自动转换类型的。
插入数据的细节3(插入中文)
要告诉mysql客户端采用gb2312编码
show variables like \'chara%\';
set character_set_client=gb2312;
insert into employee(id,username) values(\'3\',\'张三\');
要想查看时不乱码
show variables like \'chara%\';
set character_set_results=gb2312;
select * from employee;
将所有员工薪水修改为5000元。
update employee set salary=5000;
将姓名为’bbb’的员工薪水修改为3000元。
update employee set salary=3000 where username=\'bbb\';
将姓名为’bbb的员工薪水修改为4000元,job改为ccc。
update employee set salary=4000,job=\'ccc\' where username=\'bbb\';
将bbb的薪水在原有基础上增加1000元。
update employee set salary=salary+1000 where username=\'bbb\';
更新要注意的问题
update employee set username=\'ccc\',salary=9000,birthday=\'1980-09-09\',.....................
update where id=1;
这个地方忘记写where,后果是很严重的。
删除表中名称为’zs’的记录。
delete from employee where username=\'bbb\';
删除表中所有记录。
delete from employee;
使用truncate删除表中记录。
truncate table employee;
5. 查询语句
试验所需材料:
创建1个 student.sql 文件,并写入如下内容:
create table student(
id int,
name char(20),
chinese float,
english float,
math float
);
insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(1,\'张小明\',89,78,90);
insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(2,\'李进\',67,98,56);
insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(3,\'王五\',87,78,77);
insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(4,\'李一\',88,98,90);
insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(5,\'李来财\',82,84,65);
insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(6,\'张进宝\',55,85,45);
insert into student(id,name,chinese,english,math) values(7,\'黄蓉\',75,65,30);
将该文件导入某数据库,如:
use tt
source e:\\student.sql
处理mysql客户端输入和显示时的乱码问题,下面代码在mysql客户端执行:
要告诉mysql客户端采用gb2312编码
show variables like \'chara%\';
set character_set_client=gb2312;
要想查看时不乱码
show variables like \'chara%\';
set character_set_results=gb2312;
上述准备工作作完后,进行下面的查询练习:
查询表中所有学生的信息。
select * from student;
查询表中所有学生的姓名和对应的英语成绩。
select name,english from student;
过滤表中重复的英语数据。
select distinct english from student;
在所有学生总分上加10分特长分。
select name,(chinese+english+math)+10 from student;
统计每个学生的总分。
select name,(chinese+english+math) from student;
使用别名表示学生分数。
select name as 姓名,(chinese+english+math)+10 as 总分 from student;
select name 姓名,(chinese+english+math)+10 总分 from student;
查询姓名为王五的学生成绩
select * from student where name=\'王五\';
查询英语成绩大于90分的同学
select * from student where english>\'90\';
查询总分大于200分的所有同学
select name from student where (chinese+english+math)>200;
查询英语分数在 80-90之间的同学。
select name from student where english>80 and english<90;
select name from student where english between 80 and 90; == select name from student where english>=80 and english<=90;
查询数学分数为89,90,91的同学。
select * from student where math in(89,90,91);
查询所有姓李的学生成绩。
select * from student where name like \'李%\';
select * from student where name like \'李_\';
查询数学分>80,语文分>80的同学。
select * from student where math>80 and chinese>80;
对数学成绩排序后输出。
select name,math from student order by math;
对总分排序后输出,然后再按从高到低的顺序输出
select name 姓名,(chinese+english+math) 总分 from student order by (chinese+english+math) desc;
select name 姓名,(chinese+english+math) 总分 from student order by 总分 desc;
对姓李的学生成绩排序输出
select * from student where name like \'李%\' order by (chinese+english+math) desc;
统计一个班级共有多少学生?
select count(name) from student;
select count(*) from student;
统计数学成绩大于90的学生有多少个?
select count(*) from student where math>80;
统计总分大于250的人数有多少?
select count(*) from student where (chinese+english+math)>250;
关于 count的函数的细节 (count只统有值的行)
统计一个班级数学总成绩?
select sum(math) from student;
统计一个班级语文、英语、数学各科的总成绩
select sum(chinese),sum(english),sum(math) from student;
统计一个班级语文、英语、数学的成绩总和
select sum(chinese+english+math) from student;
统计一个班级语文成绩平均分
select sum(chinese)/count(*) from student;
统计一个班级语文成绩平均分
select avg(chinese) from student;
求一个班级总分平均分
select avg(chinese+math+english) from student;
求班级最高分和最低分
select max(chinese+math+english),min(chinese+math+english) from student;
对订单表中商品归类后,显示每一类商品的总价
select product,sum(price) from orders group by product;
查询购买了几类商品,并且每类总价大于100的商品
select product from orders group by product having sum(price)>100;
6. mysql 表的约束

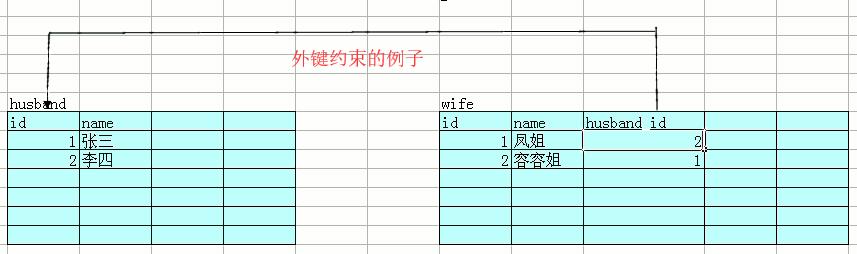
定义主键约束(每一个表必须有一个主键列)
create table student
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(40)
);
定义主键自动增长
create table student
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40)
);
定义唯一约束
drop table student;
create table student
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40) unique
);
定义非空约束
drop table student;
create table student
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40) unique not null
);
定义外键约束
create table husband
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(40)
);
create table wife
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(40),
husband_id int,
constraint husband_id_FK foreign key(husband_id) references husband(id)
);
7. 数据库表的设计
从应用程序建立对象后,需将 复杂对象 存入数据库的这种迫切需求开始,理解本节内容。
复杂对象: 就是对该象中的属性,存放着其他类型对象。后面的列子中对象多数均为复杂对象。简单对象的话,直接用 mysql 建表存储就完事了。
7.1 1对多或多对1关系的设计
数据库表的 1:n 或 n:1 的设计原则:
- 先不管对象间的关系,直接设计本对象的基本属性;
- 多的那一方,再增加外键。
示例场景,如下图:
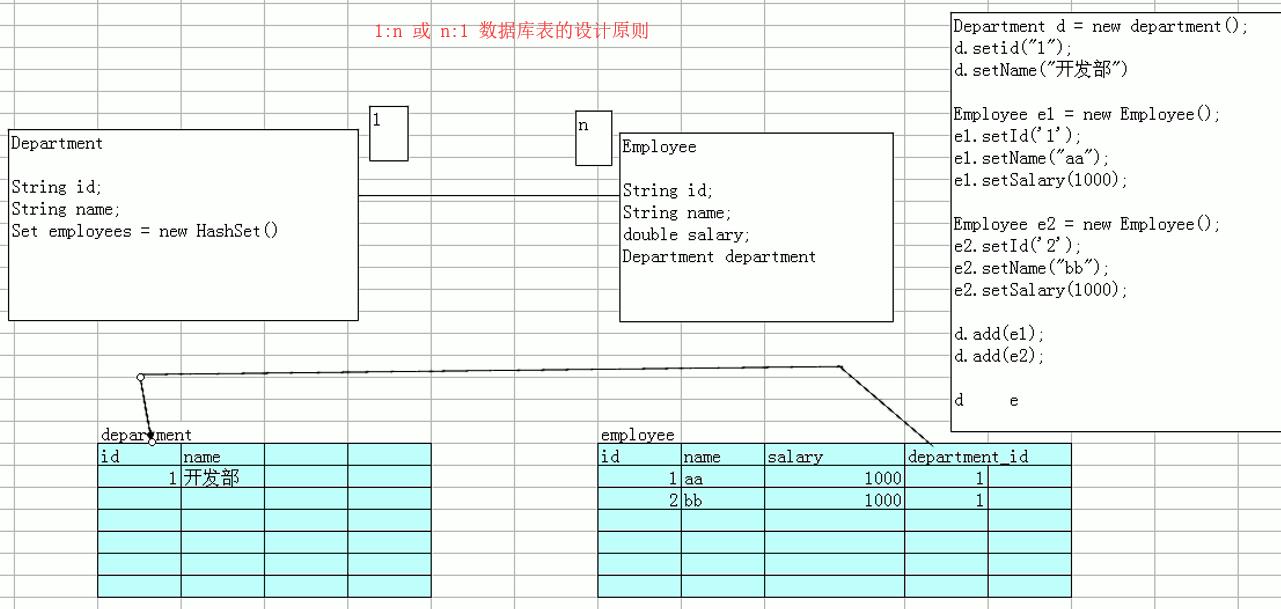
建立表的sql语句:
一对多或多对一的对象存到数据库时,表的设计方案
部门和员工
create table department
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(40)
);
create table employee
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(40),
salary decimal(8,2),
department_id int,
constraint department_id_FK foreign key(department_id) references department(id)
);
7.2 多对多关系的设计
多对多关系的话,就需建立一个中间表。
示例场景,如下图:
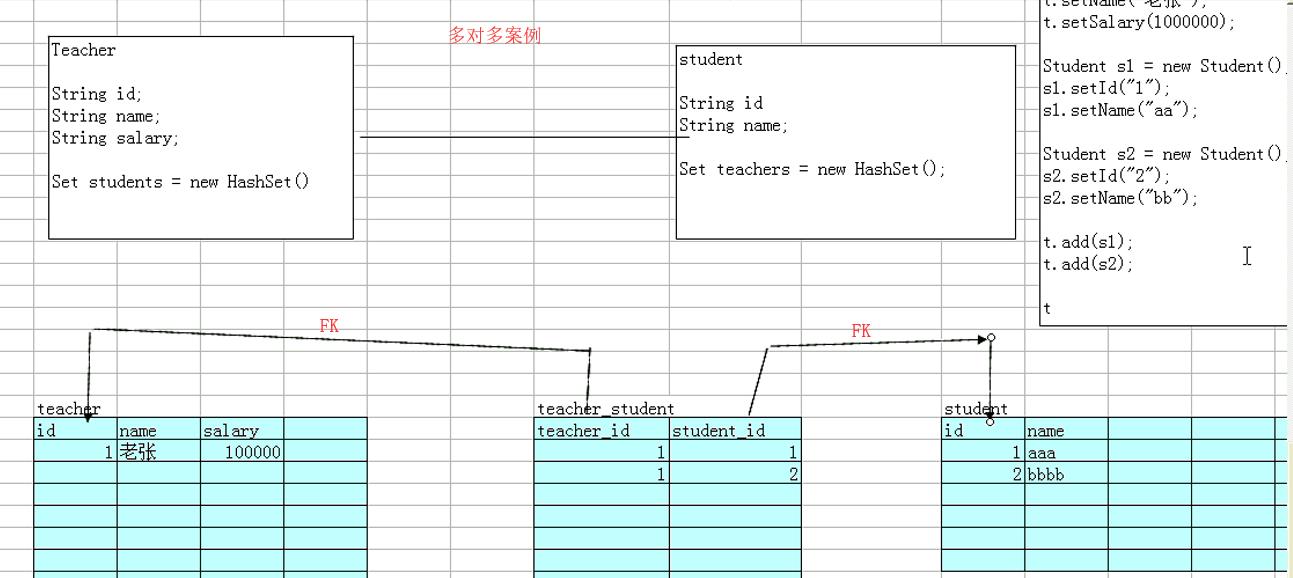
建立表的sql语句:
多对多对象的表的设计(老师和学生)
create table teacher
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(40),
salary decimal(8,2)
);
create table student
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(40)
);
create table teacher_student
(
teacher_id int,
student_id int,
primary key(teacher_id,student_id),
constraint teacher_id_FK foreign key(teacher_id) references teacher(id),
constraint student_id_FK foreign key(student_id) references student(id)
);
不过, teacher_student 表中的主键是值得商榷的。通常应该单独建立 id 主键列,而不建议用双列做主键。
7.3 1对1关系的设计
1对1案例,人和身份证。 1对1一般是有 主从关系 的。
人为主,身份证为从。既人可以没身份证,但身份证不能没有人与之对应。
示例场景,如下图:
身份证外键列不仅要加外键约束,还要加唯一性约束和非空约束,保证了1:1的关系。下图也表达了1:1关系中的一种主从关系特性。
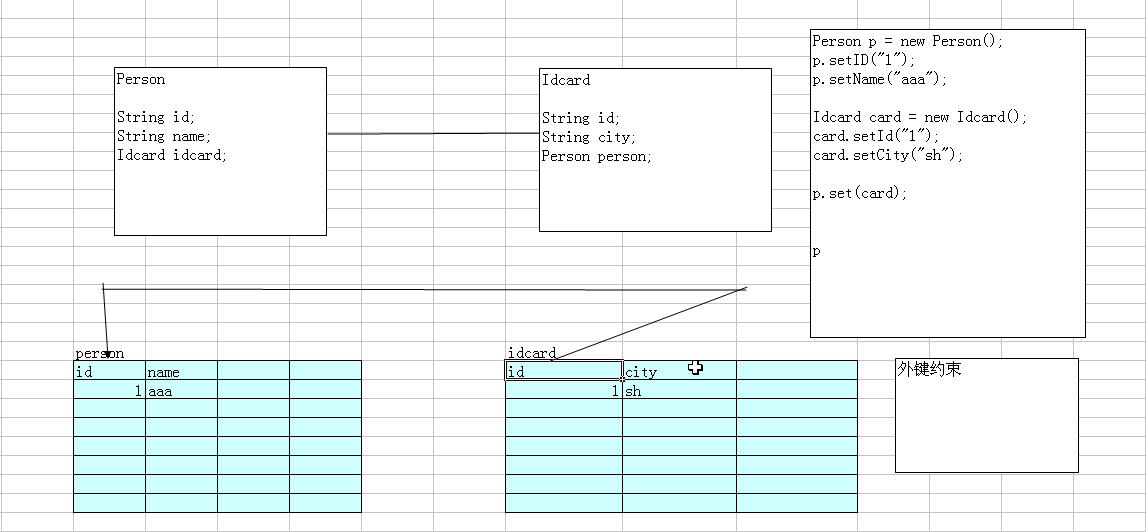
上图中,把身份证表的id列设为主键约束和外键约束,恰好表达了身份证外键列还要加唯一性和非空这两种约束,故没必要单独设计1个列为外键约束列了。
建立表的sql语句:
一对一的对象的数据库设计
create table person
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(40)
);
create table idcard
(
id int primary key,
city varchar(40),
constraint id_FK foreign key(id) references person(id)
);
8. 自关联对象的数据库设计
案例:家族管理系统
每个人都有1个爸爸,有好多孩子。 爸爸,孩子,包括你,都是 Person 对象。
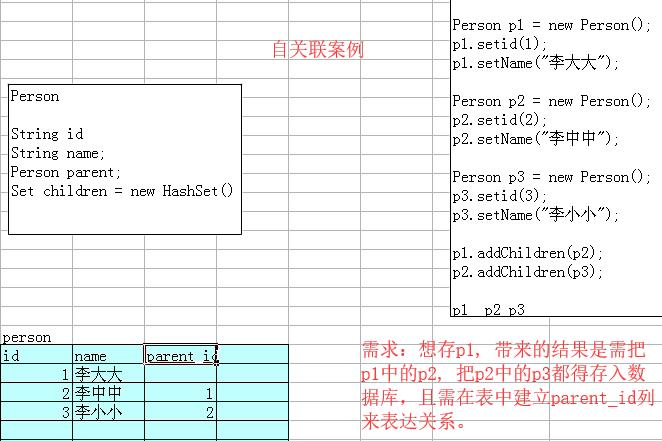
建立表的sql语句:
自连接的表
create table person
(
id int primary key,
name varchar(40),
parent_id int,
constraint parent_id_FK foreign key(parent_id) references person(id)
);
设计一个无限制分类的表:
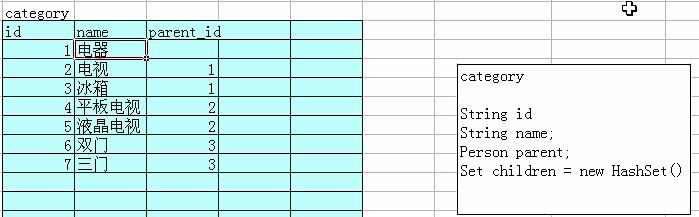
该表理论上可存无限制分类,实际操作中涉及到递归,递归有层数限制,故实际中该表无法实现无限制分类。需用数据结构中的二叉树来实现。
以上是关于day13 MySQL 及数据库相关的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章