1.键值对
以键值对的形式处理数据并输出结果
具体含义:
对于java map,其内容是指定类型的给定健到相关值的一组映射,健与值的数据类型可能不同
key,value
键必须是唯一的,而值并不一定是唯一的
每个值必须与键相关联,但键可能没有值
对键进行明确的定义非常重要,他决定了计数是否区分大小写,这将产生不同的结果
为什么使用键值对:
键值数据这一简单的模型具有广泛的适用性
并行处理计数分而治之
高端数据挖掘约束模型
MapReduce组委一系列键/值变换
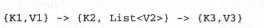
理解:
MapReduce作业的map方法的输入是一系列的键值对,称之为k1,v1
Map方法的输出(之后作为reduce方法的输入)是一系列的键以及与之关联的值得列表,称之为k2,v2,每个mapper仅仅输出一系列的单个的键值对,他们通过shuffle方法组合成键与值的列表
MapReduce作业的最终输出是另遗传键值对,称之为k3,v3
问题:
- 键值对的概念是什么?
a) Hadoop创造并专用的概念
b) 表述我们经常看到但并没有这样考虑的事物间关系的一种方法
c) 一个计算机科学的学术概念
- 用户名和密码组合是键值对的一个例子吗?
是的,这是一个键值对的明显的例子
不是,密码更像是用户名的一个属性,他们之间没有索引-类型的关系
通常我们并不这样认为,但是hadoop仍可以将用户名和密码作为键值对组合来进行处理
MapReduce的Hadoop java api
MapReduce java api

- mapper类


2.Reduce类


3.Driver类
负责与hadoop框架通信并指定运行MapReduce作业所需的配置元素的驱动程序


4.简单的MapReduce程序
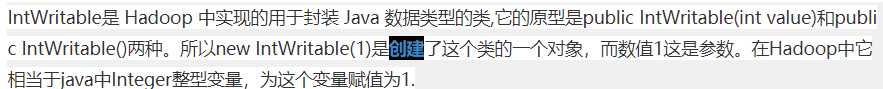
package com.sdd.hadoopTest; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobConf; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; /** * hadoop test * */ public class WordCount1 { public static class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable> { /* * IntWritable是 Hadoop 中实现的用于封装 Java 数据类型的类,它的原型是public IntWritable(int * value)和public IntWritable()两种。所以new * IntWritable(1)是创建了这个类的一个对象,而数值1这是参数。在Hadoop中它相当于java中Integer整型变量,为这个变量赋值为1. */ private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); private Text word=new Text(); public void map(Object key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] words=value.toString().split(" "); for (String str : words) { word.set(str); context.write(word, one); } } } public static class WordCountReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>{ public void reduce(Text key,Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int total=0; for (IntWritable val : values) { total++; } context.write(key, new IntWritable(total)); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException { Configuration configuration=new Configuration(); Job job=new Job(configuration,"word count"); job.setJarByClass(WordCount1.class); job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(WordCountReduce.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 :1); } }
原理分析:
在其主方法中通过驱动程序设置的完整JOB类,以内置类的形式定义的mapper和reducer
如何实践键值转换的????????
指定textInputFormat作为输入数据的格式,默认情况下,这种格式提供给mapper的数据中,键指的是文件中的行号,值指的是该行的内容。
对于输入源中的每行文本,mapper都会执行一次,每次运行都会获取该行内容并把它切分成词语,之后,他会使用Context对象以<word,1>的格式输出每个新的键值,这些输出就是我们所说的k2,v2值
Reduce的输入时一个键和一组与该键对应的值。Hadoop对每个键执行一次reduce,前面的reduce简单的统计Iterable对象中的数字,并以<word,count>的形式给出每个词的输出,这些输出就是我们所说的k3,v3
总结:

Hadoop运行jar文件:

查看WordCount的运行全貌













使用request作为conbiner:
package com.sdd.hadoopTest; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Iterator; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobConf; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; /** * hadoop test * */ public class WordCount1 { public static class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable> { /* * IntWritable是 Hadoop 中实现的用于封装 Java 数据类型的类,它的原型是public IntWritable(int * value)和public IntWritable()两种。所以new * IntWritable(1)是创建了这个类的一个对象,而数值1这是参数。在Hadoop中它相当于java中Integer整型变量,为这个变量赋值为1. */ private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); private Text word=new Text(); public void map(Object key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] words=value.toString().split(" "); for (String str : words) { word.set(str); context.write(word, one); } } } /* * 使用request作为combiner */ public static class WordCountConbiner extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>{ public void combiner(Text key,Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int total=0; for (IntWritable val : values) { total+=val.get(); } context.write(key, new IntWritable(total)); } } public static class WordCountReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>{ public void reduce(Text key,Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int total=0; for (IntWritable val : values) { total++; } context.write(key, new IntWritable(total)); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException { Configuration configuration=new Configuration(); Job job=new Job(configuration,"word count"); job.setJarByClass(WordCount1.class); job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class); job.setCombinerClass(WordCountConbiner.class);//添加combinter job.setReducerClass(WordCountReduce.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 :1); } }